Note 1, Esd rating, Note 3 – Atec Superior-Electric-L116b User Manual
Page 5: Note 2, Note 4, Note 6, Note 7, Note 8
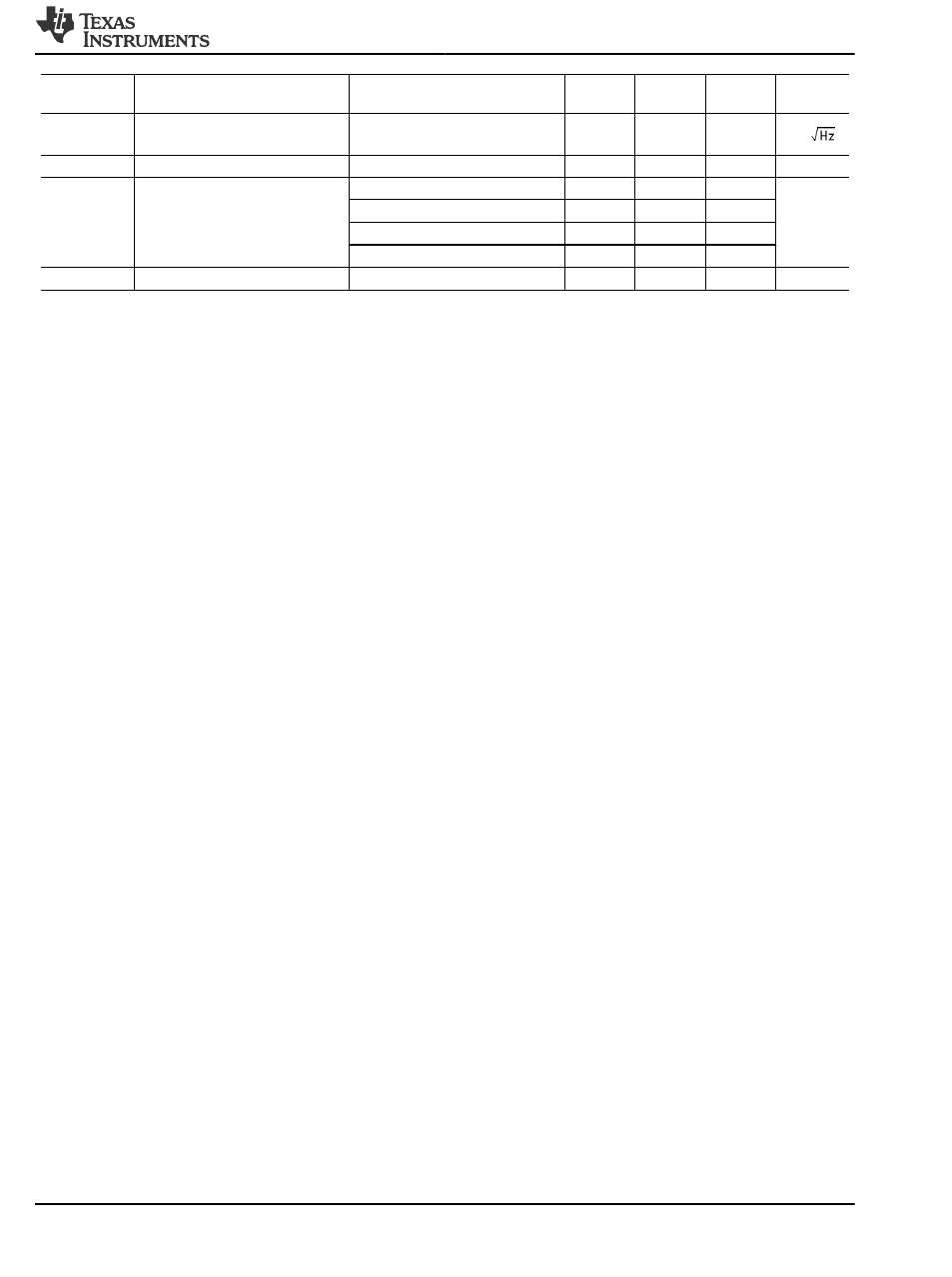
Symbol
Parameter
Conditions
Min
Typ
(
)
Max
Units
e
n
Output Noise
BW = 10Hz to 10kHz
V
O
= 3.3V
0.7
µV/
V
O
(LEAK)
Output Leakage Current
V
O
= V
O
(NOM) + 1V @ 10V
IN
0.5
12
µA
V
EN
Enable Voltage (LP38692 Only)
Output = OFF
0.4
V
Output = ON, V
IN
= 4V
1.8
Output = ON, V
IN
= 6V
3.0
Output = ON, V
IN
= 10V
4.0
I
EN
Enable Pin Leakage
V
EN
= 0V or 10V, V
IN
= 10V
-1
0.001
1
µA
Note 1:
Absolute maximum ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the component may occur. Operating ratings indicate conditions for which the device
is intended to be functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. For guaranteed specifications, see Electrical Characteristics. Specifications do not
apply when operating the device outside of its rated operating conditions.
Note 2:
At elevated temperatures, device power dissipation must be derated based on package thermal resistance and heatsink values (if a heatsink is used).
The junction-to-ambient thermal resistance (
θ
J-A
) for the TO-252 is approximately 90°C/W for a PC board mounting with the device soldered down to minimum
copper area (less than 0.1 square inch). If one square inch of copper is used as a heat dissipator for the TO-252, the
θ
J-A
drops to approximately 50°C/W. The
SOT-223 package has a
θ
J-A
of approximately 125°C/W when soldered down to a minimum sized pattern (less than 0.1 square inch) and approximately 70°C/W
when soldered to a copper area of one square inch. The
θ
J-A
values for the LLP package are also dependent on trace area, copper thickness, and the number of
thermal vias used (refer to application note AN-1187 and the
section in this datasheet). If power dissipation causes the junction temperature to
exceed specified limits, the device will go into thermal shutdown.
Note 3:
ESD is tested using the human body model which is a 100pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5k resistor into each pin.
Note 4:
Typical numbers represent the most likely parametric norm for 25°C operation.
Note 5:
If used in a dual-supply system where the regulator load is returned to a negative supply, the output pin must be diode clamped to ground.
Note 6:
Output voltage line regulation is defined as the change in output voltage from nominal value resulting from a change in input voltage.
Note 7:
Output voltage load regulation is defined as the change in output voltage from nominal value as the load current increases from 1mA to full load.
Note 8:
Dropout voltage is defined as the minimum input to output differential required to maintain the output within 100mV of nominal value.
LP38690
LP38692
Copyright © 1999-2012, Texas Instruments Incorporated
5
