Determining minimum number of remote paths, Analyzing workload, planning data paths, Analyzing workload – HP XP7 Storage User Manual
Page 32
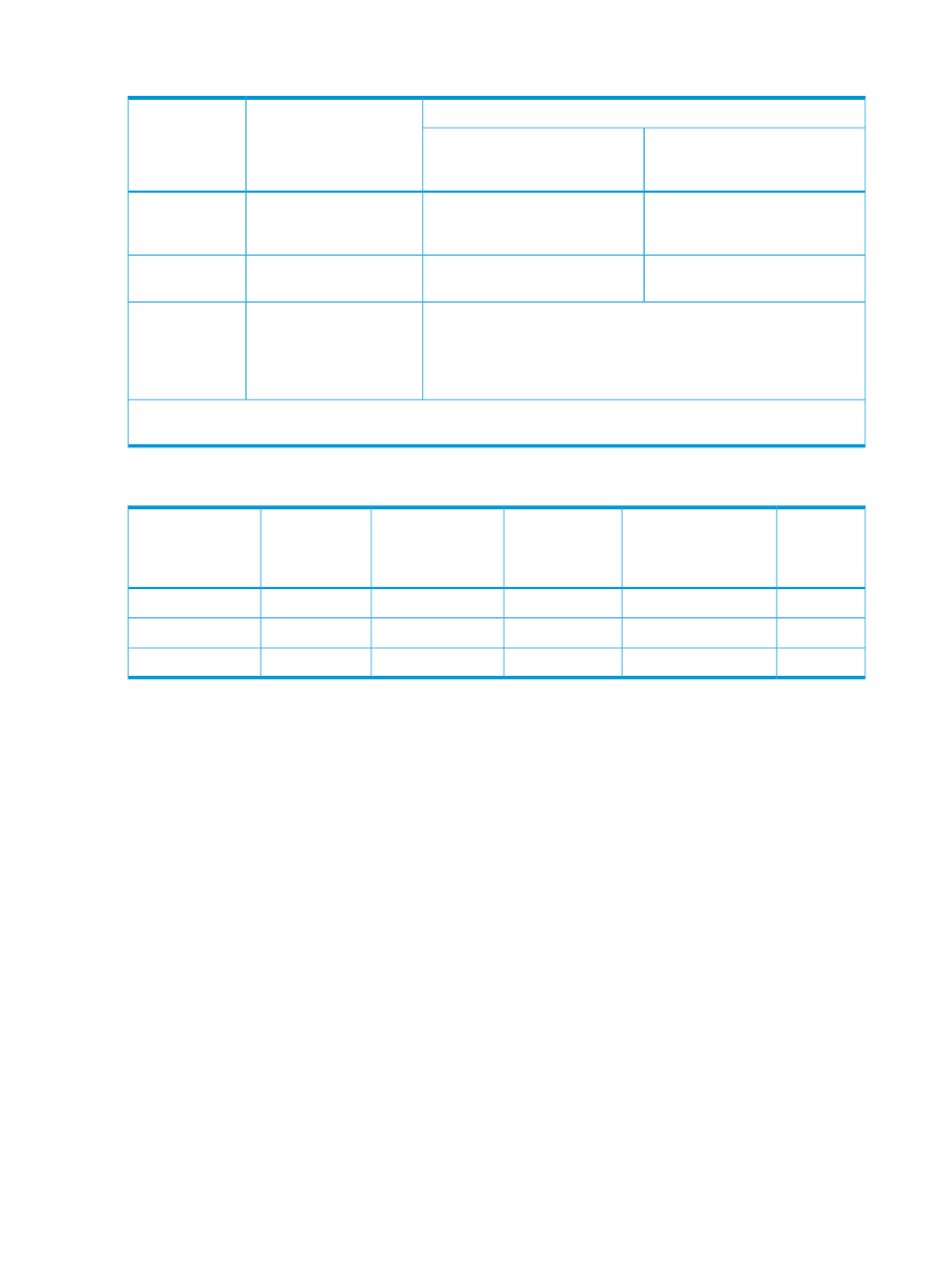
The following table shows the initial copy pace used for the response time calculation.
Initial, update copy in progress
Initial copy only in progress
Interface
When initial copy pace specified
at the time of pair creation is 9 to
15
When initial copy pace specified
at the time of pair creation is 1 to
8
8
User-specified value between 1
and 8
User-specified value
Business
Continuity
Manager
8
User-specified value between 1
and 8
User-specified value
Remote Web
Console
8(*)
15(*)
PPRC command
(TSO/ICKDSF)
and CU
emulation is
I-2107
(*) When a PPRC command (TSO/ICKDSF) is used and the CU emulation type is I-2107, the initial copy pace specified
is invalid. Therefore, the fixed value will be set.
The following table shows example settings.
Round trip
time
specified
[ms]
Number of maximum
initial copy VOLs
Initial copy pace
Number of data
paths between
MCU/RCU
Data path speed
between
MCU/RCU
(MB/ms)
Round trip time
between MCU RCU
[ms]
160
64
15
4
0.1
0
220
64
15
4
0.1
30
360
64
15
4
0.1
100
Determining Minimum Number of Remote Paths
You specify the minimum number of remote paths to the secondary system when you set up the
Cnt Ac-S Z association between primary and secondary systems. Using the Minimum Number of
Paths option, you set a minimum value from one to eight paths, with one being the default.
If the number paths in Normal status drops below the specified minimum, the primary storage
system splits the pair to avoid impact to host performance.
•
To maintain high performance in the primary storage system, HP recommends setting the
minimum number at two.
•
For a pair with important data, set the minimum at one. This allows the system to continue
update operations to the secondary system.
•
You can protect data integrity between P-VOL and S-VOL in the event that the system splits the
pair because the number of paths is lower then the minimum. With the Fence Level setting
(specified during the initial copy), you decide whether, when the pair is split due to an error,
the host continues to access the P-VOL or is denied access. See
after a split—Fence Level options” (page 36)
for more information.
Analyzing workload, planning data paths
You optimize copy operations and performance by carefully planning bandwidth, number of data
paths and host interface paths, and number of ports. This is discussed in:
32
Planning for Continuous Access Synchronous Z
