KROHNE CORIMASS MFC 85 Interface EN User Manual
Page 7
7
2.3
HART
®
Protocol Structure
HART
®
follows the basic Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model, developed by
the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) [3]. The OSI model provides the
structure and elements of a communication system. The HART
®
protocol uses a reduced OSI
model, implementing only layers 1,2 and 7.
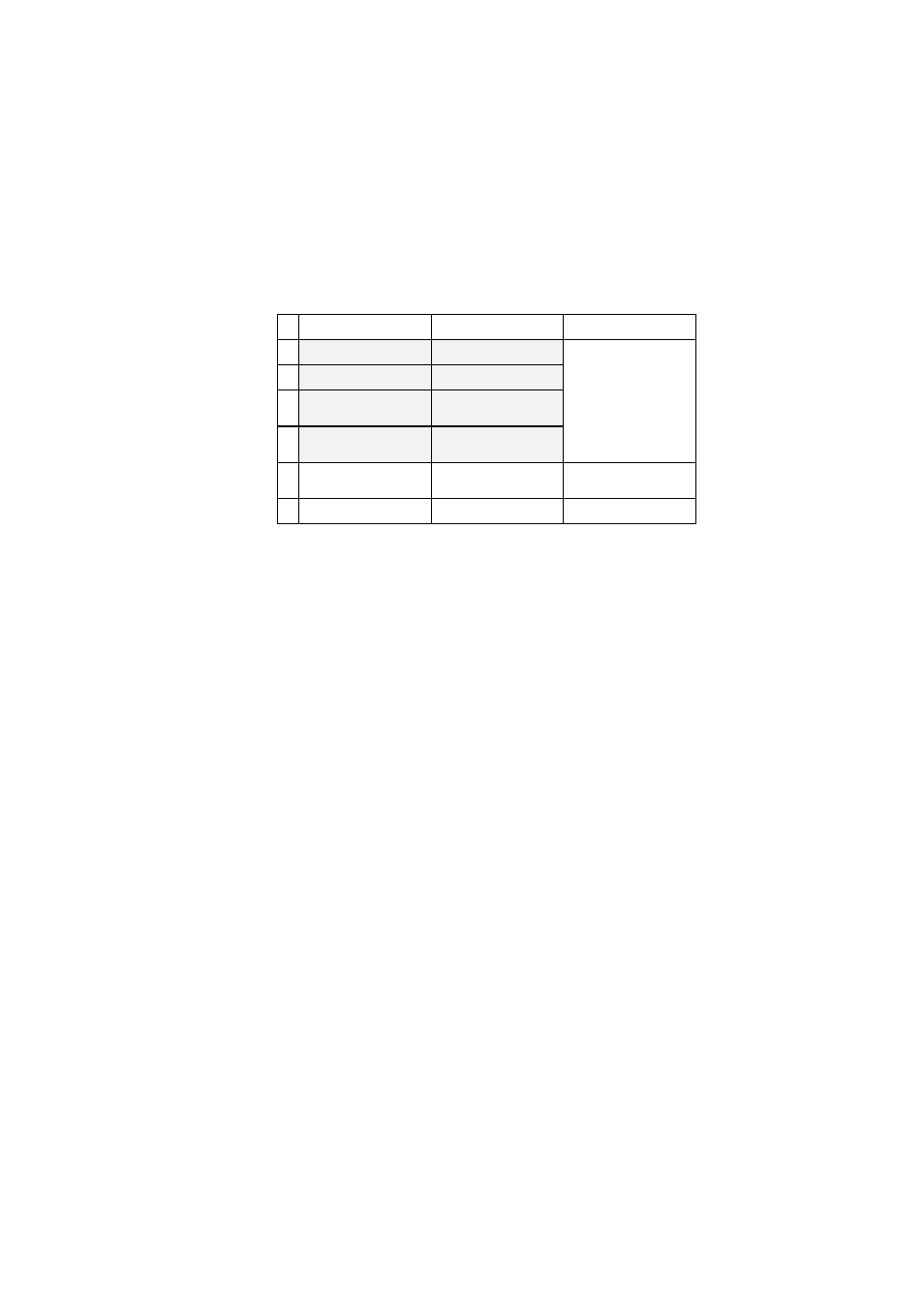
OSI Reference Model
Open Systems Interconnection
Layer
Function
HART
®
7
Application
provides formatted data
HART instructions
6
Presentation
converts data
5
Session
handles the dialogue
4
Transport
secures the transport
connection
3
Network
establishes network
connections
2
Link
establishes the data
link connection
HART protocol
regulations
1
Physical
connects the equipment
Bell 202
The HART
®
protocol implements layers 1,2 and 7 from the OSI model
Layer 1, the Physical layer, operates on the FSK principle, based on the Bell 202
communication standard:
Data transfer rate:
1200 bit/s
Logic ‘0’ frequency: 2200 Hz
Logic ‘1’ frequency: 1200 Hz
The vast majority of existing wiring is used for this type of digital communication. For short
distances, unshielded, 0.2 mm
2
two-wire lines are suitable. For longer distances (up to
1500 m), single, shielded bundles of 0.2 mm
2
twisted pairs can be used. Beyond this,
distances up to 3000 m can be covered using single, shielded, twisted 0.5 mm
2
pairs.
A minimum resistance of 230 ohms must be available in the communication circuit.
Layer 2, the Link layer, establishes the format for a HART
®
message. HART
®
is a
master/slave protocol. All the communication activities originate from a master, e.g. a display
terminal. This addresses a field device (slave), which interprets the command message and
sends a response.
