Dake Model Zip 28 User Manual
Page 13
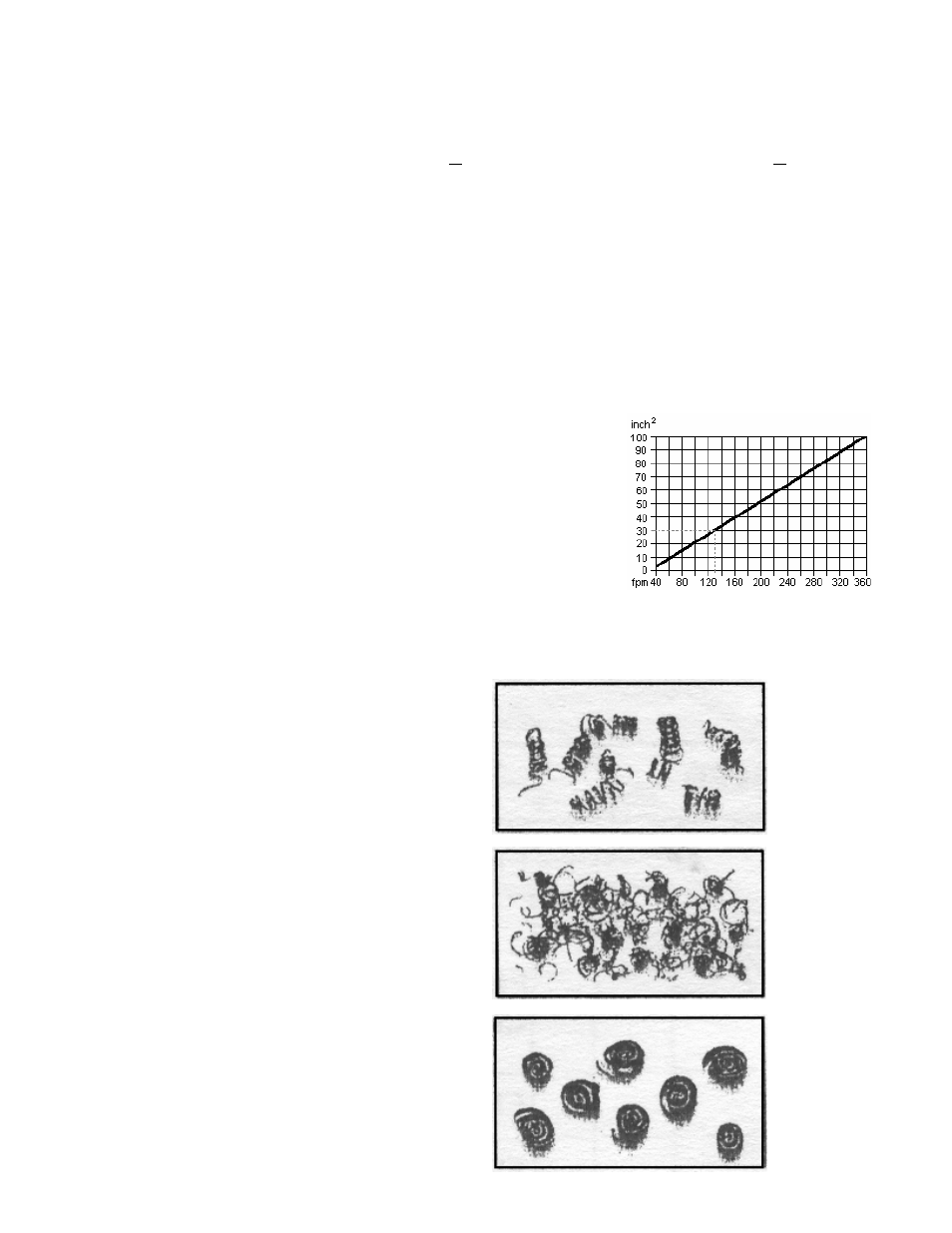
13
2. Figure out number of square inches the material is, e.g. 4” x 4” solid = 16 sq inches.
3. Decrease your head feed pressure to ½ of normal cutting rate - “soft material” and ¾ of the
normal cutting rate for “hard material”.
4. Start machine cutting. Increase speed slightly when blade has cut distance equal to the width
of the blade.
5. Increase speed again slightly as the blade reaches the halfway point of the cut. Finish the
cut without increasing feed again.
6. Start the next cut with the same feed rate as you ended the last cut. Increase the feed rate
again before reaching the halfway point.
7. Repeat step 7 until the blade has cut the recommended number of square inches determined
from the graph below. The cutting time at this point should be at the recommended cutting time,
but adjust if needed.
Total area required for blade break-in can be figured using this
graph, e.g. 4” x 4” = 16 sq. inches of 1020 mild steel cut at 214 fpm
requires 30 square inches of material to be cut at break-in speeds
(dotted line). Dividing the recommended square inches of material
area needed for break-in by the square inches of material will tell
you how many pieces to cut at the break-in speeds. Approximately
2 pieces will need to be cut at break-in speeds in this example.
Determine cutting speeds and feeds by the chip.
1. Look at the sample chip drawing to determine optimum cutting parameters.
Long spiral-shaped chips indicate ideal cutting.
Very fine or pulverized chips indicate lack of feed
And/ or cutting pressure.
Thick and/ or blue chips indicate overload or the
Blade or too much cutting pressure.
