COSA Xentaur COSA 9610 User Manual
Page 7
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL – COSA 9610™
Page 7 of 44
1.2.2.
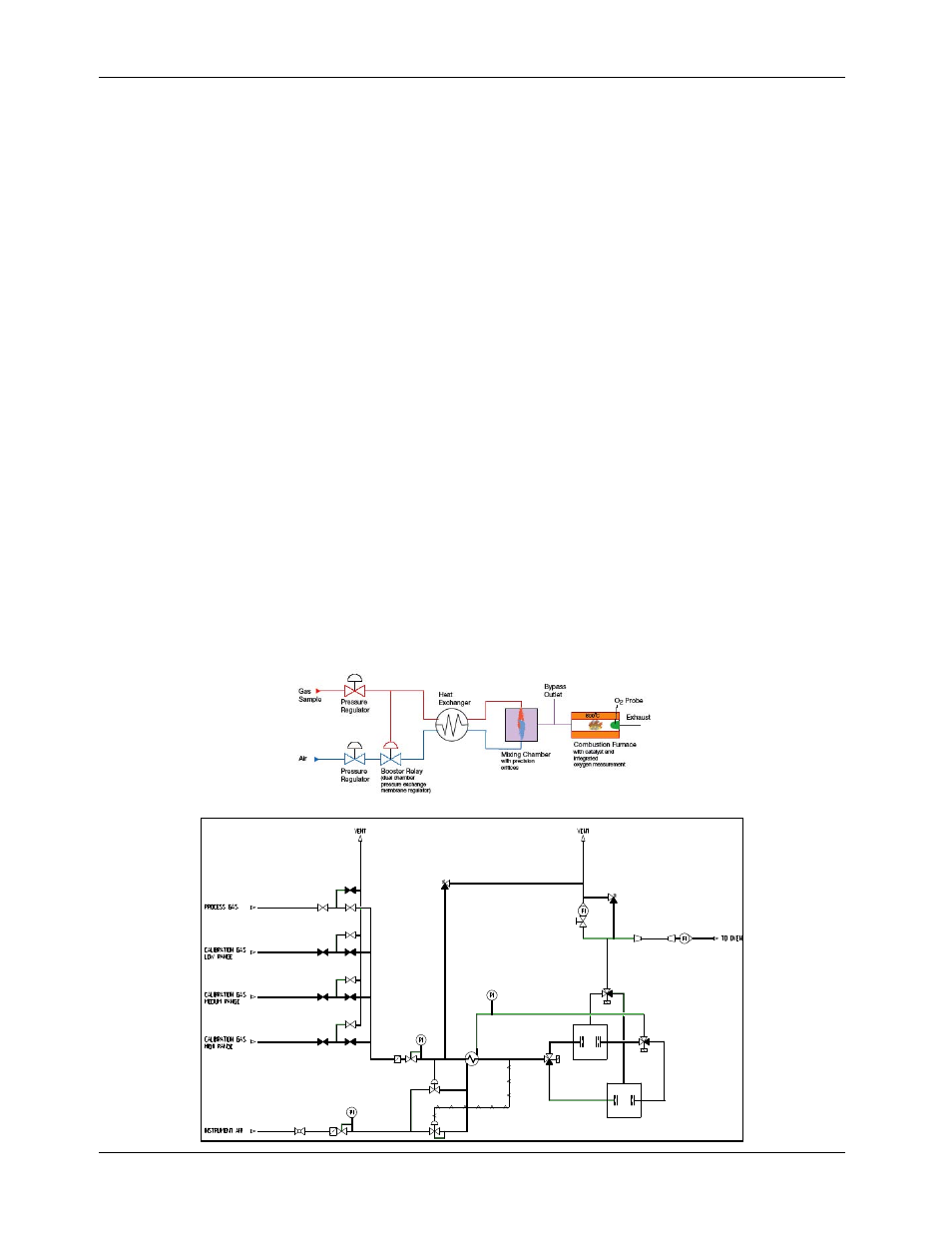
The sample system (SCS)
In the sample conditioning system (SCS), gas and air are mixed in a constant proportion,
such that a small excess of air is present (± 2.5% oxygen) in the flue gas. The gas and air
pressure, are equalized by a dome-loaded pressure reducer (or booster relay), where the
gas pressure governs the air pressure.
The booster relay has a temperature reducing effect; the gas/air mixing proportion can
therefore vary as consequence of variations in viscosity. Therefore, the temperature of the
gas and the air are equalized in a heat exchanger. The gas and air temperature are still at
surrounding temperatures, however, as long as gas and air fluctuate to the same extent
this hardly influences the mixing proportion. In case of large surrounding temperature
fluctuations, the calibration sequence has to be performed more often. Hereafter gas and
air are mixed in the mixing chamber. The mixing chamber is equipped with orifices in the
inlet nozzles. The gas and airflow are determined by a critical expansion over the orifices.
The turbulence created provides a homogeneous mixture.
The diameter ratio of the orifices, together with the ratio between gas and air pressure,
determine the mixing proportion.
After the mixing chamber, the mixture flow is divided into an excess flow to vent and a
flow to oven. The flow to the burning oven will be approximately 30-50 Nl/hr. The vented
stream is approximately 500 Nl/hr with a maximum 1000 Nl/hr.
