Theory of operation, Associating a tib with a comparator i/o module, Transmitter status – CTI Products TIB TSAM Interface User Manual
Page 9: Controlling the transmitter, Theory of operation 3.1 a, Ssociating a, With a, Omparator, I/o m, Odule
TIB Hardware Reference
Theory of Operation
CTI Products, Inc.
68-10911-100
4
3.
Theory of Operation
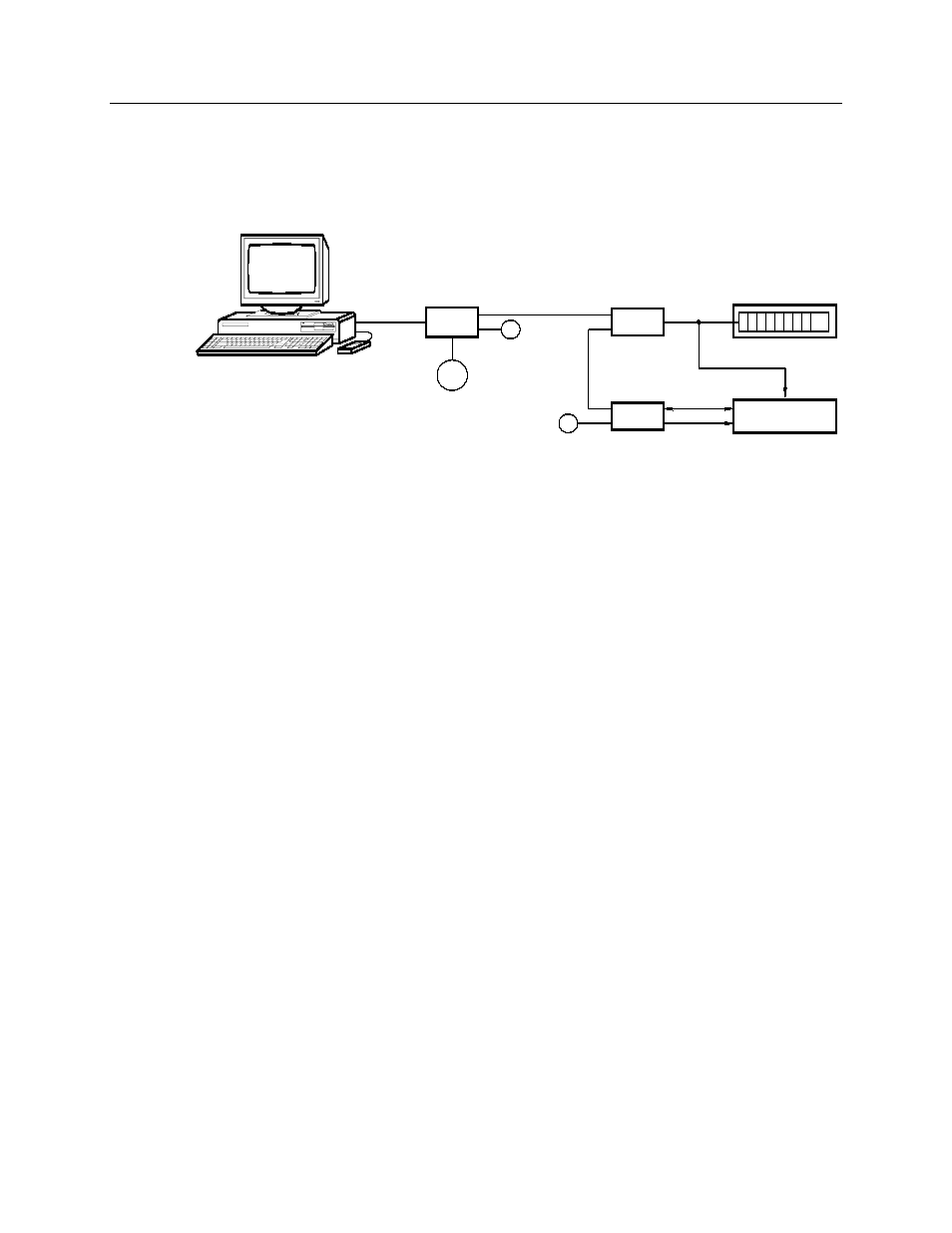
This section describes the operation of the TIB module in an MCN comparator
display system.
COM 2
COM 1
CA-80119-100
CIB
1
COMPARATOR
HIB
P/S
OUT
IN
T
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
T
TSAM
TIB
VOTE LINES
FORCE SELECT
TX SELECT
LOCAL PC
Figure 3 - Basic System Configuration
3.1
Associating a TIB with a Comparator I/O Module
When installing a system, you need to configure the TIB with the address of the
CIB it will be operating with. Section 7.1 describes how to enter this extra
address. By having the address of the CIB, the TIB knows which receivers are
associated with its transmitters.
3.2 Transmitter
Status
The TIB monitors the TSAM’s 8 Tx Select lines to determine which transmitter is
currently active. Whenever the TSAM steers to a transmitter, the TSAM updates
the Tx Select lines to indicate the currently active transmitter. The TIB sends the
status information to a HIB over the MCN network so that the transmitter status
can be displayed on the PC.
3.3
Controlling the Transmitter
When a receiver is FORCE VOTED from the PC, the HIB sends a FORCE VOTE
command to the CIB, the TIB that is associated with that CIB also receives the
command and activates the Tx Select line for the specified receiver/transmitter.
The TIB then activates the Force Select output line for approximately 100
milliseconds. After this 100 milliseconds, the Tx Select lines and the Force Select
line are deactivated so that the TIB can resume monitoring the transmitter status.
