Safety function, 2 specification of the safety function – KROHNE TT 51 SERIES EN User Manual
Page 7
SAFETY FUNCTION
4
7
TT 51 SERIES
www.krohne.com
09/2010 - 4000869801 - AD TT 51 SIL R01 en
Safety function
4.1 Description of the failure categories
The following definitions of the failure are used during diagnostic calculations:
4.2 Specification of the safety function
The safety function of the TT 51 transmitter is the quality and reliability of the transmitter signal
output, i.e. measurement performance, error detection and error indication in the signal-
processing path of the transmitter.
The valid range of the output signal is between 3.8 mA and 20.5 acc. to NE 43.
The failure information is defined by two selectable alarm levels: Fail Low (Downscale ≤ 3.6 mA)
and Fail High (Upscale ≥ 21 mA).
The configuration of the transmitter is protected by the password in the software ConSoft. The
password is then stored in the transmitter.
The TT 51 checks sensor errors (sensor break or sensor short) for both channels if it is
configured in this manner.
A software SIL-switch is available in the transmitter, handled by the PC-configuration software
ConSoft. It is also password-protected. It can also be changed by HART
®
communication, still
password-protected.
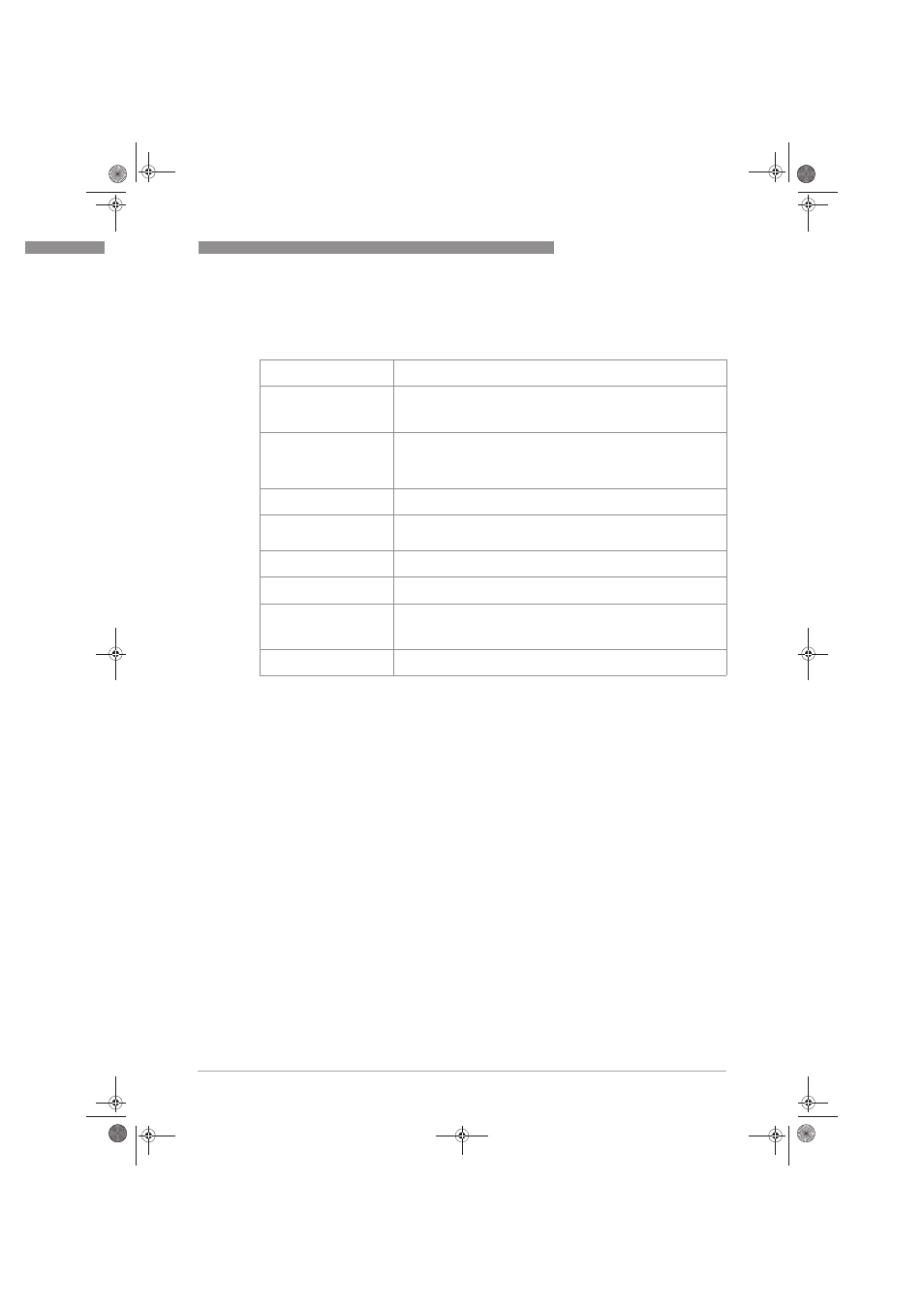
Fail-Safe State
The fail-safe state is defined as the output reaching the user defined
threshold value.
Fail - Safe
A safe failure (S) is defined as a failure that causes the
module/(sub)system to go to the defined fail-safe state without a demand
from the process. Safe failures are divided into safe detected (SD) and safe
undetected (SU) failures.
Fail Dangerous
A dangerous failure is defined as a failure of the temperature transmitter
TT 51 C not responding to a demand from the process, i.e. being unable to
go to the defined fail-safe state, and the output current deviates by more
than 2% of measuring span of the actual temperature measurement
value.
Fail Dangerous Undetected
Failure that is dangerous and that is not being diagnosed by internal
diagnostics.
Fail Dangerous Detected
Failure that is dangerous but is detected by internal diagnostics and
causes the output signal to go to the predefined alarm state (These
failures may be converted to the selected fail-safe state).
Fail High
Failure that causes the output signal to go to the maximum output current
(> 21 mA) acc. to NAMUR NE 43.
Fail Low
Failure that causes the output signal to go to the minimum output current
(< 3.6 mA) acc. to NAMUR NE 43.
No Effect
Failure of a component that is part of the safety function but is neither a
safe failure nor a dangerous failure and has no effect on the safety
function. For the calculation of the SFF it is treated like a safe undetected
failure.
Not part
Failures of a component which is not part of the safety function but part of
the circuit diagram.
.book Page 7 Thursday, September 9, 2010 4:19 PM
