Rainbow Electronics MAX1182 User Manual
Page 18
MAX1182
Dual 10-Bit, 65Msps, +3V, Low-Power ADC with
Internal Reference and Parallel Outputs
18
______________________________________________________________________________________
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
For a waveform perfectly reconstructed from digital
samples, the theoretical maximum SNR is the ratio of the
full-scale analog input (RMS value) to the RMS quantiza-
tion error (residual error). The ideal, theoretical minimum
analog-to-digital noise is caused by quantization error
only and results directly from the ADC’s resolution
(N-Bits):
SNR
dB[max]
= 6.02
dB
x N + 1.76
dB
In reality, there are other noise sources besides quanti-
zation noise e.g. thermal noise, reference noise, clock
jitter, etc. SNR is computed by taking the ratio of the
RMS signal to the RMS noise, which includes all spec-
tral components minus the fundamental, the first five
harmonics, and the DC offset.
Signal-to-Noise Plus Distortion (SINAD)
SINAD is computed by taking the ratio of the RMS sig-
nal to all spectral components minus the fundamental
and the DC offset.
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB)
ENOB specifies the dynamic performance of an ADC at
a specific input frequency and sampling rate. An ideal
ADC’s error consists of quantization noise only. ENOB
is computed from:
ENOB
SINAD
dB
dB
dB
=
−
1 76
6 02
.
.
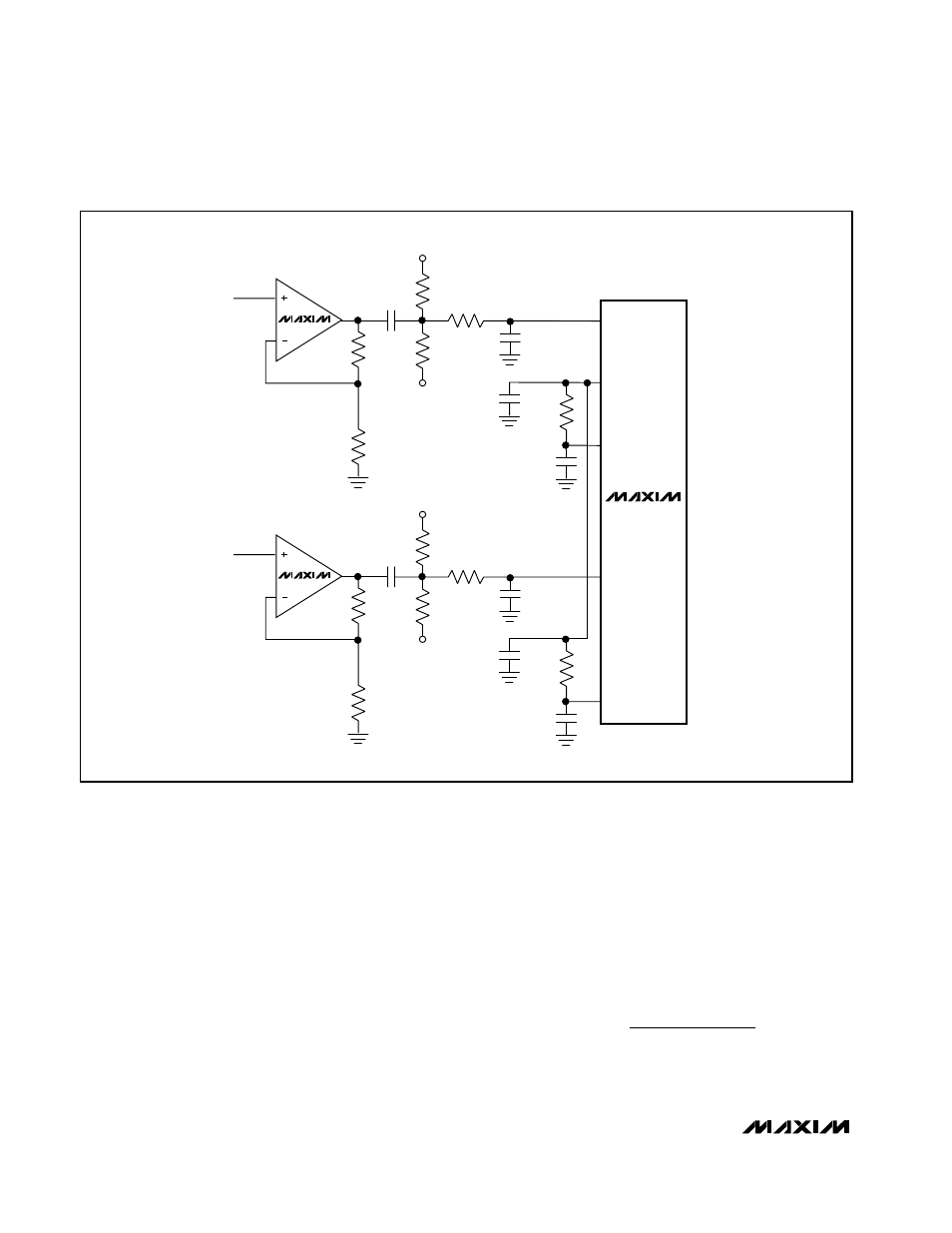
MAX1182
0.1
µF
1k
Ω
1k
Ω
100
Ω
100
Ω
C
IN
22pF
C
IN
22pF
INB+
INB-
COM
INA+
INA-
0.1
µF
R
ISO
50
Ω
R
ISO
50
Ω
REFP
REFN
V
IN
MAX4108
0.1
µF
1k
Ω
1k
Ω
100
Ω
100
Ω
C
IN
22pF
C
IN
22pF
0.1
µF
R
ISO
50
Ω
R
ISO
50
Ω
REFP
REFN
V
IN
MAX4108
Figure 7: Using an Op Amp for Single-Ended, AC-Coupled Input Drive
