LEESON Permanent Magnet AC Motors User Manual
Page 6
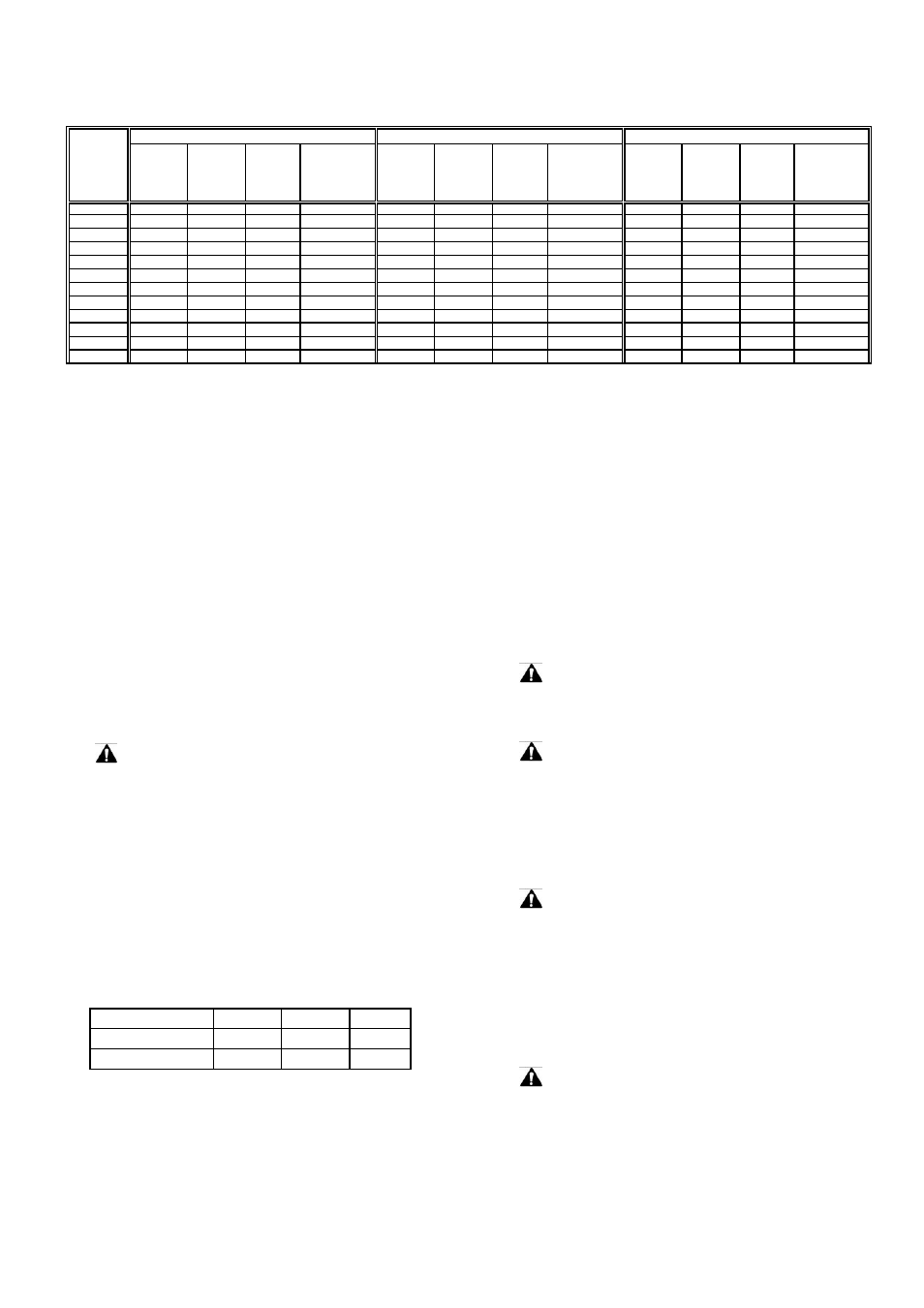
Table 3-3 Recommended Minimum Sheave Diameters, Belt Type, Number of Belts and Deflected Force
Motor Hp
1200 rpm
1800 rpm
3600 rpm
Min
Sheave
Dia (in)
Belt
Type
Max
#
of
Belts
Avg.
Deflected
Force
(lbs)
Min
Sheave
Dia (in)
Belt
Type
Max
#
of
Belts
Avg.
Deflected
Force
(lbs)
Min
Sheave
Dia (in)
Belt
Type
Max
#
of
Belts
Avg.
Deflected
Force
(lbs)
0.75
2.2
3VX
1
3.4
2.2
3VX
1
2.2
3VX
1
1
2.4
3VX
1
4.0
2.2
3VX
1
3.1
2.2
3VX
1
1.5
2.4
3VX
2
3.1
2.4
3VX
2.2
3VX
1
2.5
2
2.4
3VX
3
2.8
2.4
3VX
2
2.9
2.4
3VX
3
3.0
3VX
2
3.3
2.4
3VX
3
2.9
2.4
3VX
2
2.3
5
3.0
3VX
3
4.0
3.0
3VX
3
3.7
2.4
3VX
3
2.5
7.5
3.8
3VX
4
4.7
3.0
3VX
4
4.1
3.0
3VX
2
4.2
10
4.4
3VX
4
5.4
3.8
3VX
4
4.3
3.0
3VX
3
3.8
15
4.4
3VX
5
5.4
4.4
3VX
4
5.4
3.8
3VX
3
4.4
20
5.2
3VX
6
6.0
4.4
3VX
6
4.8
4.4
3VX
3
5.0
25
6.0
3VX
7
5.6
4.4
3VX
7
5.2
4.4
3VX
4
4.7
30
6.8
3VX
7
5.9
5.2
3VX
7
5.3
Notes:
1. The ratings listed above assume normal frame size assignments per NEMA MG-1 (2009) Table 13.2.
Horsepower is the nameplate motor horsepower, and RPM is the motor (driver) speed.
