Identity transfer to google search appliance, Authorization, Purpose of the authorization spi – Google Search Appliance Authentication/Authorization for Enterprise SPI Guide User Manual
Page 18
Google Search Appliance: Authentication/Authorization for Enterprise SPI Guide
18
Dw2cJKZW0578VBt33IotOaOD9AQ=
dpliQ5n4QYQe6ORy6D/
MKMs6whn6HY3JBA7WIZM0GYDAYQnTi46E1T1srrig6kPWemSd3D1tnGKOzPri1x17AQ==
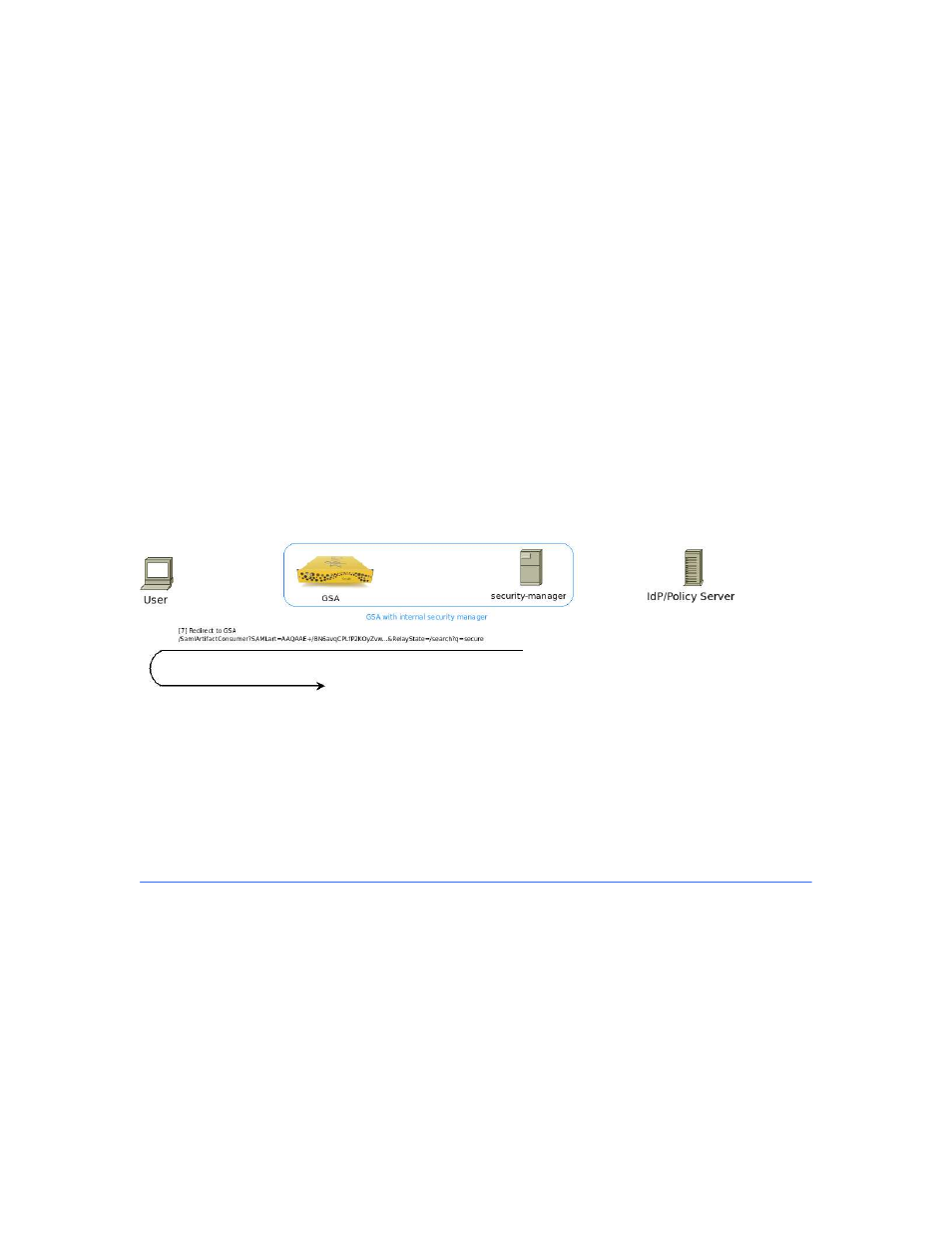
Identity transfer to Google Search Appliance
[7] After parsing the Assertion, the security manager now knows the Identity of the user performing
the search. It needs to transfer this credential back to the Google Search Appliance using the HTTP-
Redirect and HTTP-Artifact Binding. The security manager generates a brand new SAMLArtifact for use
in context with this communication and issue a 302 Redirect back to the search appliance. The security
manager knows what the user’s initial &RelayState= is from step [2][3] (using the security-manager’s
JSESSIONID).
Figure 7: Security manager redirecting via HTTP-Redirect back to the Google Search Appliance
[8] [9] Once the Google Search Appliance has the artifact, it acquires the verified identity by
communicating with the security manager internally. This part of the protocol is not shown for clarity.
Authorization
Purpose of the Authorization SPI
The Google Search Authorization SPI is exposed to allow a customer’s web service to communicate
between the Authorization SPI and the customer’s server that provides access control services, which
this document refers to as the Policy Decision Point (PDP). The PDP provides a layer between the Google
Search Appliance and the customer’s access-control system. The PDP will be implemented, tested, and
maintained by the customer.
