Technical data, Technical data 6.1 measuring principle – KROHNE OPTISENS PH 8100 EN User Manual
Page 43
TECHNICAL DATA
6
43
OPTISENS PH 8100
www.krohne.com
03/2012 - 4001925901 MA OPTISENS PH 8100 R01 en
Technical data
6.1 Measuring principle
6.1.1 pH measurement
The measuring principle of a pH electrode is based on a pH sensitive glass. When the pH
sensitive glass gets into contact with a liquid, a thin layer of hydrated gel develops on the
surface, enabling an ion exchange between the glass surface and the liquid. The so-called
Nernst potential builds up on the glass surface. If both sides of the glass are in contact with
liquids, a voltage may be detected between the two surface potentials. The voltage correlates to
the difference in H
+
ion concentration and thus to the difference of pH values in both liquids.
The pH measuring electrode contains an internal buffer solution with a known pH value. If the pH
value of the measuring medium on the outside of the electrode is equal to the pH value of the
inner buffer, the resulting voltage is 0 V.
If the pH value of the medium differs from the internal pH value, a voltage between the internal
and the external layer can be measured. From the resulting voltage, the pH difference of the two
liquids can be calculated.
The voltage is measured using a measuring electrode and a reference electrode; both are built
into the sensor. The measuring electrode is in contact with the known buffer solution in the pH
sensitive glass bulb. The reference electrode is immersed into a saturated solution of potassium
chloride (KCl). The KCl solution itself is in electrical contact with the measuring medium by
means of a diaphragm. The diaphragm prevents the measuring medium from penetrating into
the reference system but still allows electrical contact with the measuring medium.
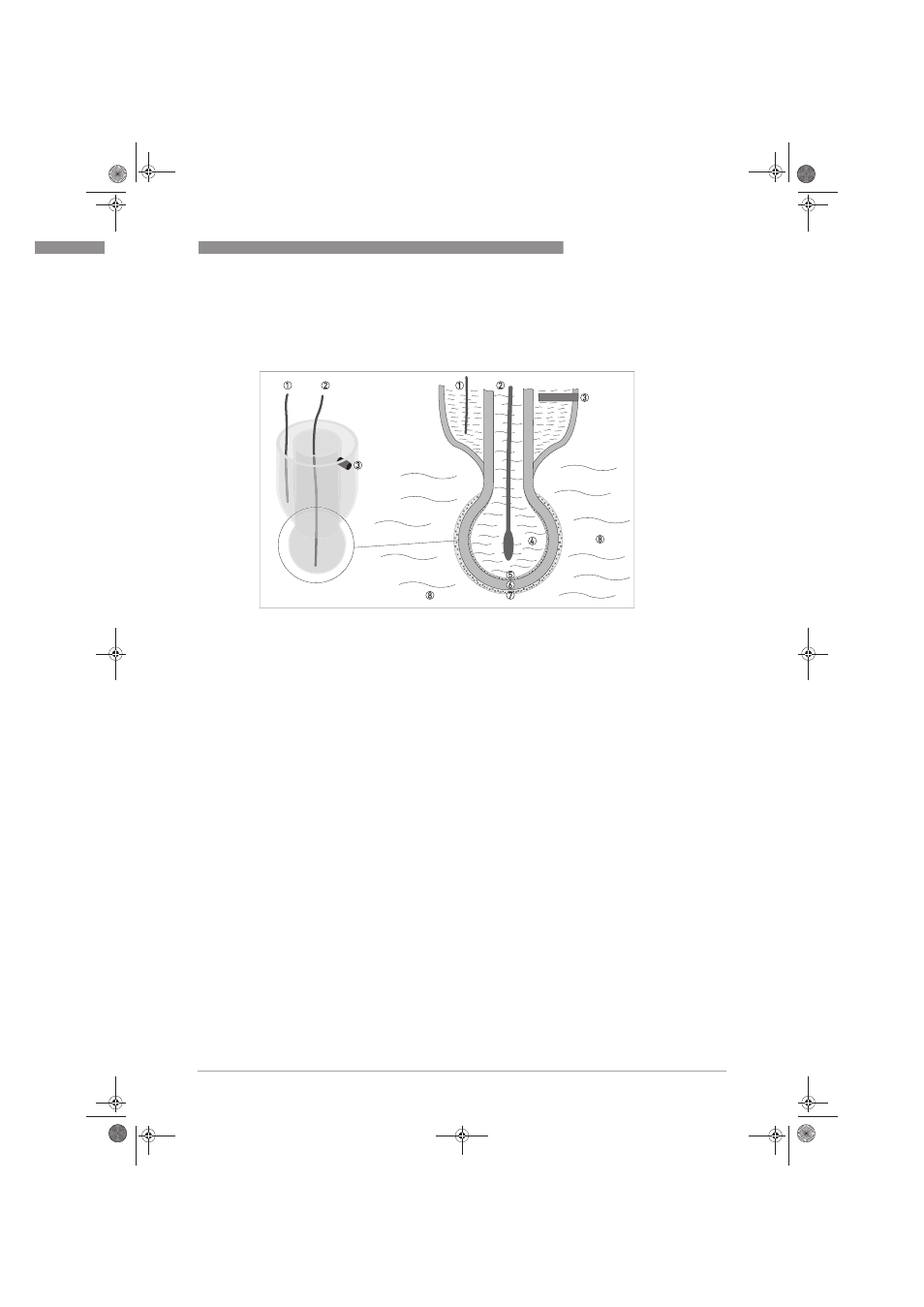
Figure 6-1: Measuring principle for pH measurement
1 Reference electrode
2 Measuring electrode
3 Diaphragm in contact with KCl solution and measuring medium
4 Inner pH 7 buffer solution
5 Surface potential on the inside (contact with buffer solution)
6 pH sensitive glass
7 Surface potential on the outside (contact with measuring medium)
8 Measuring medium
.book Page 43 Wednesday, July 4, 2012 11:07 AM
