3. typical soil water potential, r, And v – Campbell Scientific 223-L Delmhorst Cylindrical Soil Moisture Block User Manual
Page 18
223 Delmhorst Cylindrical Soil Moisture Block
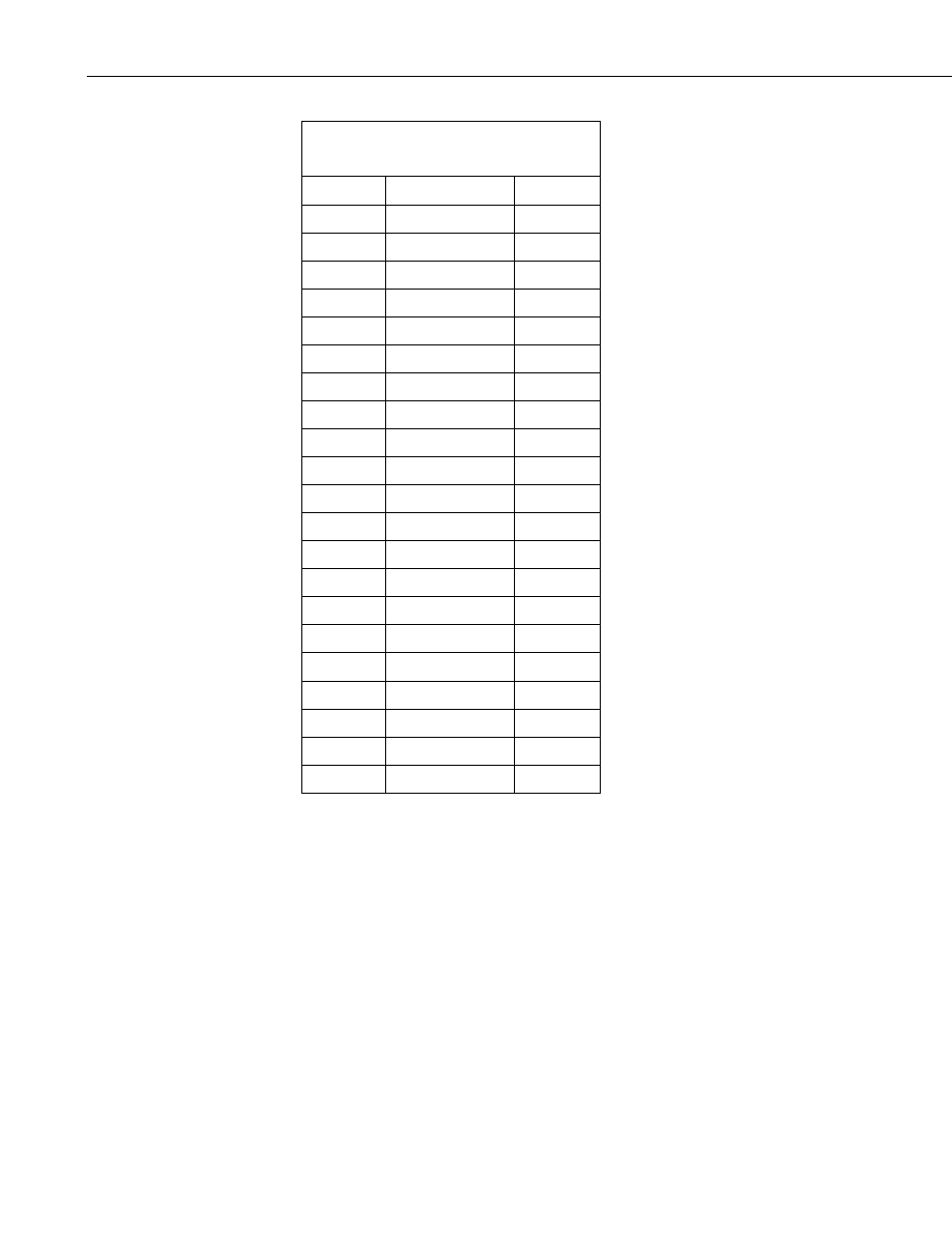
TABLE 7-3. Typical Soil Water Potential,
R
s
and V
s
/ V
x
BARS R
s
(kohms)
V
s
/V
x
0.1 0.060
0.0566
0.2 0.130
0.1150
0.3 0.260
0.2063
0.4 0.370
0.2701
0.5 0.540
0.3506
0.6 0.750
0.4286
0.7 0.860
0.4624
0.8 1.100
0.5238
0.9 1.400
0.5833
1.0 1.700
0.6296
1.5 3.400
0.7727
1.8 4.000
0.8000
2.0 5.000
0.8333
3.0 7.200
0.8780
6.0 12.500
0.9259
10.0 17.000
0.9444
11.0 22.200
0.9569
12.0 22.400
0.9573
13.0 30.000
0.9677
14.0 32.500
0.9701
15.0 35.000
0.9722
For the typical resistance values listed in TABLE 7-3, soil water potential
(bars) is calculated from sensor resistance (R
s
) using the 5th order polynomial
(FIGURE 7-2 and TABLE 7-4). TABLE 7-5 shows the polynomial error. The
nonlinear relationship of R
s
to bars rules out averaging R
s
directly.
The polynomial is entered as an expression in CRBasic or by using Edlog
instruction Polynomial (P55). The polynomial to calculate soil water potential
is fit to the 0.1 to 10 bar range using a least square fit. TABLE 7-4 lists the
coefficients and equation for the 0.1 to 10 bar polynomial.
12
