1 high voltage connections – Controlled Products Systems Group 9150-080 User Manual
Page 28
2.1 High
Voltage
Connections
Use Table 1 to determine high voltage wire size requirements. The distance shown in the chart is
measured in feet from the operator to the power source. If power wiring is greater than the maximum
distance shown, it is recommended that a service feeder be installed. When large gauge wire is
used, a separate junction box must be installed for the operator connection. The wire table is based
on stranded copper wire. Wire run calculations are based on a 3% voltage drop on the power line,
plus an additional 10% reduction in distance to allow for other losses in the system.
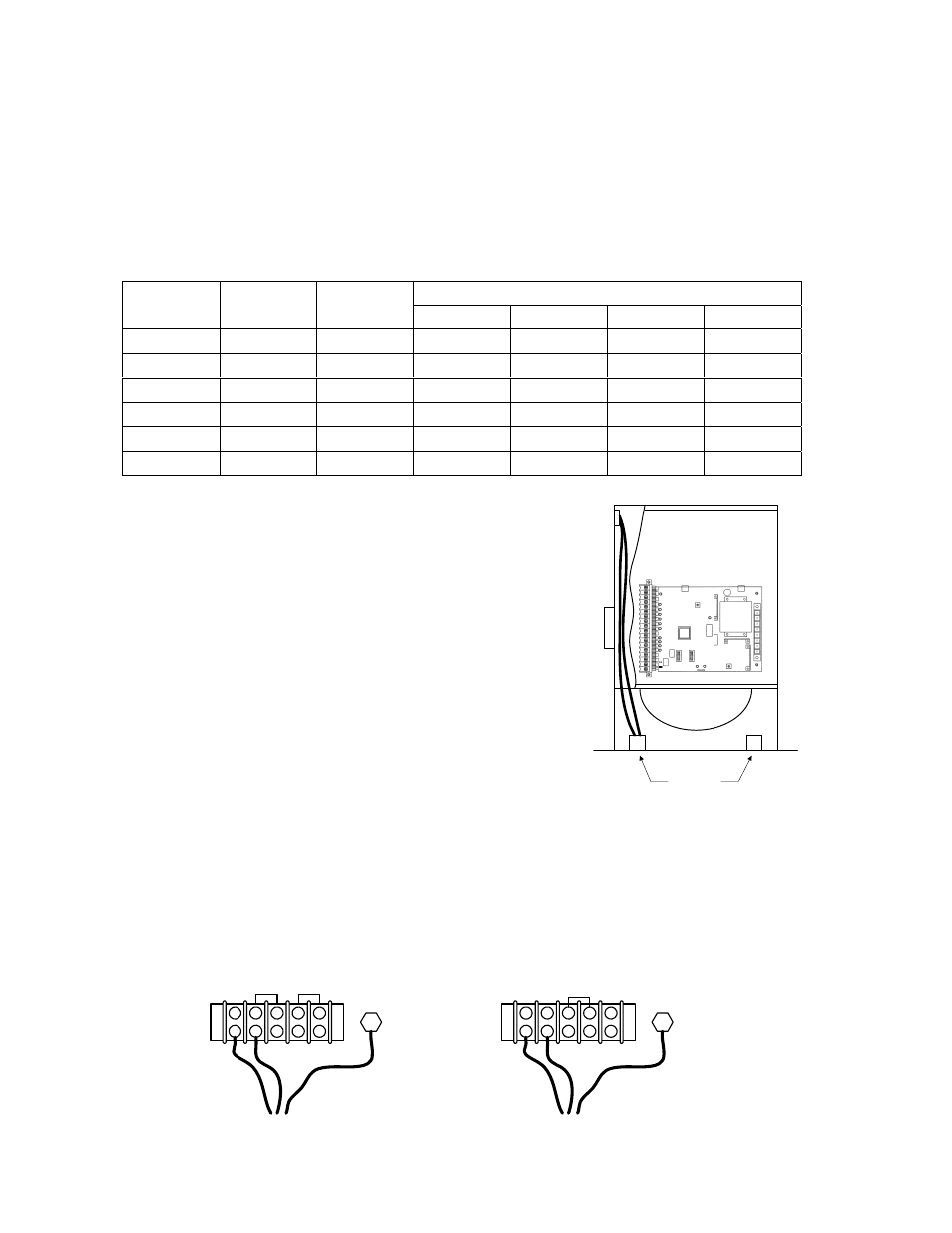
• Route incoming high voltage power through
conduit and into the operator as shown in
figure 24.
• Be sure wiring is installed in accordance with
local codes. Be sure to color code all wiring.
• Connect the power wires as shown.
• It is recommended that a surge suppresser be
installed on the high voltage power lines to
help protect the operator and circuit board from
surges and power fluctuations.
• Note: For 230 and 460 Volt 3-phase input
power, use only two legs of the incoming 3-
phase power.
Table 1
Figure 24
WIRE SIZE / DISTANCE IN FEET / SINGLE OPERATOR
MODEL VOLTS AMPS
12 AWG
10 AWG
8 AWG
6 AWG
9150 ½ HP
120
5.4
170
275
460
685
9150 ½ HP
230
2.7
685
1100
1830
2750
9150 ½ HP
460
1.35
2875
4600
7665
11500
9150 1 HP
120
9.7
130
210
350
530
9150 1 HP
230
4.9
530
845
1415
2120
9150 1 HP
460
2.5
1110
1775
2955
4435
Conduits
ON-OFF Switch
High Voltage
Terminal Strip
230 / 460 V
230 / 460 V
120 VAC NEUT
120 VAC NEUT
120 VAC HOT
GROUND
120 VAC HOT
120 VAC NEUT
120 VAC NEUT
120 VAC SWITCHED
120 VAC SWITCHED
GROUND
Page
28
9150-065-D-5-07
