Rdimm maximum memory configurations, Udimm maximum memory configurations, Advanced ecc memory configuration – HP ProLiant BL280c G6 Server-Blade User Manual
Page 30: Mirrored memory configuration, Lockstep memory configuration
Hardware options installation 30
For the latest memory configuration information, see the QuickSpecs on the HP website
RDIMM maximum memory configurations
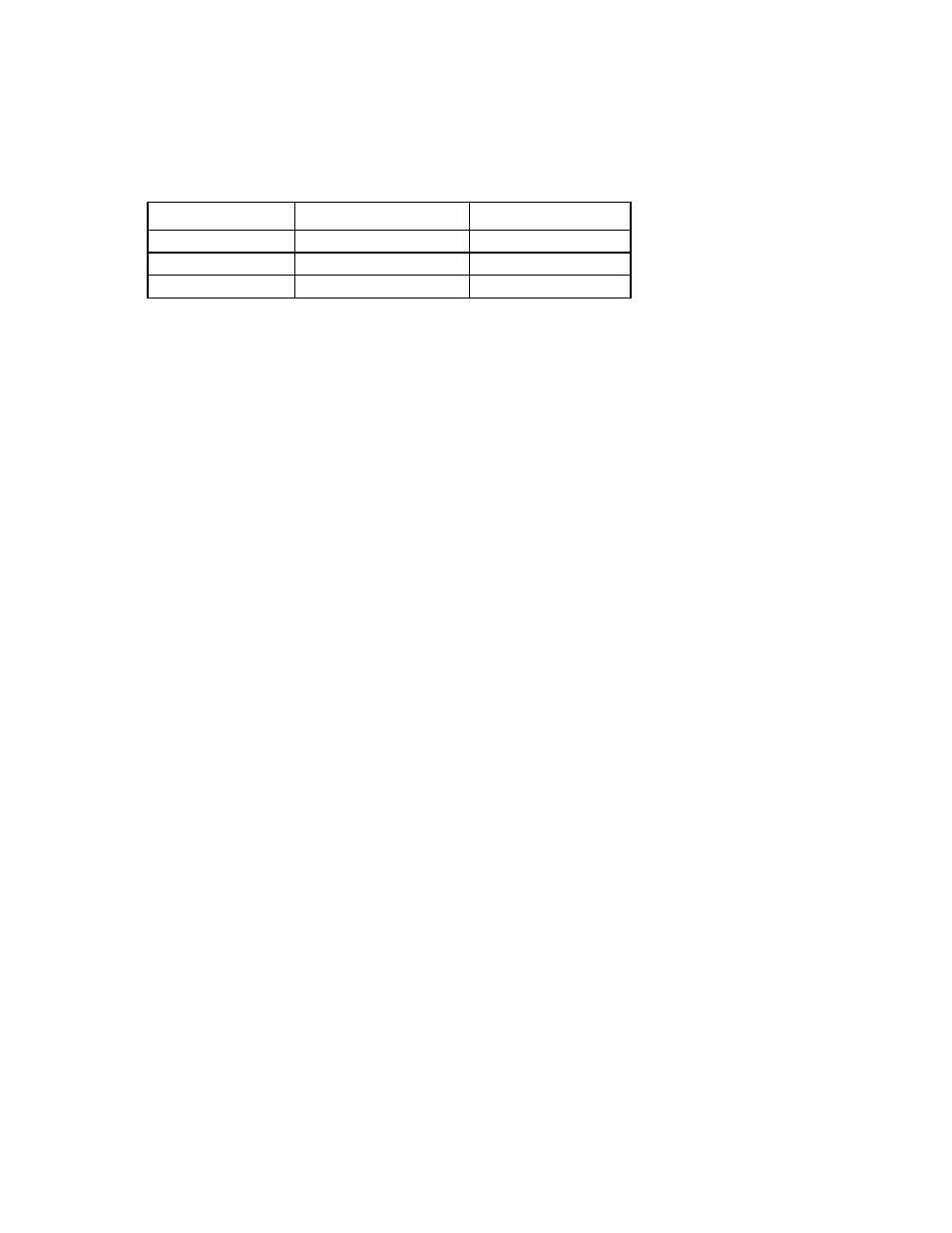
The following table lists the maximum memory configuration possible with 8-GB RDIMMs.
Rank
Single-processor
Dual-processor
Single-rank
48 GB
96 GB
Dual-rank
48 GB
96 GB
Quad-rank
32 GB
64 GB
UDIMM maximum memory configurations
The server blade supports a maximum of 12 GB with one processor and 24 GB with two processors using
2-GB single- or dual-rank UDIMMs.
Advanced ECC memory configuration
Advanced ECC memory is the default memory protection mode for this server blade. Standard ECC can
correct single-bit memory errors and detect multi-bit memory errors. When multi-bit errors are detected using
Standard ECC, the error is signaled to the server blade and causes the server blade to halt.
Advanced ECC protects the server blade against some multi-bit memory errors. Advanced ECC can correct
both single-bit memory errors and 4-bit memory errors if all failed bits are on the same DRAM device on the
DIMM.
Advanced ECC provides additional protection over Standard ECC because it is possible to correct certain
memory errors that would otherwise be uncorrected and result in a server blade failure. The server blade
provides notification that correctable error events have exceeded a pre-defined threshold rate.
Mirrored memory configuration
Mirroring provides protection against uncorrected memory errors that would otherwise result in server blade
downtime. Mirroring is performed at the channel level. Channels 1 and 2 are used; channel 3 is not
populated.
Data is written to both memory channels. Data is read from one of the two memory channels. If an
uncorrectable error is detected in the active memory channel, data is retrieved from the mirror channel. This
channel becomes the new active channel, and the system disables the channel with the failed DIMM.
Lockstep memory configuration
Lockstep mode provides protection against multi-bit memory errors that occur on the same DRAM device.
Lockstep mode can correct any single DRAM device failure on x4 and x8 DIMM types. The DIMMs in each
channel must have identical HP part numbers.
Lockstep mode uses channel 1 and channel 2. Channel 3 is not populated. Because channel 3 cannot be
populated when using Lockstep mode, the maximum memory capacity is lower than Advanced ECC mode.
Memory performance with Advanced ECC is also slightly higher.
