Computing equation, Pf pa, Ps q – Atec Yokogawa-cw240 User Manual
Page 8
8
All Rights Reserved. Copyright © 2004, Yokogawa M&C Corporation
Computing equation
Active power, Reactive power, Apparent power, Power factor and Phase angle (for phase angle, measured value for each phase)
Average value during the integration measurement, Max value and Min value
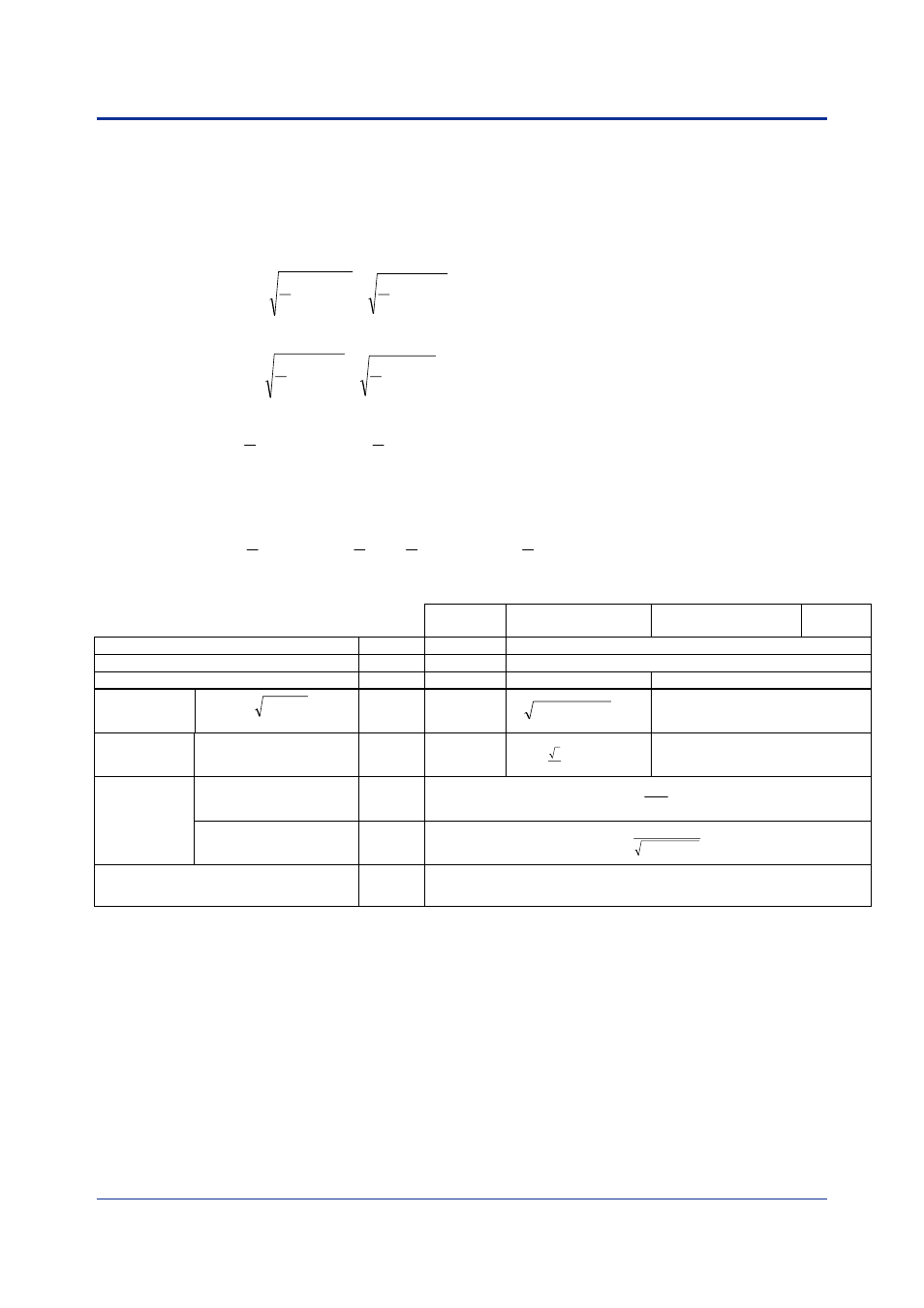
Voltage RMS value
Voltage RMS value
Current RMS value
Active power
Reactive power 1
When using reactive watt meter method
1P3W
3P3W
*6
2-wattmeter method
3P3W
3-wattmeter method
3P4W
Ave. Voltage
U ave.
(U1+U2)/2
(U1+U2+U3)/3 *1
Ave. Current
I ave.
(I1+I2)/2
(I1+I2+I3)/3 *2
Active power
∑P
P1+P2
P1+P3
P1+P2+P3 *4
Reactive
power 2 *3
∑Q
Q1+Q2
Q1+Q2+Q3 *4
Apparent
power
S=U×I
∑S
S1+S2
S1+S2+S3 *4
No use of reactive
wattmeter method *5
∑PF
Power factor
Use reactive wattmeter
method
∑PF
Phase angle *5
∑PA
Note : For distortion wave input: There may be discrepancies between the CW240 and other instruments that operate based on
other measurement principals.
*1 : Line voltage for 3P3W / Phase voltage for 3P4W
*2 : Result of I2 will be derived from vector computation when using 3P3W (2 wattmeter method)
*3 : Case of not using reactive watt meter method. In this case, do computation for each phase by multiply polarity of Q at
reactive power meter method.
*4 : Case of using 3P3W, voltage that apply for calculating each phase electric power is the phase voltage from virtual
midpoint.
*5 : Computation for each phase by multiply polarity of Q at reactive power meter method.
*6 : Case of unbalance input at 3P3W (2 wattmeter method), there may be discrepancies between CW240 and other
instruments that operated based on other measurement principals.
P1,P3,Q1,Q3,S1,S3,PF1 and PF3 are value for computing process of 2 wattmeter method, and that value have no
physical meaning.
∑
∫
=
=
=
T
t
m
T
m
m
t
u
T
dt
t
u
T
rms
U
0
2
0
2
)
(
1
)
(
1
∑
∫
=
=
=
T
t
m
T
m
m
t
i
T
dt
t
i
T
rms
I
0
2
0
2
)
(
1
)
(
1
{
}
{
}
∑
∫
=
Ч
=
Ч
=
T
t
m
m
T
m
m
m
t
i
t
u
T
dt
t
i
t
u
T
P
0
0
)
(
)
(
1
)
(
)
(
1
∑
∫
=
⎭
⎬
⎫
⎩
⎨
⎧
+
Ч
=
⎭
⎬
⎫
⎩
⎨
⎧
+
Ч
=
T
t
m
m
T
m
m
m
T
t
i
t
u
T
dt
T
t
i
t
u
T
Q
0
0
)
4
(
)
(
1
)
4
(
)
(
1
PF
PA
∑
=
∑
−1
cos
u(t):Input signal for voltage
i(t):Input value for Current
T:Input signal for 1 cycle
m:Phase
(
)
3
1
2
3
S
S
+
2
2
P
S
Q
−
=
2
2
P
S
∑
−
∑
S
P
PF
∑
∑
=
∑
2
2
Q
P
P
PF
∑
+
∑
∑
=
∑
