Faults and remedial action – SPP Pumps Instream User Manual
Page 11
Operators Instructions for
Instream Centrifugal Pumps
Manual No/Rev
W23-001E / 8
Our policy is one of continuous improvement and we reserve the right to alter specifications at any time
Page 11 of 16
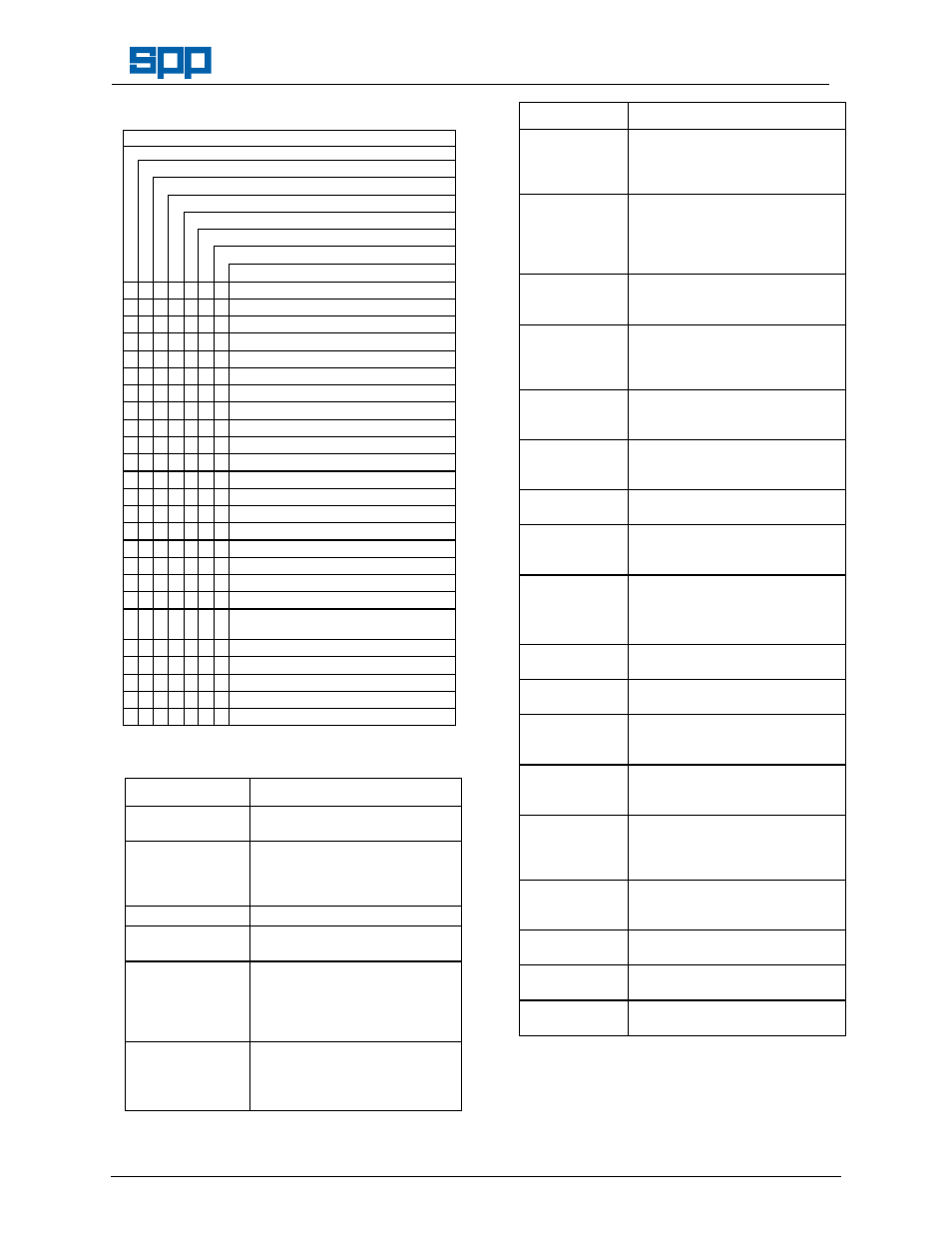
7. Faults and Remedial Action
POTENTIAL FAULT OR DEFECT:
No liquid delivered.
