Rainbow Electronics DS2890 User Manual
Page 18
DS2890
18 of 28
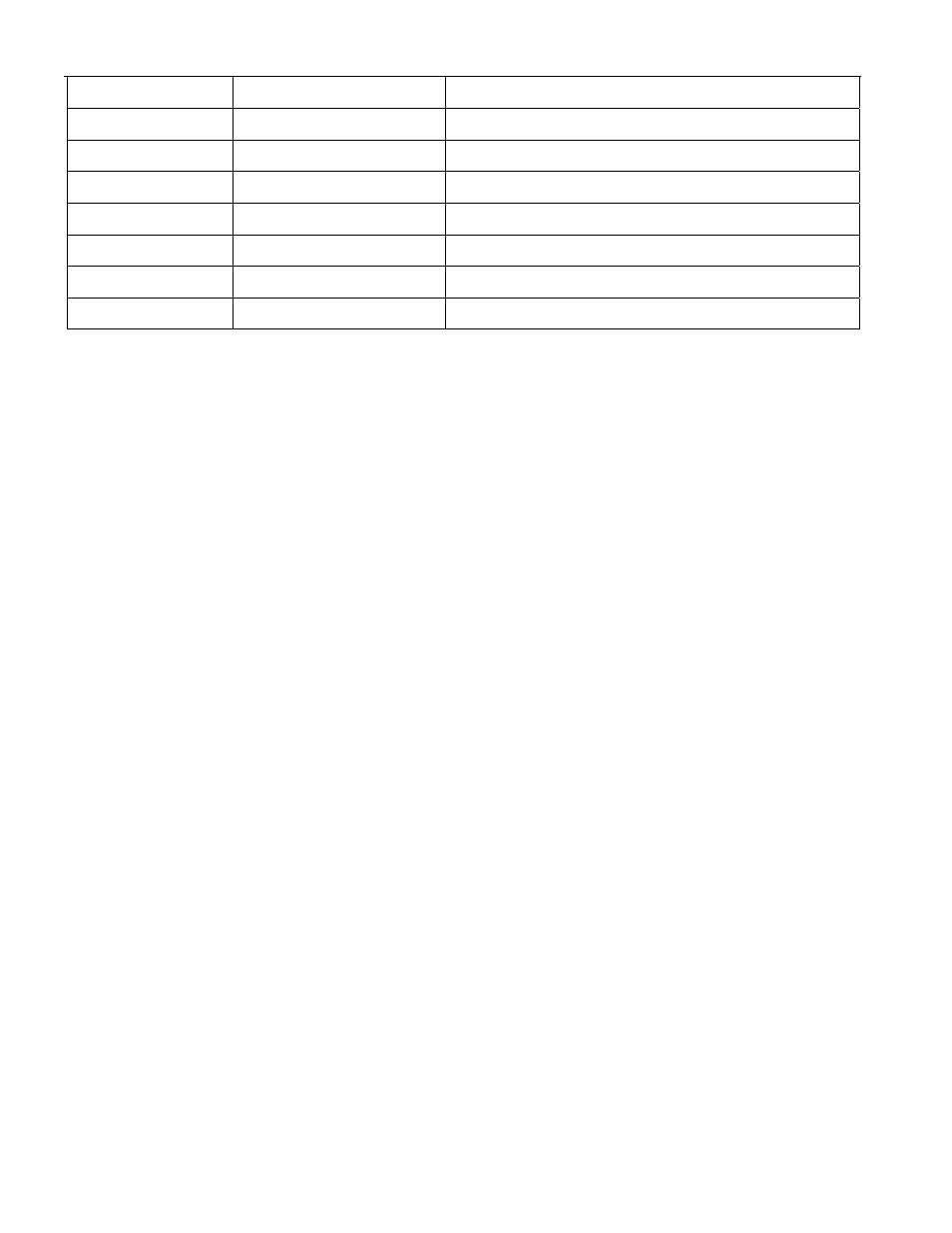
MASTER MODE
DATA (LSB FIRST)
COMMENTS
TX
C3h
Issue Wiper Increment Command
RX
Read new wiper position
TX
C3h
Issue Wiper Increment Command
RX
Read new wiper position
TX
99h
Issue Wiper Decrement Command
RX
Read new wiper position
TX
Reset
Reset Pulse
1-WIRE SIGNALING
The DS2890 requires strict protocols to ensure data integrity. The protocol consists of four types of
signaling on one line: Reset Sequence with Reset Pulse and Presence Pulse, Write 0, Write 1 and Read
Data. Except for the presence pulse the bus master initiates all these signals. The DS2890 can
communicate at two different speeds, regular speed and Overdrive Speed. If not explicitly set into the
Overdrive mode, the DS2890 will communicate at regular speed. While in Overdrive Mode the fast
timing applies to all waveforms.
The initialization sequence required to begin any communication with the DS2890 is shown in
Figure 19. A Reset Pulse followed by a Presence Pulse indicates the DS2890 is ready to send or receive
data. The bus master transmits (TX) a reset pulse (t
RSTL
, minimum 480 µs at regular speed, 48 µs at
Overdrive Speed). The bus master then releases the line and goes into receive mode (RX). The 1-Wire
bus is pulled to a high state via the pull-up resistor. After detecting the rising edge on the data contact, the
DS2890 waits (t
PDH
, 15-60 µs at regular speed, 2-6 µs at Overdrive speed) and then transmits the
Presence Pulse (t
PDL
, 60-240 µs at regular speed, 8-24 µs at Overdrive Speed). A Reset Pulse of 480 µs or
longer will exit the Overdrive Mode returning the device to regular speed. If the DS2890 is in Overdrive
Mode and the Reset Pulse is no longer than 80 µs the device will remain in Overdrive Mode.
READ/WRITE TIME SLOTS
The definitions of write and read time slots are illustrated in Figure 20 (a-c). The master initiates all time
slots by driving the data line low. The falling edge of the data line synchronizes the DS2890 to the master
by triggering an internal timing circuit. During write time slots, the timing circuit determines when the
DS2890 will sample the data line. For a read data time slot, if a “0” is to be transmitted, the timing circuit
determines how long the DS2890 will hold the data line low. If the data bit is a “1”, the DS2890 will not
hold the data line low at all.
