PASCO CI-6730A Flow Rate Sensor User Manual
Page 3
012-08624A
Flow Rate Sensor
3
Flow Rate Activity
Equipment required: Flow Rate Sensor (CI-6730A),
ScienceWorkshop 500 interface, DataStudio software, a set
of four AA batteries, pad of paper and pencil
Note: Calibration of the Flow Rate Sensor is not required.
1. Plug the Flow Rate Sensor into a 500
ScienceWorkshop interface and set up your
experiment in DataStudio; then disconnect the 500
interface from your computer.
2. Near the shore of a stream bed, insert the propeller of
the Flow Rate Sensor about 2 inches below the surface
of a moving stream. Hold the pole vertically and keep
the propeller housing steady.
3. On the 500 interface, press the LOG button to take a
reading. To end data collection, press the LOG
button again.
4. On a piece of paper, draw a diagram of the stream and
shoreline. With a pencil, mark a point on the stream
diagram to indicate where you took the measurement.
5. Repeat steps 2-4 at different locations and depths as
follows: a) near the shoreline at one foot b) midstream at
one foot c) midstream at two feet and d) midstream at
three feet.
6. Reconnect the 500 to your computer. Use the
Connect button on the main toolbar to retrieve data
into DataStudio.
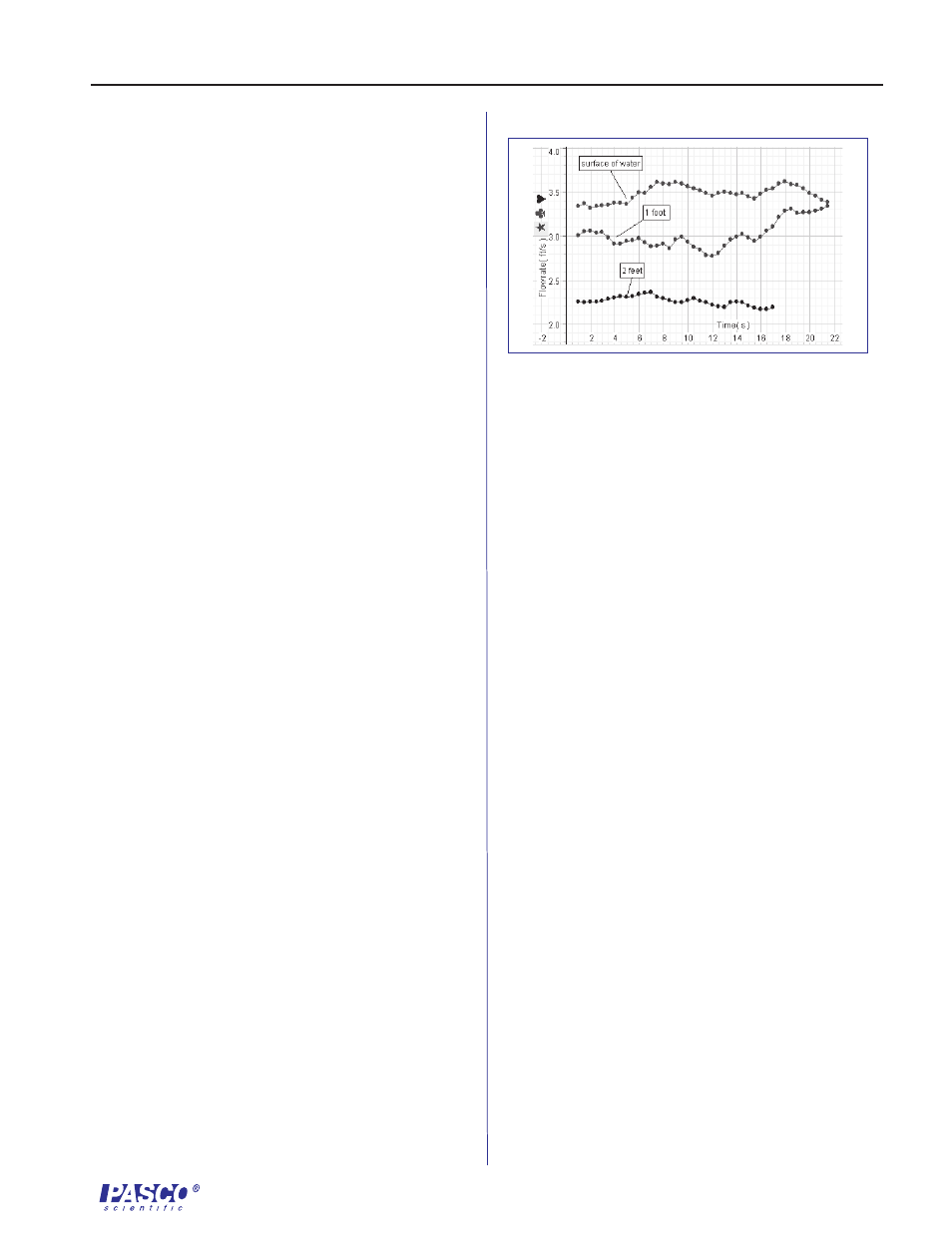
7. In DataStudio, compare the flow rate at the different
depth increments and/or different locations. Is the
flow rate higher midstream or near the shore? What
effect might depth have on the flow rate?
Sample Data
➤ Note: The instruction sheet has been written with
the assumption that the user has a basic familiarity
with DataStudio. Users can gain basic skills with
DataStudio by doing the tutorial in the DataStudio
CD-ROM. For more information on datalogging
with the 500 interface, see “Remote Data Logging”
in the table of contents of the DataStudio online help.
Determining Total Water Output in a
Stream Bed
1. With a measuring tape or other device, measure the
width of the steam bed. Record the stream width
(in meters) on a piece of paper.
2. With the Flow Sensor measurement scale, take depth
measurements (in meters) at equally spaced intervals
across the stream. (For an accurate depth
measurement, submerge the sensor until the propeller
housing rests on the bottom of the stream bed. Keep
the pole vertical.) Record each depth measurement on a
piece of paper.
3. With the Flow Rate Sensor connected to a 500
ScienceWorkshop interface, take a flow rate
measurement (in m/s) for each of the intervals. (Be
sure to take a separate data run for each measurement.)
Estimating the total water output:
1. Calculate the cross-sectional area of the stream:
Multiply each interval width by each depth you
measured to calculate the area for each interval; then
add the areas for each of the intervals to obtain the total
cross-sectional area of the stream. (Note: The more
intervals you use, the closer your approximation of the
area will be to the actual area.)
2. Connect the interface to your computer. Open
DataStudio and retrieve your flow rate data for each of
the intervals. Average the flow rate recorded for each
of the intervals.
Use the equation, output = average flow rate x area to
determine the total water output in a stream bed.
Field Procedure:
•
If using the Flow Rate Sensor from a boat, tether
the boat such that the boat does not move during
measurements. Boat movement may interfere with
an accurate flow rate measurement.
