Static parameter definitions, Dynamic parameter definitions – Rainbow Electronics MAX1182 User Manual
Page 17
MAX1182
Dual 10-Bit, 65Msps, +3V, Low-Power ADC with
Internal Reference and Parallel Outputs
______________________________________________________________________________________
17
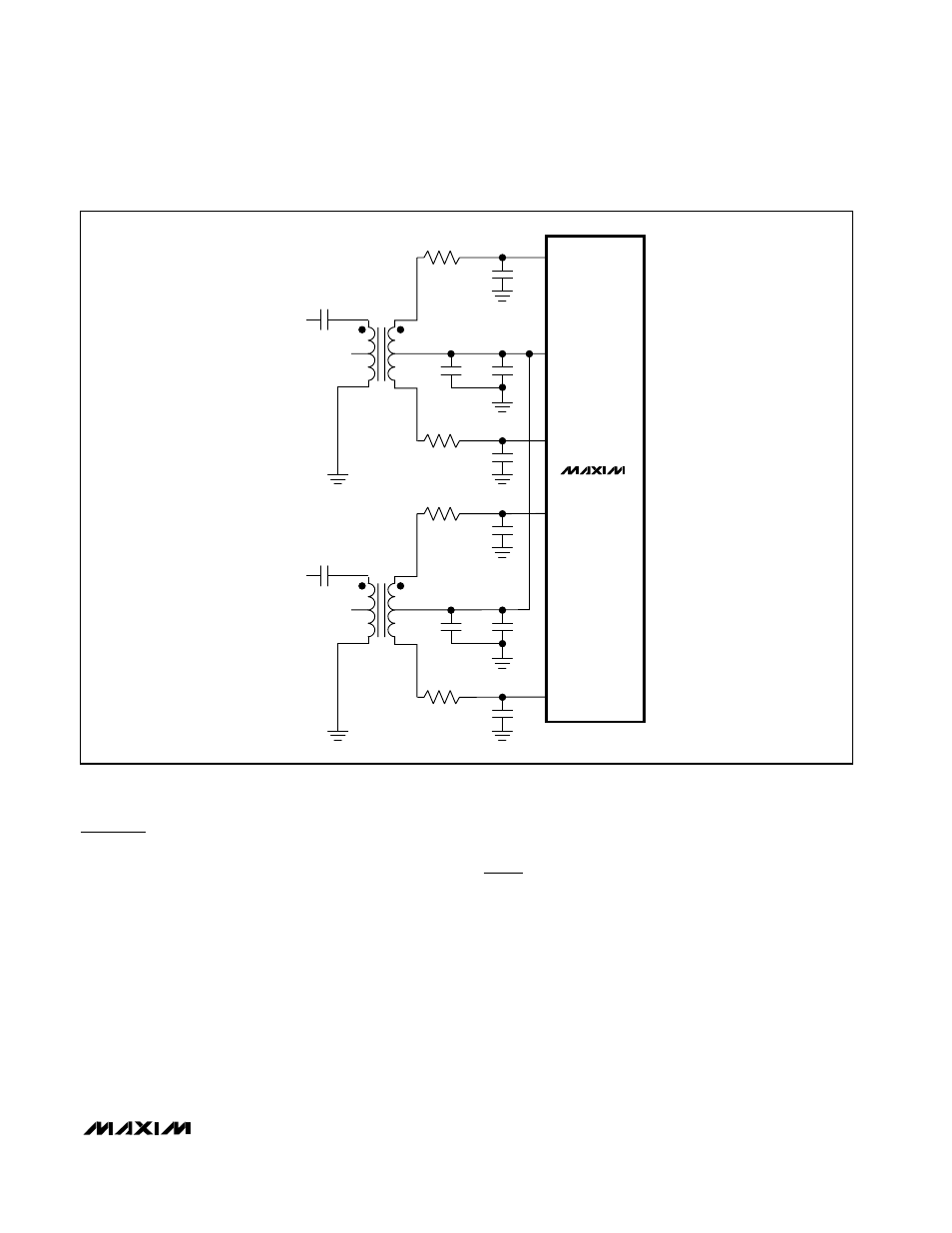
Figure 6. Transformer-Coupled Input Drive
MAX1182
T1
N.C.
V
IN
6
1
5
2
4
3
22pF
22pF
0.1
µF
0.1
µF
2.2
µF
25
Ω
25
Ω
MINICIRCUITS
TT1–6
T1
N.C.
V
IN
6
1
5
2
4
3
22pF
22pF
0.1
µF
0.1
µF
2.2
µF
25
Ω
25
Ω
MINICIRCUITS
TT1–6
INA-
INA+
INB-
INB+
COM
Static Parameter Definitions
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
Integral nonlinearity is the deviation of the values on an
actual transfer function from a straight line. This straight
line can be either a best straight-line fit or a line drawn
between the endpoints of the transfer function, once
offset and gain errors have been nullified. The static lin-
earity parameters for the MAX1182 are measured using
the best straight-line fit method.
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
Differential nonlinearity is the difference between an
actual step-width and the ideal value of 1LSB. A DNL
error specification of less than 1LSB guarantees no
missing codes and a monotonic transfer function.
Dynamic Parameter Definitions
Aperture Jitter
Figure 9 depicts the aperture jitter (t
AJ
), which is the
sample-to-sample variation in the aperture delay.
Aperture Delay
Aperture delay (t
AD
) is the time defined between the
falling edge of the sampling clock and the instant when
an actual sample is taken (Figure 9).
