Experiment 2: charles’ law, V = c t, Theory setup procedure – PASCO TD-8592 SMALL PISTON HEAT ENGINE APPARATUS User Manual
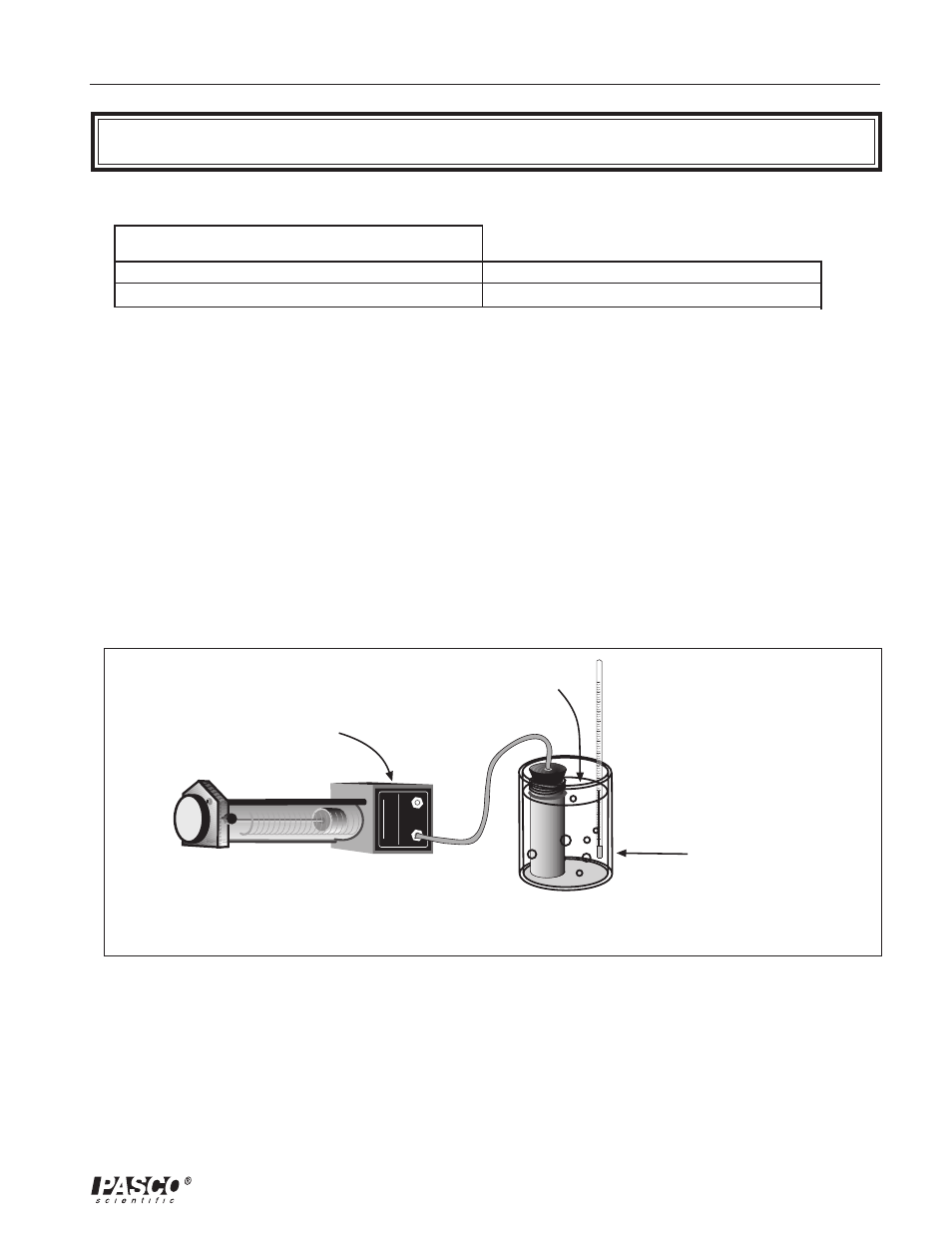
Page 10: Figure 2.1: experiment setup
012-08375A
Small Piston Heat Engine
5
Hot
HEAT ENGINE
GAS
LAW
APPARATUS
Piston Dia.: 32.5mm±0.1
TD-8572
CAUTION:
Max. Pres.: 345
kPa. Use Gases Only
DO NOT
Immerse in any Liquid
DO NOT Lubricate Piston or Cylinder
Pressure Port Mating Connector:
P
AS
CO Part No. 640-021
P
is
to
n
&
P
la
tf
o
rm
M
as
s:
3
5.
0
g
±
0.
6
Experiment 2: Charles’ Law
Charles’ law states that at a constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass or quantity of gas varies
directly with the absolute temperature:
V = cT
(at constant pressure, P, where temperature, T, is
expressed in degrees Kelvin)
➀ Using the one-holed stopper and plain tubing, connect the base apparatus and the air chamber.
➁
Close the shut-off valve on the tubing from the unused port.
➂
Turn the base apparatus on its side. (In this position, the force acting on the apparatus is the
atmospheric pressure and is equal throughout the range of operation of the piston.)
Theory
Setup
Procedure
➀
Place the air chamber in a container of hot water. After the chamber equilibrates to the
temperature, record the temperature and the height of the piston.
➁
Add ice to the container and record the temperature and pressure at regular time intervals.
➂
Calculate the gas volumes at the various piston positions you measured and make a graph of plots of tempera-
ture versus volume. (Hint: The diameter of the piston is 15.9± 0.1 mm.)
Equipment Required:
• Small Piston Heat Engine
• Thermometer
• Container of hot water
• Ice
Do not allow the tip of the
thermometer to touch the
bottom of the container.
Add ice.
Close the shut-off valve on
the tubing from the unused
port.
Figure 2.1: Experiment setup
