Bryant Gas Heating/Electric Cooling Units 581B User Manual
Page 8
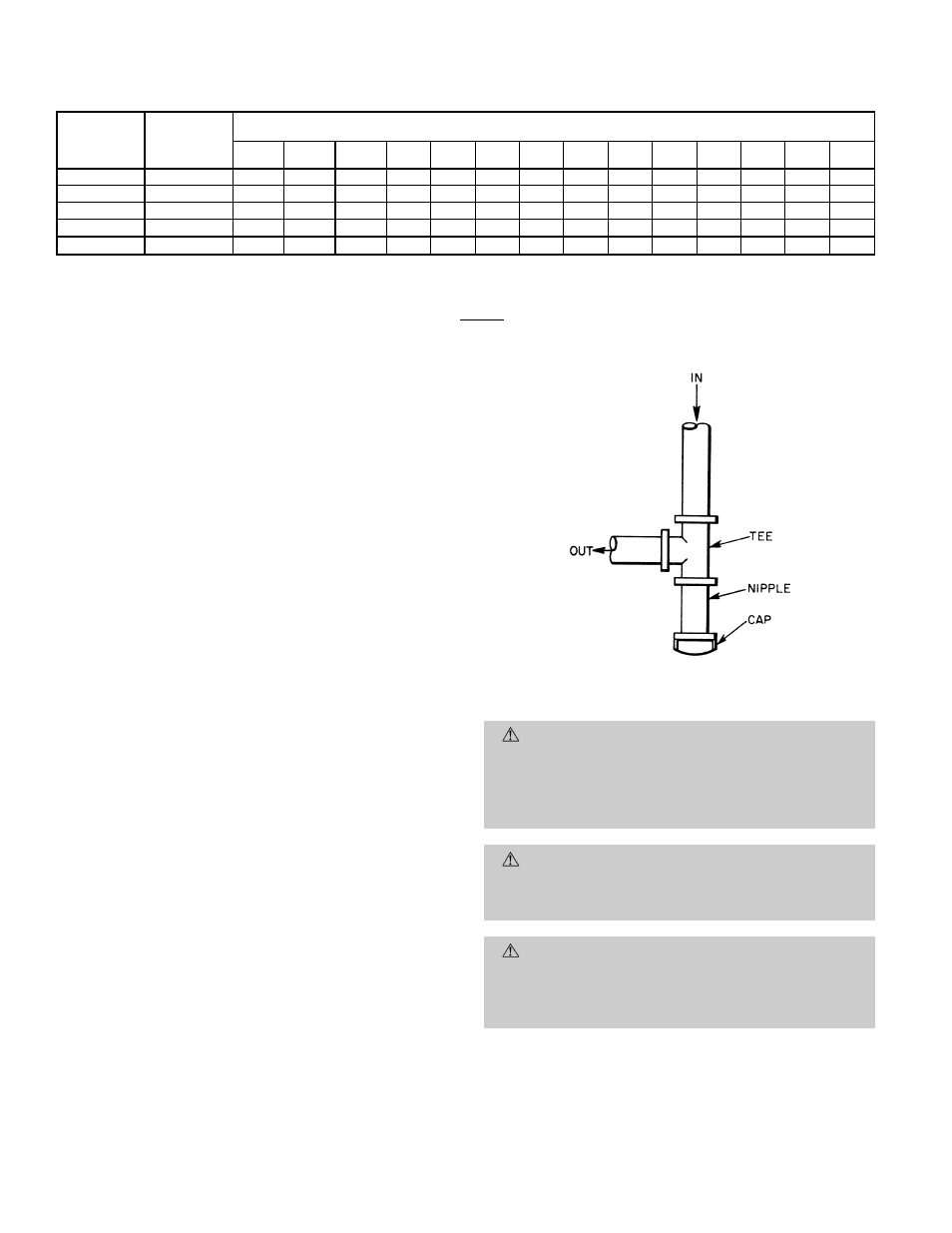
Table 2 — Maximum Gas Flow Capacity of Pipe in Cubic Ft of Gas Per Hour
for Gas Pressures of 0.5 Psig or Less and a Pressure Drop of 0.5 in. wg
(Based on a 0.60 Specific Gravity Gas)
NOMINAL
IRON PIPE
SIZE
(in.)
