Theory of operation, Comparator status, Controlling the comparator – CTI Products CIB Comparator Interface User Manual
Page 10: System example, 1 comparator status, 2 controlling the comparator, 3 system example
CIB Hardware Reference
Theory of Operation
CTI Products, Inc.
68-10854-135
4
3.
Theory of Operation
This section describes the operation of the CIB module in an MCN comparator
display system.
3.1 Comparator
Status
The CIB can accept VOTE, RECEIVE, DISABLE, and FAIL receiver status
indications from the comparator. Some comparators do not support all of these
status monitoring signals. Refer to section 7 for details about wiring the CIB to a
particular comparator. The CIB sends the status information to a User Interface
Module over the MCN network. User Interface Modules, such as the IIB (I/O
Interface Module) or HIB (Host Computer Interface Module) then display the
comparator status information on a console or PC.
3.2
Controlling the Comparator
When a User Interface Module sends FORCE VOTE or DISABLE commands, the
CIB translates the commands and activates the appropriate I/O lines of the
comparator.
The CIB updates the comparator with the latest control information whenever a
FORCE VOTE or DISABLE command is received from a User Interface Module.
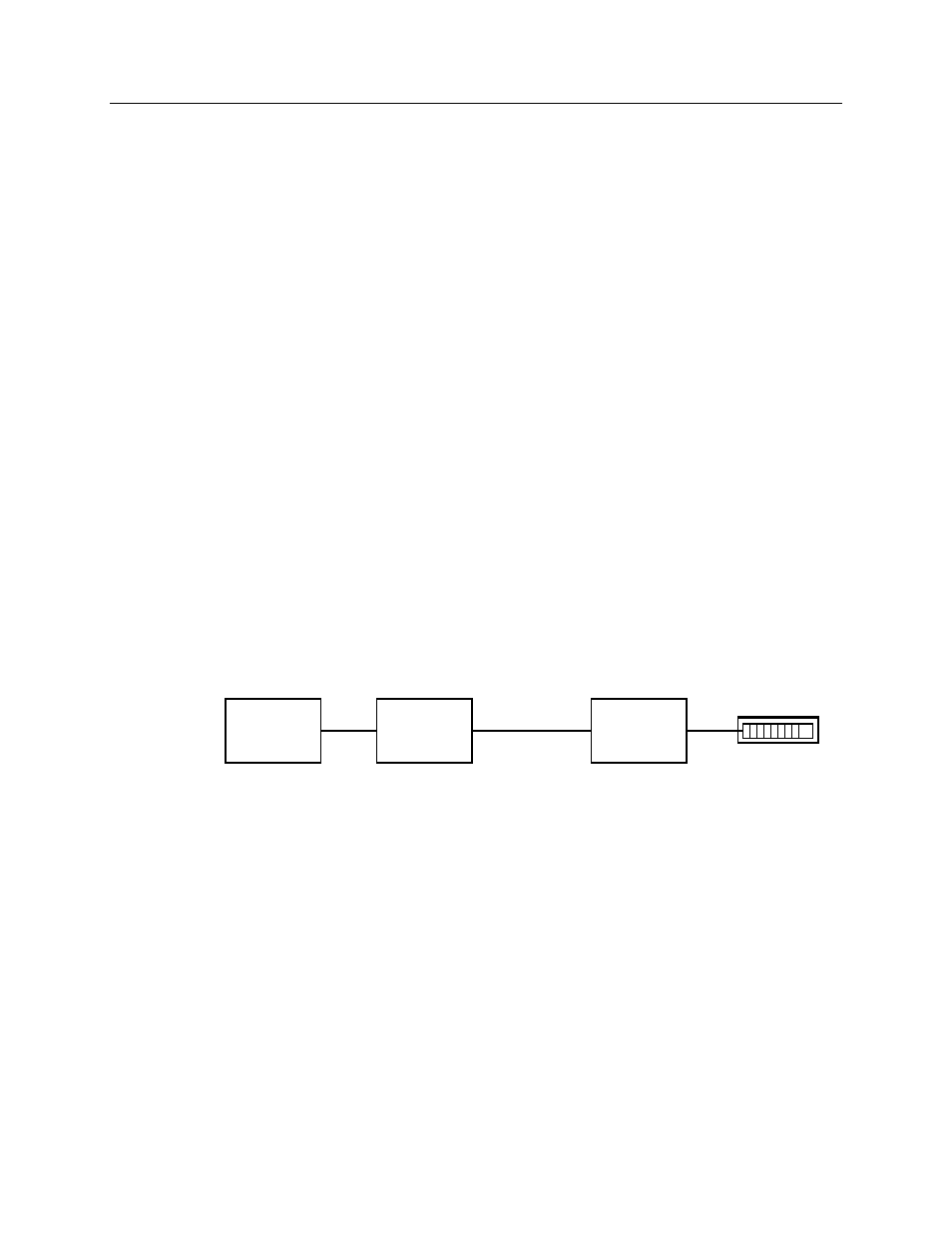
3.3 System
Example
Figure 3 shows an example comparator display system using the CIB module.
CA-80052-100
OPERATOR
STATION
USER
INTERFACE
MODULE
MCN NETWORK
CIB
1
COMPARATOR
Figure 3 - CIB System Example
When the comparator detects that a receiver is active, it drives the RECEIVE
inputs to the CIB. If the receiver is also voted by the comparator, the comparator
drives the VOTE input as well. The CIB detects these inputs and sends receive
and vote messages to the User Interface Module. The User Interface Module then
indicates that the receiver is active and voted. If the User Interface Module is an
IIB, the IIB activates the VOTE and RX outputs for that receiver.
