Air vacuum valve data, Cla-val, Cla - val – Cla-Val 35 Series User Manual
Page 2
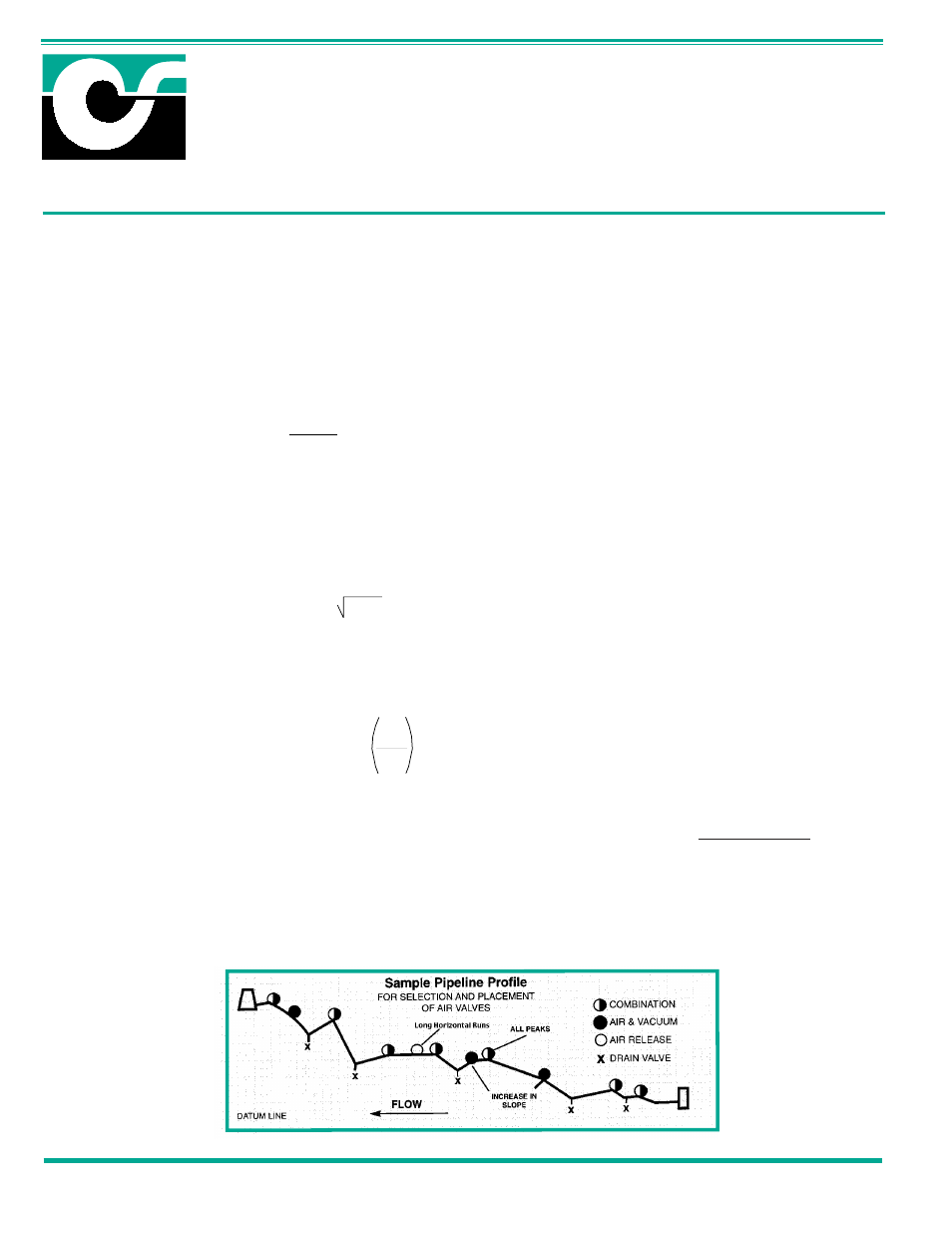
Air and Vacuum Valve Sizing
1.
Series 35 Air and Vacuum Valves should be sized to handle the maximum amount of air to be exhausted or admitted into the
pipeline and not exceed an acceptable pressure differential across the valve.
2.
Each high point or change in grade must be examined independently when determining valve size. Use the steepest slope
for calculations.
3.
Use the flow capacity charts (A) and (B) on page 13 to assist sizing Air and Vacuum Valves.
4.
Determine the smallest valve size capable of exhausting air equal to the filling rate of the pipeline in CFS while
not exceeding a pressure differential of 2 psi across the valve orifice. (Based on pump capacity).
The following formula is recommended to calculate the rate of flow in CFS for filling the pipeline:
Where: CFS = Cubic feet per second
GPM= Gallons per minute
5.
Determine the smallest valve size capable of admitting air equal to the potential flow in CFS while not exceeding a pressure
differential of 5 psi across the valve orifice. (Based on gravity flow).
The following formula should be used to calculate the rate of flow in CFS that can occur within the pipeline under gravity flow
conditions. (During Initial Ffilling • During Intentional Draining • During A Pipeline Rrupture)
Where: Q = Flow of water in cubic feet per second
C = Coefficient in Chezy’s formula =110
S = Slope in feet per foot of length
D = Inside pipe diameter in inches
6.
If thin wall pipe is being used, the risk of pipeline collapse due to the formation of vacuum must be considered. The following formula
may be used to calculate the collapsing pressure of thin walled cylindrical steel pipe using a safety factor of four:
Where: P = Collapsing pressure in psi
T = Thickness of pipe in inches
D = Diameter of pipe in inches
7.
For other pipe materials or thickness consult pipe manufacturer for pipe collapsing pressure.
8.
Determine the smallest valve size capable of admitting the required air in CFS (as found in step 5) without exceeding the
collapsing pressure (as found in step 6) or 5 psi, whichever is less. Do not exceed a pressure differential greater than 5 psi.
9.
Finally compare the valve size determined in step 4 with the valve size determined in steps 5 or 6. If they differ, always
select the larger valve size.
Note: Cla-Val has available upon request, a Slide Rule Air Vacuum Valve Calculator that greatly reduces the amount of time
necessary to size valves for pipeline service.
P = 16,250,000
D
3
T
Q = .0007872 C S D
5
CFS =
GPM
448.83
AIR VACUUM VALVE DATA
CLA-VAL
TM
¤
CLA
-
VAL
'
copyright Cla-Val 2003 Printed in USA Specifications subject to change without notice.
P.O. Box 1325 ¥ Newport Beach, CA 92659-0325 ¥ Phone: 949-722-4800 ¥ Fax: 949-548-5441 ¥ E-mail: [email protected] ¥ Website cla-val.com
E-35 Sizing Guide (R-5/00)
