Serial interface, A. ttl and rs-232 serial – Pololu Qik 2s12v10 User Manual
Page 15
4. Serial Interface
You can use the serial interface for three general purposes: querying the qik for information, setting its
configuration parameters, and sending it motor commands. Motor commands are strictly one-way; the qik
responds to all other commands by transmitting a single byte that either represents information that has been
requested or feedback on the effect of the issued command.
4.a. TTL and RS-232 Serial
The qik requires a logic-level (0 to 3.3-5 V, or “TTL”), non-inverted serial input connected to its serial receive
line, RX, or an RS-232 (inverted, ±3-15 V) serial input connected to its SIN pin. The serial interface is
asynchronous, meaning that the sender and receiver each independently time the serial bits; asynchronous serial
is available in computer serial ports (typically RS-232) and as hardware modules called “UARTs” on many
microcontrollers (typically TTL). Asynchronous serial output can also be “bit-banged” by a standard digital
output line under software control.
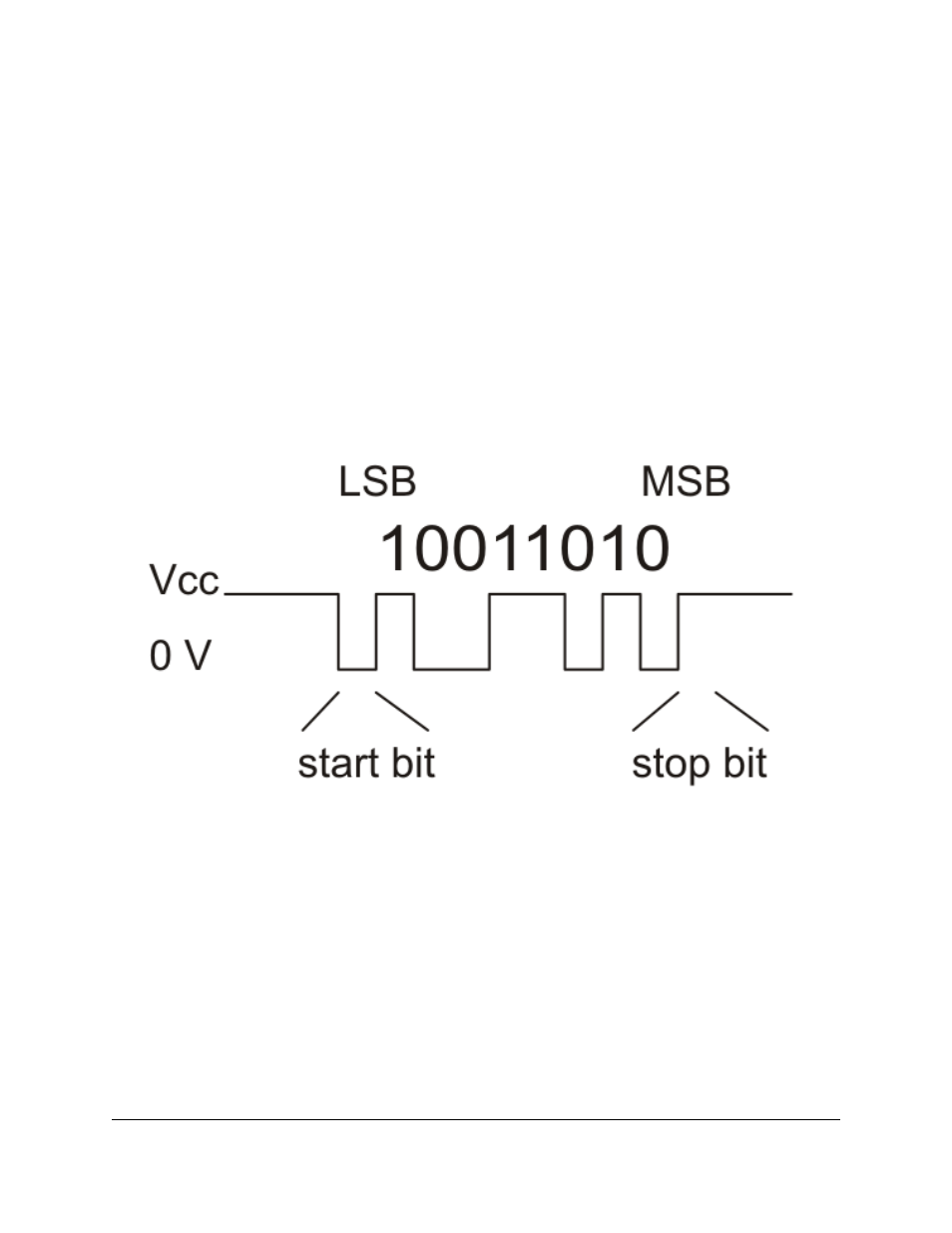
The data format is 8 data bits, one stop bit, with no parity, which is often expressed as 8-N-1. The diagram below
depicts a typical asynchronous, non-inverted TTL serial byte:
Diagram of a non-inverted TTL serial byte.
A non-inverted TTL serial line has a default (non-active) state of high. A transmitted byte begins with a single
low “start bit”, followed by the bits of the byte, least-significant bit (LSB) first. Logical ones are transmitted as
high (Vcc) and logical zeros are transmitted as low (0 V), which is why this format is referred to as “non-inverted”
serial. The byte is terminated by a “stop bit”, which is the line going high for at least one bit time. Because each
byte also requires start and stop bits, each byte takes 10 bit times to transmit, so the fastest possible data rate
in bytes per second is the baud rate divided by ten. At the maximum baud rate of 115,200 bits per second, the
maximum realizable data rate, with a start bit coming immediately after the preceding byte’s stop bit, is 11,520
bytes per second.
The voltage on the RX pin should not go below 0 V and should not exceed 5 V. The qik can accept a 3.3 V
serial input on this line, so you can send commands to the qik with a microcontroller running at 3.3 V. The qik
provides logic-level (0 – 5 V) serial output on its serial transmit line, TX, in response to commands that request
Qik 2s12v10 User's Guide
© 2001–2012 Pololu Corporation
4. Serial Interface
Page 15 of 33
