Raid 0 – CalDigit RAIDShield User Manual
Page 35
34
34
RAID 0:
RAID 0 links each drive in the array as one huge drive. Storage capacity is determined by the smallest drive in the array.
That capacity is then applied to format all other drives in the array. If using a 40 GB, 60 GB, and 50 GB drive in a RAID 0
array, your system will see one huge drive of 120 GB (40 GB×3).
RAID 0 offers double or more performance under sustained data transfers when one drive per ATA port is used. In such a
configuration, unlike Fibre, ATA drives are always available to the system. Fibre requires more management of the Fibre
bus.
RAID 0: Striped disk array without fault tolerance
Characteristics: Recommended
use:
RAID 0 implements a striped disk array, the data
is broken down into blocks and each block is
written to a separate disk drive.
I/O performance is greatly improved by spreading
the I/O load across many channels and drives.
Fastest and most efficient array type but offers no
fault-tolerance.
Storage capacity = (No. of disks) × (capacity of
smallest disk)
Video production and
editing
Image editing
Pre-press
applications
Any application
requiring high
bandwidth
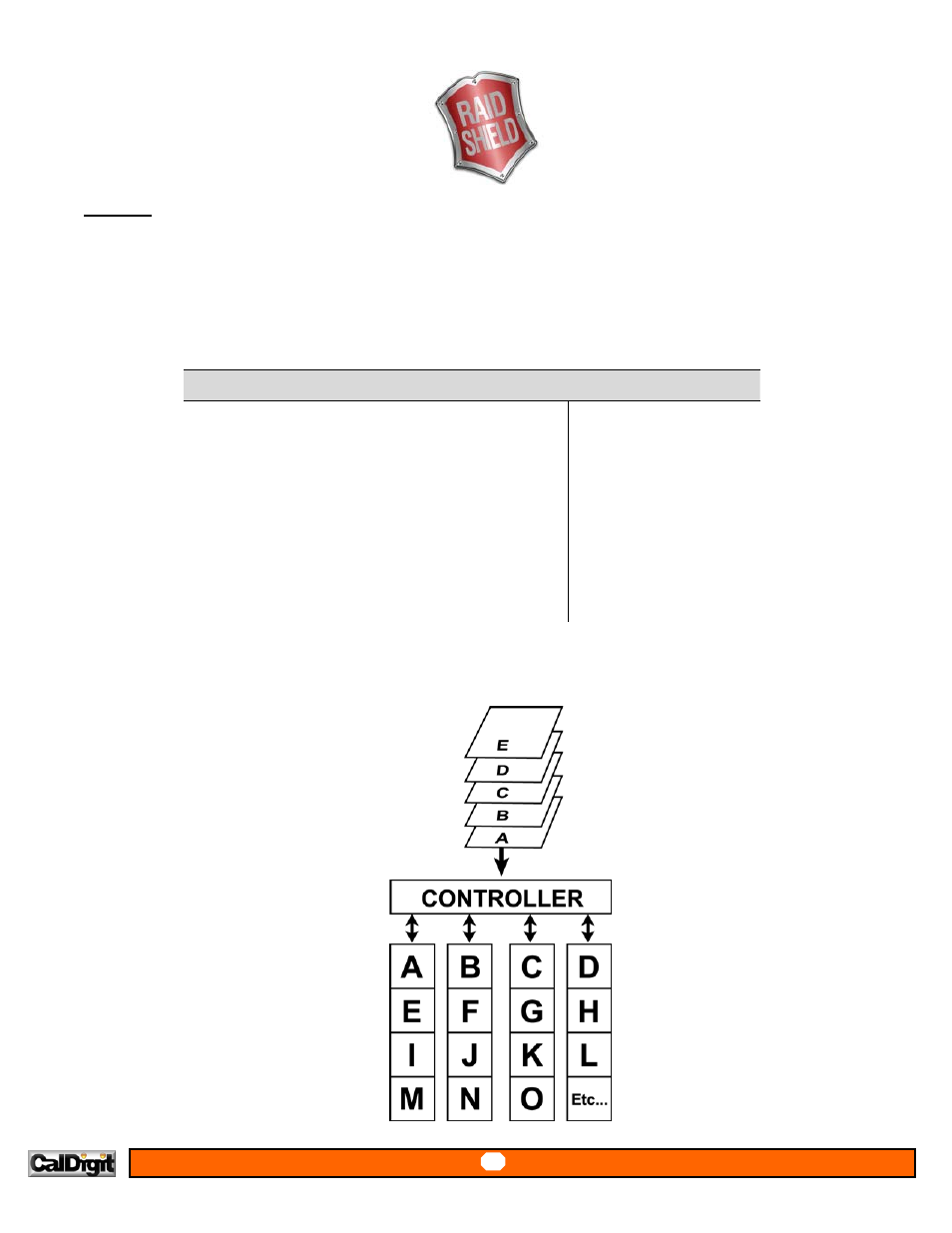
The diagram below represents the writing of data on a RAID 0 array composed of four HDDS connected to the controller.
Data blocks are distributed across all disks in the array.
Arrangement of data blocks saved on a Level 0 RAID
