Thermal Transfer Systems TEMA Designations of Heat Exchangers User Manual
Page 3
missing tubes result in larger annular spaces and can contribute to reduced flow across the
effective tube surface, resulting in reduced thermal performance. Some designs include
sealing strips installed in the shell to help block the bypass steam.
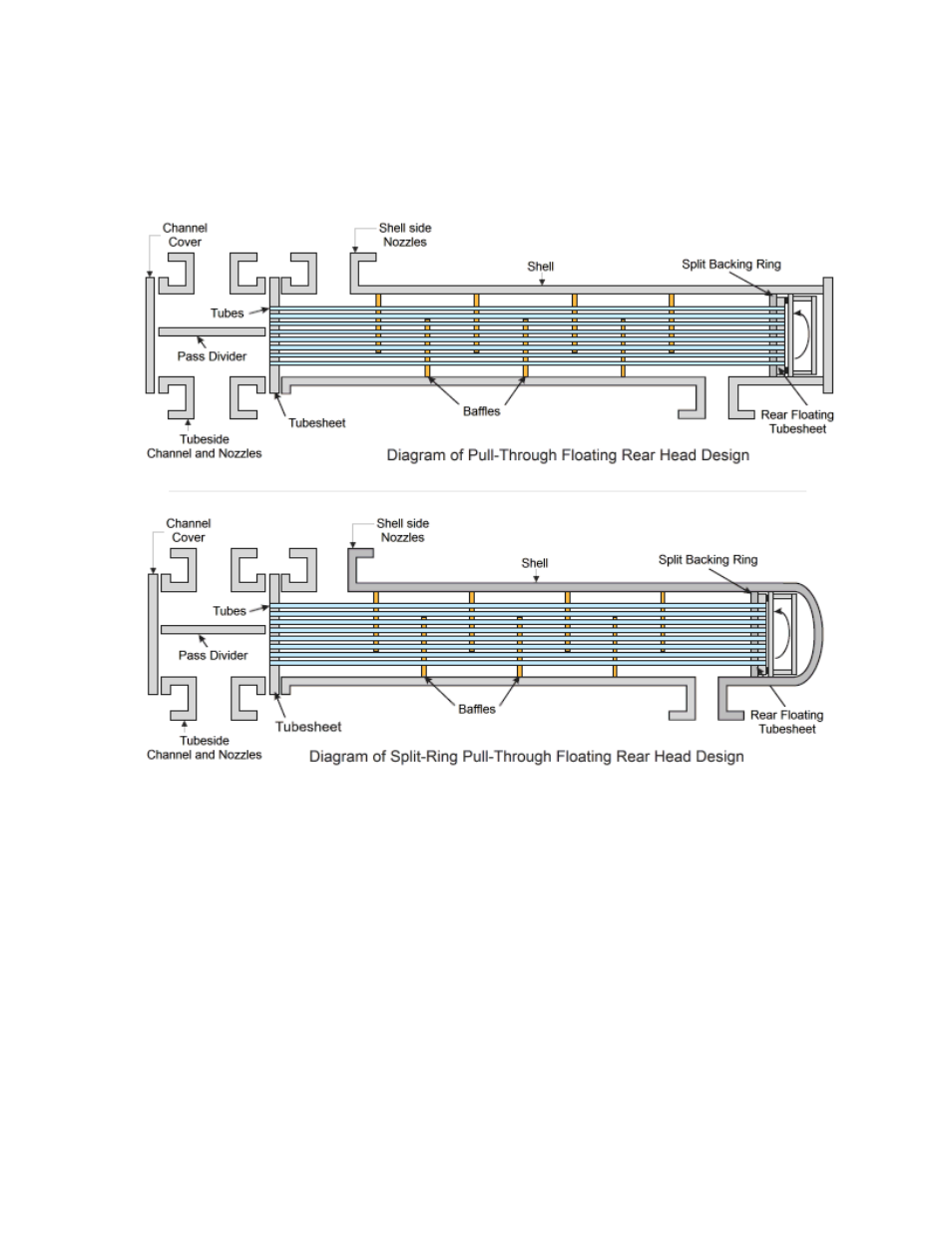
Another floating head design that partially addresses the above disadvantages is a "split-ring
floating head". Here the floating head bonnet is bolted to a split backing ring instead of the
tubesheet. This eliminates the bolt circle diameter and allows a full complement of tubes to fill
the shell. This construction is more expensive than a common pull through design, but is in
wide use in petrochemical applications. For applications with high pressures or temperatures,
or where more positive sealing between the fluids is desired, the pull-through design should
be specified. Two other types, the "outside packed lantern ring" and the "outside packed
stuffing box" designs offer less positive sealing against leakage to the atmosphere than the
pull though or split ring designs, but can be configured for single tube pass duty.
SHELL CONSTRUCTIONS
The most common TEMA shell type is the "E" shell as it is most suitable for most industrial
process cooling applications. However, for certain applications, other shells offer distinct
advantages.
For example, the TEMA-F shell design provides for a longitudinal flow plate to be installed
inside the tube bundle assembly. This plate causes the shell fluid to travel down one half of
the tube bundle, then down the other half, in effect producing a counter-current flow pattern
which is best for heat transfer.
This type of construction can be specified where a close approach temperature is required and
SOURCE: WWW.WERMAC.ORG/