2.
Minimum sheave diameters are from NEMA standards where applicable.
3.
For variable speed applications or values outside these recommendations, consult motor manufacturer.
4.
Selections are based on a 1.4 belt service factor, 5 to 1 speed reduction and various Power Transmission Manufacturers’ catalogs.
5.
These selections are for Narrow V-belt sections only. Consult motor manufacturer for details on conventional V-belt sections (A, B, C, D and E), or
other belt types.
6.
“Average Deflected Force” is per section 3.3.4.4 of this document and is the force required to deflect the center of a belt 1/64 of the belt span
distance. Tolerance on this force is ±1 lbf for forces
≤
10 lbs, and ±2 lbs for forces >10 lbs as measured utilizing a belt tension gage.
7.
When more than one belt is required, the belts must be a matched set (matched for length).
8.
If possible, the lower side of the belt should be the driving side to increase the length of wrap on the sheave.
9.
Do not exceed nameplate maximum
RPM.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
NOTICE: VFD / Motor Setup
It is the responsibility of the startup personnel during set up of the
VFD / motor system to properly tune the drive to the motor for the
specific application per the VFD user manual. The correct voltage
boost, volts per hertz, and overload current level settings are
application dependent and unique to each motor design. Current
setting shall not exceed nameplate service factor amps. Failure to
connect over temperature devices (when provided) will void the
warranty.
3.3.5.1
Overspeed Capability
Do not exceed nameplate maximum RPM without first contacting
manufacturer.
WARNING:
ELECTRICAL HAZARD
Shaft rotation produces voltage in PM motors even when motor is
disconnected from power source. Do not operate the motor or
allow equipment to back drive the motor above the maximum
RPM listed on the motor nameplate. Failure to do so may cause
serious injury or death to personnel or damage the motor or
system equipment.
3.3.5.2 Cable Lengths:
These motors are equipped with an
insulation system designed for use with variable frequency
drives. For optimum insulation life, limit VFD to motor cable
lengths as documented in Table 3-5. For additional information,
or for installations requiring longer cable runs, please contact the
motor manufacturer
.
Table 3-5 Max Cable Lengths
These values are based on 3 kHz carrier frequency. Add
suitable VFD output-side filters when exceeding the listed
values.
Frame Size
230V
460 V
575 V
NEMA 180-280
2000 ft.
2000 ft.
650 ft.
IEC 112-180
600 m.
600 m.
200 m.
3.3.5.3
VFD Grounding:
See Grounding section 3.4.4
3.3.5.4 Stray Voltage on Accessory Leads
VFDs will couple stray voltage to accessories such as
RTDs, thermistors, thermostats and space heaters. The
leads of these elements must be properly insulated and
control input circuits must be designed to withstand this
voltage.
3.3.6
ACCESSORIES / PROVISIONS
3.3.6.1
General:
Carefully read and understand the accessory
manufacturer’s instructions, supplied with motor. Contact the
manufacturer for additional information.
3.3.6.2 Brake Motors
WARNING
: Backup Brake System
Failure of the brake may put people in the vicinity of the motor at
risk for serious personal injury or death, or cause damage to
nearby equipment. If people or equipment will be in the vicinity of
the motor, a backup system should be supplied.
WARNING
: Vertical
Motor
Premature Brake Failure
Motors with brakes that are designed for vertical applications are
equipped with springs to support the brake pressure plate.
Mounting a horizontal brake motor vertically shaft up or down
may require a pressure plate spring modification. Failure to
modify the brake for the vertical application may result in
premature brake failure, creating a risk of serious personal injury
or death and/or equipment damage. If in question, consult brake
literature or brake manufacturer.
WARNING
: DO NOT CONNECT BRAKE SOLENOID to
the output of a VFD. The brake solenoid must be wired to 50/60
Hz line power for proper operation. Failure to do so may result in
brake damage, potentially leading to serious injury, death, or
equipment damage.
3.3.6.3
Space Heaters
Motors provided with space heaters have two leads that are
brought into the conduit box or into an auxiliary box. These leads
are marked”H1”, “H2” (”H3”, “H4” if a second space heater is
supplied). See the space heater nameplate on motor for heater
rating.
WARNING:
DIVISION 2 EXPLOSION HAZARD
The space heater temperature rating when used in Class I,
Division 2 motors shall
NOT
exceed 80% of the auto ignition
temperature of the hazardous gas or vapor. See the space
heater nameplate on motor for heater Temperature Code and
heater rating. Failure to follow this instruction could result in
serious personal injury, death and/or property damage.