INTERNAL
DIAMETER
(in.)
LENGTH OF PIPE, FT*
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
125
150
175
200
1
⁄
2
.622
175
120
97
82
73
66
61
57
53
50
44
40
—
—
3
⁄
4
.824
360
250
200
170
151
138
125
118
110
103
93
84
77
72
1
1.049
680
465
375
320
285
260
240
220
205
195
175
160
145
135
1
1
⁄
4
1.380
1400
950
770
600
580
530
490
460
430
400
360
325
300
280
1
1
⁄
2
1.610
2100
1460
1180
990
900
810
750
690
650
620
550
500
460
430
Refer to Table 10-2, National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), latest edition.
*This length includes an ordinary number of fittings.
NOTE: Typical natural gas heating value is 1000 Btuh per cubic ft.
115,000
For example: A 115,000 Btuh input unit equals 115 cubic ft per hour or
= 115 cubic ft/hr.
1,000
When installing the gas supply line, observe local codes per-
taining to gas pipe installations. Refer to the NFGC ANSI
Z223.1-1992 (in Canada, CAN/CGA B149.1, [2]-M86) or NFPA
54-1992, in the absence of local building codes. Adhere to the
following pertinent recommendations:
1. Avoid low spots in long runs of pipe. Grade all pipe
1
⁄
4
inch in every 15 ft to prevent traps. Grade all hori-
zontal runs downward to risers. Use risers to connect to
heating section and to meter.
2. Protect all segments of piping system against physical
and thermal damage. Support all piping with appropri-
ate straps, hangers, etc. Use a minimum of one hanger
every 6 ft. See Fig. 10. For pipe sizes larger than
1
⁄
2
in.,
follow recommendations of national codes.
3. Apply joint compound (pipe dope) sparingly and only to
male threads of joint when making pipe connections. Use
only pipe dope that is resistant to action of liquefied pe-
troleum gases as specified by local and/or national codes.
Never use Teflon-coated tape.
4. Install sediment trap in riser leading to heating sec-
tion. This drip leg functions as a trap for dirt and con-
densate. Install trap where condensate can not freeze.
Install this sediment trap by connecting a piping tee to
riser leading to heating section, so that straight-
through section of tee is vertical. See Fig. 11. Then, con-
nect capped nipple into lower end of tee. Extend capped
nipple below level of gas controls.
5. Install an accessible, external, manual main shut-off valve
in gas supply pipe within 6 ft of heating section.
6. Install ground-joint union close to heating section be-
tween unit manual shutoff and external manual main
shut-off valve.
7. Pressure-test all gas piping in accordance with local and
national plumbing and gas codes before connecting pip-
ing to unit.
NOTE:
When pressure testing the gas supply system after
the gas supply piping has been connected to the unit gas valve,
the supply piping must be disconnected from the gas valve
during any pressure testing of the piping systems at test pres-
sure in excess of 0.5 psig. When pressure testing the gas sup-
ply piping system at test pressures equal to or less than
0.5 psig, the unit heating section must be isolated from the
gas piping system by closing the external main manual shut-
off valve and slightly opening the ground-joint union. After
pressure test is completed, retighten ground-joint union.
CAUTION:
Unstable operation may occur when the
gas valve and manifold assembly are forced out of po-
sition while connecting improperly routed rigid gas pip-
ing to the gas valve. Use a backup wrench when mak-
ing connection to avoid strain on, or distortion of, the
gas control piping.
CAUTION:
If a flexible conductor is required or al-
lowed by the authority having jurisdiction, black iron
pipe shall be installed at the gas valve and extend a
minimum of 9 in. outside the unit casing.
WARNING:
Never use a match or other open flame
when checking for gas leaks. Never purge gas line into
combustion chamber. Failure to adhere to this warning
could result in an explosion causing personal injury or
death.
8. Check for gas leaks at all field- and factory-installed gas
lines after all piping connections have been completed.
Use soap-and-water solution (or method specified by lo-
cal codes and/or regulations).
Fig. 11 — Sediment Trap
—8—
