LEESON Permanent Magnet AC Motors User Manual
Page 10
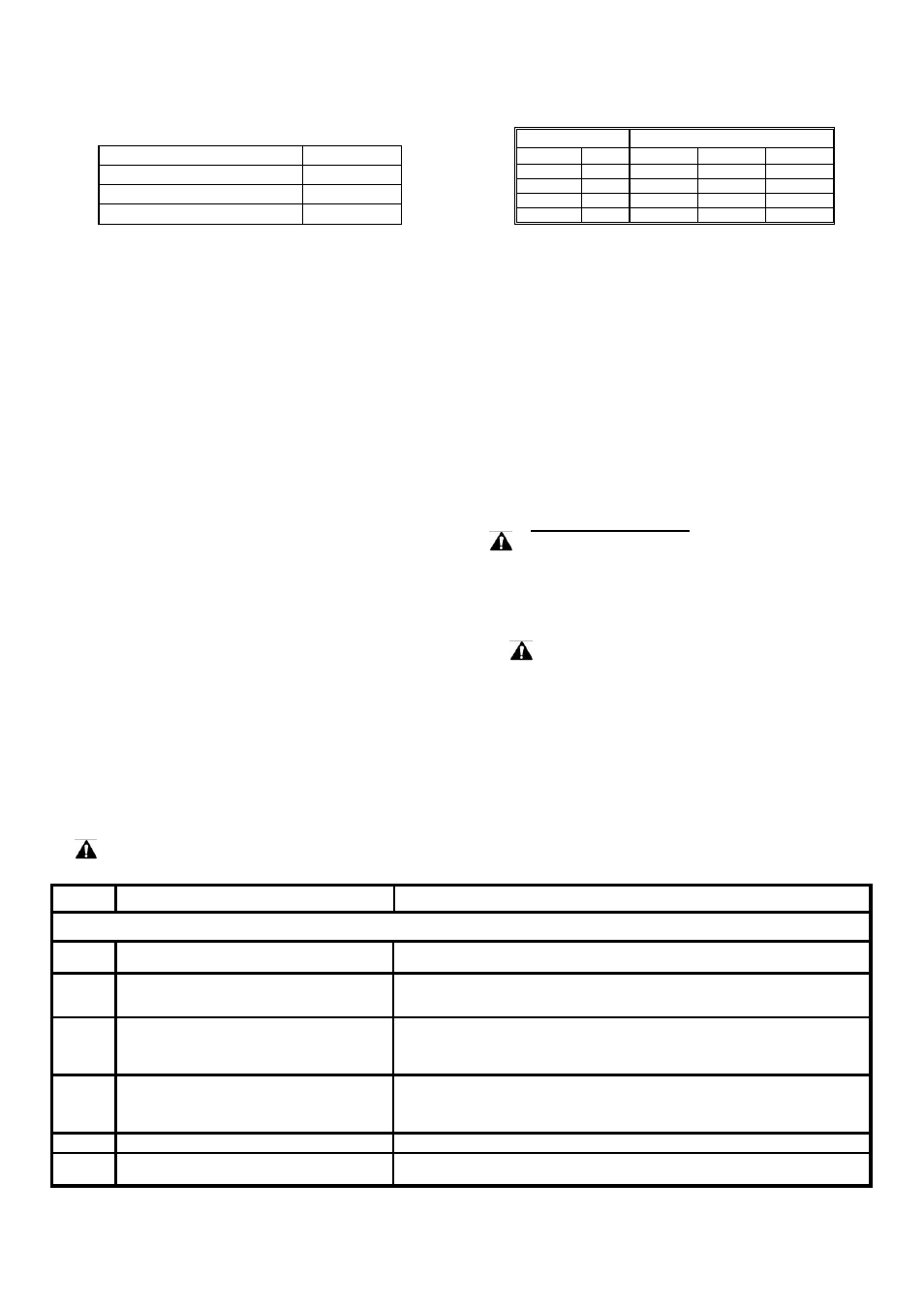
Table 4-3 Construction Multiplier
Construction
Multiplier
Angular Contact or Roller Bearing
0.5
Vertical Motor
0.5
All others
1.0
Table 4-4 Relubrication Amounts
Frame Size
Volume
NEMA
IEC
Cu. In.
