Rainbow Electronics DS2422 User Manual
Page 3
DS2422/DS2423
3 of 25
is entered. After the 48
th
bit of the serial number has been entered, the shift register contains the CRC
value. Shifting in the 8 bits of CRC should return the shift register to all 0s.
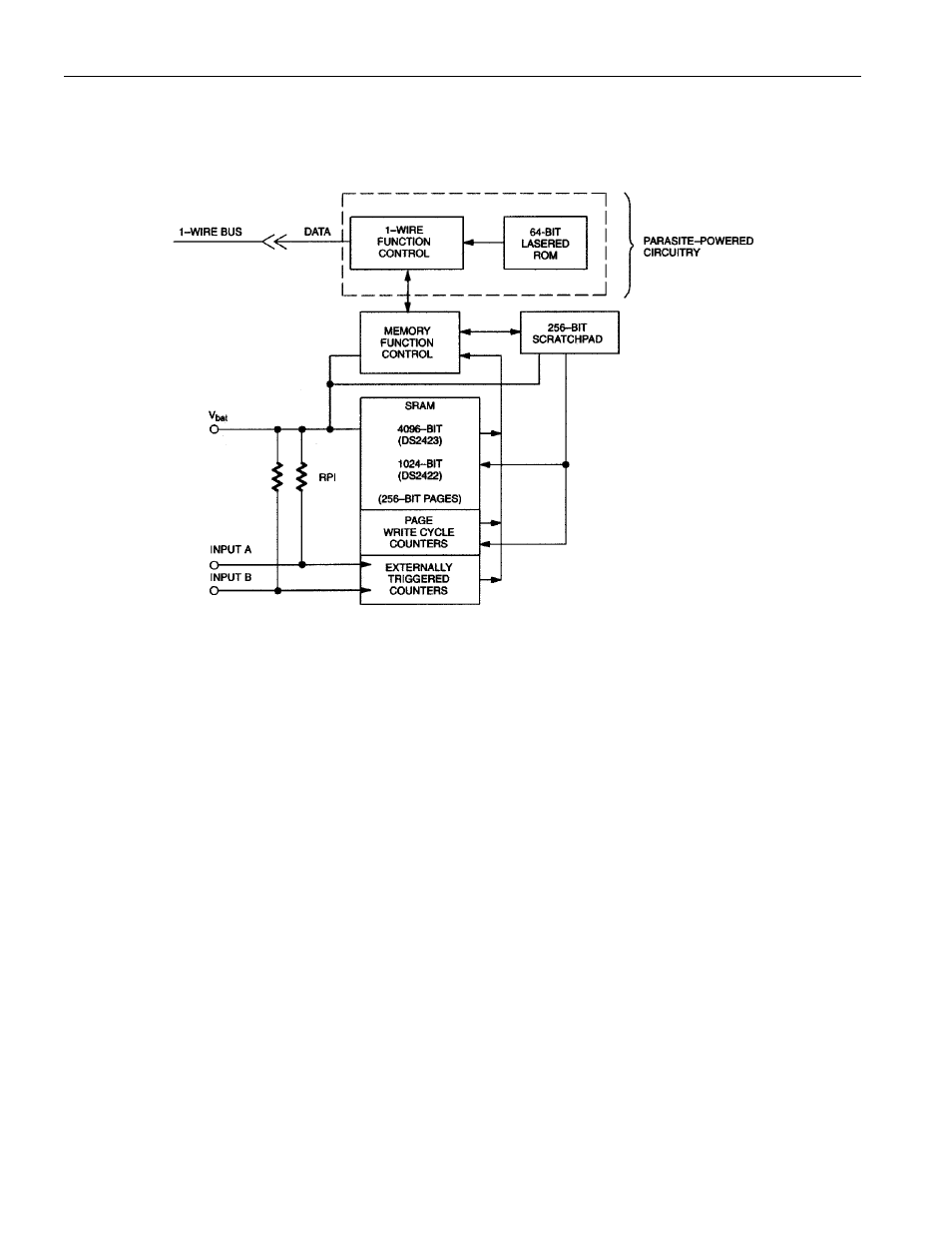
BLOCK DIAGRAM Figure 1
MEMORY
The memory map in Figure 5 shows a 32-byte page called the scratchpad and an additional 32-byte pages
called memory. The DS2422 contains pages 0 through 3 that make up the 1024-bit SRAM. The DS2423
contains pages 0 through 15 that make up the 4096-bit SRAM. The scratchpad is an additional page that
acts as a buffer when writing to memory.
ADDRESS REGISTERS AND TRANSFER STATUS
Because of the serial data transfer, the DS242X employs three address registers called TA1, TA2, and E/S
(Figure 6). Registers TA1 and TA2 must be loaded with the target address to which the data will be
written or from which data will be sent to the master upon a Read command. Register E/S acts like a byte
counter and Transfer Status register. It is used to verify data integrity with write commands. Therefore,
the master only has read access to this register. The lower 5 bits of the E/S register indicate the address of
the last byte that has been written to the scratchpad. This address is called Ending Offset. Bit 5 of the E/S
register, called PF or “partial byte flag,” is set if the number of data bits sent by the master is not an
integer multiple of 8. Bit 6 has no function; it always reads 0. Note that the lowest 5 bits of the target
address also determine the address within the scratchpad, where intermediate storage of data will begin.
This address is called byte offset. If the target address (TA1) for a Write command is 03CH for example,
then the scratchpad will store incoming data beginning at the byte offset 1CH and will be full after only 4
bytes. The corresponding ending offset in this example is 1FH. For best economy of speed and efficiency,
the target address for writing should point to the beginning of a new page, i.e., the byte offset will be 0.
Thus the full 32-byte capacity of the scratchpad is available, resulting also in the ending offset of 1FH.
However, it is possible to write one or several contiguous bytes somewhere within a page. The ending
offset together with the Partial Flag support the master checking the data integrity after a Write command.