Insufficient liquid delivered.
Liquid delivered at low pressure.
Loss of liquid after starting.
Excessive vibration.
Motor runs hotter than normal.
Excessive noise from pump cavitation.
PROBABLE CAUSES
Pump not primed.
Speed too low.
Speed too high.
Air leak in suction pipework.
Air leak in mechanical seal.
Air or gas in liquid.
Discharge head too high (above rating).
Suction lift too high.
Not enough head for hot liquid.
Inlet pipe not submerged enough.
Viscosity of liquid greater than rating
Liquid density higher than rating.
Insufficient nett inlet head.
Impeller plugged up or blocked.
Wrong direction of rotation.
Excessive wear ring clearance.
Damaged impeller.
Rotor binding.
Defects in motor.
Voltage and/or frequency lower than
rating.
Foundation not rigid.
Misalignment of pump and driver.
Rotor out of balance.
Shaft bent.
Impeller too small.
For remedial action refer to the following tables:
CAUSE
REMEDIAL ACTION
Pump not primed.
Fill pump and suction pipe
completely with fluid.
Speed too low.
Check that the motor is correctly
connected and receiving the full
supply voltage also confirm that
the supply frequency is correct.
Speed too high.
Check the motor voltage.
Air leak in suction
pipework
Check each flange for suction
draught, rectify as necessary.
Air leak in
mechanical seal.
Check all joints, plugs and
flushing lines, if fitted. Note that
prolonged running with air in the
mechanical seal will result in
damage and failure of the seal.
Air or gas in liquid. It may be possible to increase the
pump performance to provide
adequate pumping.
CAUSE
REMEDIAL ACTION
Discharge head
too high (above
rating).
Check that valves are fully open
and for pipe friction losses. An
increase in pipe diameter may
reduce the discharge pressure.
Suction lift too
high.
Check for obstruction of pump inlet
and for inlet pipe friction losses.
Measure the static lift, if above
rating, raise the liquid level or
lower the pump.
Not enough
head for hot
liquid.
Reduce the positive suction head
by raising the liquid level.
Inlet pipe not
submerged
enough.
If the pump inlet cannot be
lowered, provide a baffle to
smother the inlet vortex and
prevent air entering with the liquid.
Liquid density
higher than
rating.
Refer to SPP Pumps Ltd. for
guidance to increase the size or
power of the motor or engine.
Insufficient nett
inlet head.
Increase the positive suction head
by lowering the pump or raising
the liquid level.
Impeller
blocked.
Dismantle pump and clean the
impeller.
Wrong direction
of rotation.
Check driver rotation with the
direction arrow on the pump
casing.
Excessive wear
ring clearance.
Replace the wear rings when the
clearance exceeds the maximum
tolerances.
Damaged
impeller.
Replace if damaged or vanes are
eroded.
Rotor binding.
Check for shaft run out, and
replace if necessary.
Defects in
motor.
Ensure that motor is adequately
ventilated. Refer to manufacturers
instructions.
Voltage and/or
frequency lower
than rating.
If voltage and frequency are lower
than the motor rating, arrange for
provision of correct supply.
Foundation not
rigid.
Ensure that the foundation bolts
are tight; check that foundations
match SPP Pumps Ltd.
Recommendations.
Misalignment of
pump and
driver.
Check shaft run-out and replace if
necessary.
Rotor out of
balance.
Check impeller for damage,
replace as necessary.
Shaft bent.
Check shaft run-out and replace if
needed.
Impeller too
small.
Refer to SPP Pumps Ltd. for
options to fit a larger impeller.