Fluid oz
ml
180
110
0.50
0.28
8.0
210
130
0.75
0.42
12.5
250
160
1.00
0.55
16.0
280
180
1.50
0.83
25.0
For regreasing while operating multiply volume by 125%.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.2.4
LUBRICATION PROCEDURE
(For Motors with Regreasing Provisions)
NOTICE:
BEARING DAMAGE WARNING
Added grease must be compatible with the original equipment’s
grease. If a grease other than those stated in 4.2.1 is to be
utilized, contact the motor manufacturer. Nameplate information
supersedes section 4.2.1 (GREASE TYPE). New grease must be
free of dirt. Failure to follow these instructions and procedure
below may result in bearing and/or motor damage.
NOTICE:
GREASE DRAIN PLUGGED
Old grease may completely block the drain opening and must be
mechanically removed prior to regreasing. Forcing a blocked
drain open by increased greasing pressure may collapse bearing
shields and / or force excess grease through the bearings and
into the motor.
For an extremely dirty environment, contact the motor
manufacturer for additional information.
LUBRICATION PROCEDURE:
1.
Clean the grease inlet plug or zerk fittings prior to regreasing.
2.
(If present) Remove grease drain plug and clear outlet hole
blockage.
3.
Add grease per Table 4-4
4.
Re-install grease inlet and drain plugs (if removed).
4.2.5
EXAMPLE: LUBRICATION
Assume - NEMA 286T (IEC 180), 1750 RPM Vertical motor
driving an exhaust fan in an ambient temperature of 43° C and
the atmosphere is moderately corrosive.
1.
Table 4-1 list 10,000 hours for standard conditions.
2.
Table 4-2 classifies severity of service as “Severe” with a
multiplier of 0.5.
3.
Table 4-3 lists a multiplier value of 0.5 for “Vertical”
4.
(Eq. 4.2) Interval = 10,000 hrs x 0.5 x 0.5 = 2500 hrs
5.
Table 4-4 shows that 1.5 cubic inch of grease is to be added.
Relubricate every 2,500 hrs of service with 1.5 cubic inch of
recommended grease.
4.3
TROUBLE-SHOOTING
WARNING:
READ INSTRUCTIONS
:
Before trouble-shooting a motor, carefully read and fully understand
the warnings, cautions, & safety notice statements in this manual.
Failure to do so could cause severe injury, death, and/or equipment
damage.
4.3.1
GENERAL TROUBLE SHOOTING
WARNINGS:
1.
Disconnect power to the VFD and verify VFD DC output
voltage is zero before performing service or
maintenance.
2.
Always keep hands, hair, and clothing away from
moving parts.
3.
Be sure required safety guards are in place before
starting equipment.
4.
If the problem persists, contact the manufacturer.
Motor Trouble-shooting Cause / Corrective Action - Table 4-5
Before conducting any trouble-shooting, be sure to read and follow all safety warnings and
instructions.
Failure to do so could cause severe injury, death, and/or equipment damage.
Issue
Likely Cause
Corrective Action
Motor fails to start upon initial installation
A
Low or no input voltage to VFD.
(1) Ensure that rated input voltage is present at VFD. Ref. Section 3.4.1.2.
(2) Check line fuses. Ref. Section 3.4.1.1.
B
Motor leads are not connected or miswired in
conduit box or at VFD output terminals.
(1) Match motor lead wiring to motor nameplate connection diagram for operating
voltage. Ref. Section 3.4.3.
(2) Check continuity between VFD and motor terminals. Ref. Section 3.4.5.
C
Driven load exceeds motor/VFD capacity. VFD
may trip on overload fault.
(1) Verify that VFD current / torque limit setting equals motor rated service factor amps
(these parameters may be set to zero at the factory for safety purposes). Ref Section
3.3.5
(2) Verify that motor and VFD rating are adequate for application.
D
Load is jammed or motor is binding. VFD trips on
overload fault.
(1) Verify that motor & load turn freely. Ref. Section 3.4.5.
(2) Disconnect motor from load & ensure motor turns freely. Ref. Section 3.4.5.
(3) Verify that motor starts when disconnected from load. Ref. Section 3.4.5.
(4) Remove excessive / binding load if present.
E
Acceleration time set too short.
Increase acceleration to maximum acceptable time for the application.
F
VFD programmed incorrectly. VFD trips on
overload fault.
(1) Repeat checks listed above.
(2) Consult VFD service manual. Ref. Section 3.3.5.
