Experiment 2: surface area and terminal velocity – PASCO ME-9595 Car Sail User Manual
Page 8
®
Model No. ME-9595
Car Sail
7
Experiment 2: Surface Area and Terminal
Velocity
Introduction
After establishing the concept of terminal velocity in Experiment 1,
students can use this experiment to investigate the relationship
between the surface area of the sail and terminal velocity.
Procedure
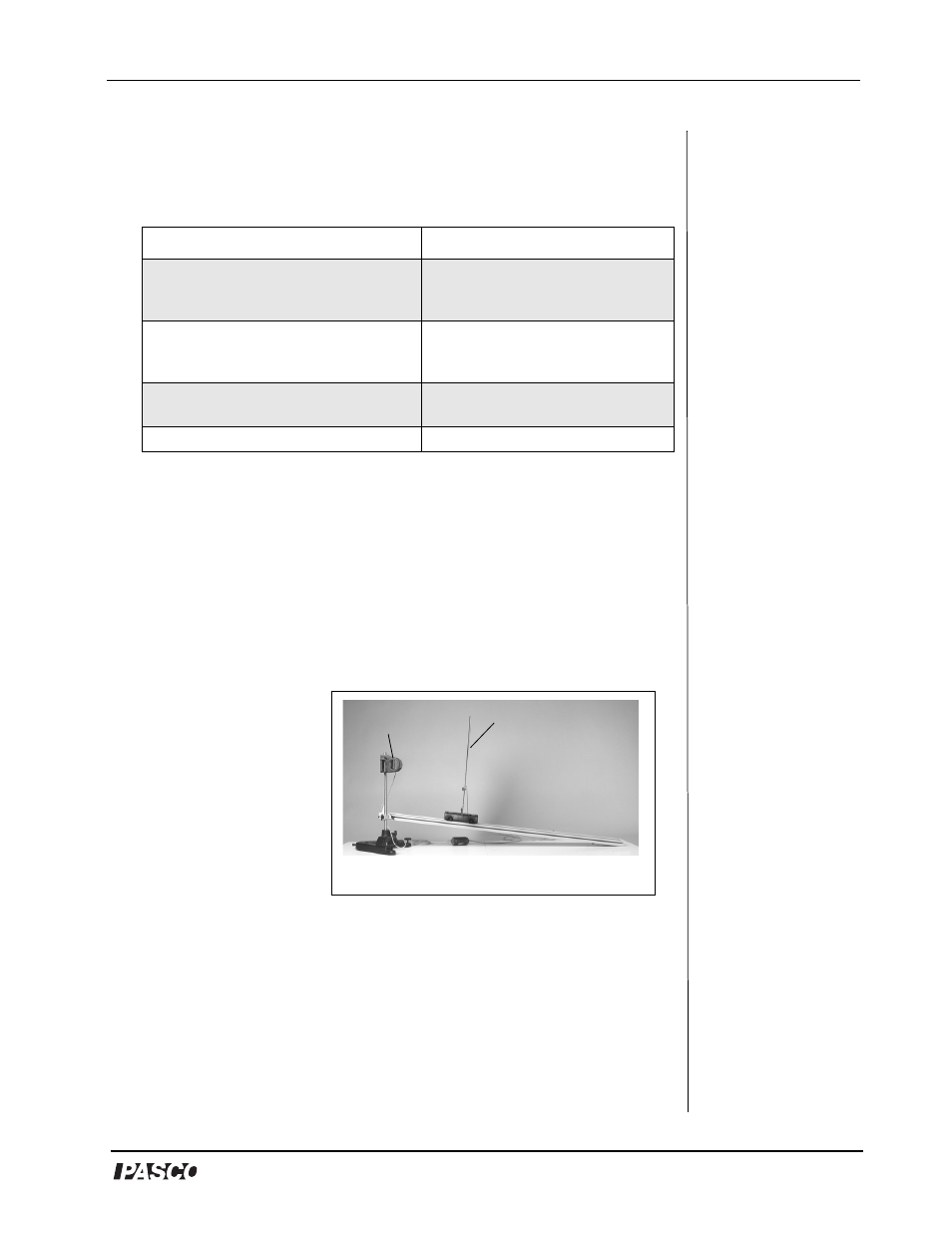
1. Mount a steel rod to a base support.
2. Clamp a Dynamics
Track to the rod, and
incline the Dynamics
Track at a small angle
(5 degrees or less).
3. Clamp a Motion
Sensor to the upper
end of the rod.
4. Connect the Motion
Sensor to an interface (PASPORT or ScienceWorkshop) connected
to your computer.
5. Set the range switch on the Motion Sensor to the near (cart) setting.
6. In DataStudio, create a Velocity-Time graph. (For DataStudio setup
instructions, see Appendix A).
7. Place the car on the track with the smallest sail attached.
Equipment Required:
Car Sail (ME-9595)
DataStudio Software, version 1.5
or later (various, see PASCO
catalog)
Motion Sensor (PS-2103 or CI-6742)
ScienceWorkshop or PASPORT
interface (various, see PASCO
catalog)
PAScar, GOcar, or Dynamics Cart
(ME-6950 or ME-6951 or ME-9430)
Dynamics Track (ME-9453)
Base and Support Rod (ME-9355)
Figure 3: Car moving down an incline
Motion
Sensor
Car Sail
PAScar
Car Sail
Motion
Sensor
