Example of navigation registers, Image capture (fast spi), Communication protocol – Rainbow Electronics AT77C104B User Manual
Page 24
24
AT77C104B
5347B–BIOM–08/04
Example of Navigation
Registers
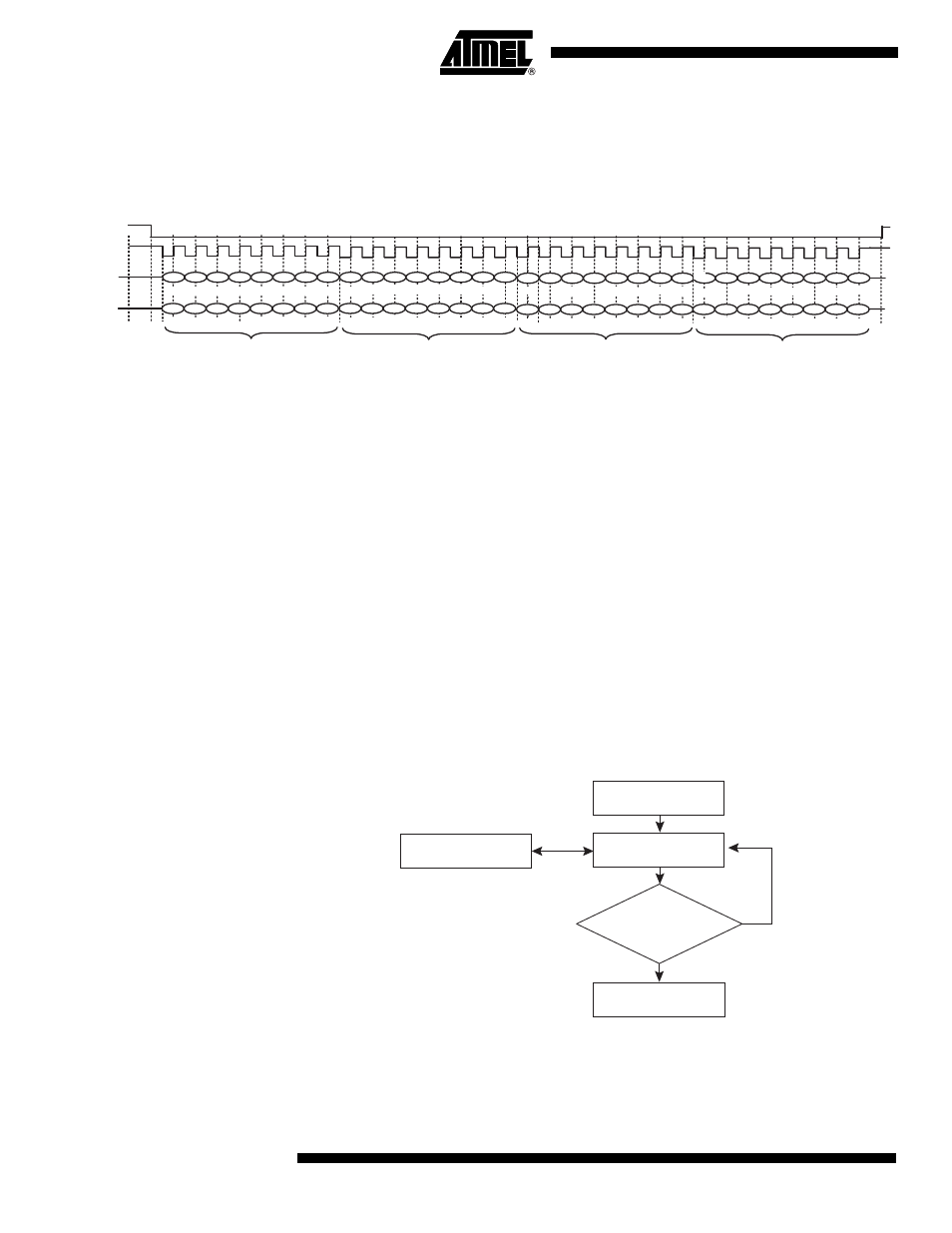
Figure 12 represents a typical reading sequence of the three navigation registers.
Refer to “Appendix C” on page 34 for flowchart
Figure 12. Reading of the Navigation Registers
Image Capture (Fast SPI)
This serial interface enables full-speed acquisition of the sensor’s pixels by the host.
This interface only supports the serial clock (SCK) and one data line: MISO (Master In/
Slave Out).
Communication Protocol
When the sensor is in acquisition mode, the host can receive pixels through the fast SPI
(FSS/ = 0). The host must transmit the communication clock (SCK) to receive the pixels.
This clock must have a regular frequency to obtain constant fingerprint slices (See “Reg-
istration Integration Time” on page 27).
With the sensor configured to acquisition mode, the controller can proceed to fast
accesses.
Figure 13. Example of an 8-bit Access
During an 8-bit access, the sensor transmits two pixels (each pixel is coded on 4 bits).
SCK
MISO
MOSI
Reading of Navigation
Register Requested
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
X
X
1
X
X X
X
X
X
X
0
X
X
X
X
X
X
0
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
0
X
Emission of the First
Navigation Register
(No Overflow, Y Negative Movement
Click Detected, Black Slice)
Emission of the Second
Navigation Register
(X Absolute Movement
= 24 Pixels)
Emission of the Third
Navigation Register
(Y Absolute Movement
= 144 Pixels)
FSS/ = 0
Sending of Dummy Data
0b0000000
Reception of 2 Pixels
End of
Communication
?
Sending of 2 Pixels (8 Bits)
FSS/ = 1
No
Yes
Controller
Sensor
