Detailed description, Pin description – Rainbow Electronics MAX6660 User Manual
Page 5
MAX6660
Remote-Junction Temperature-Controlled
Fan-Speed Regulator with SMBus Interface
_______________________________________________________________________________________
5
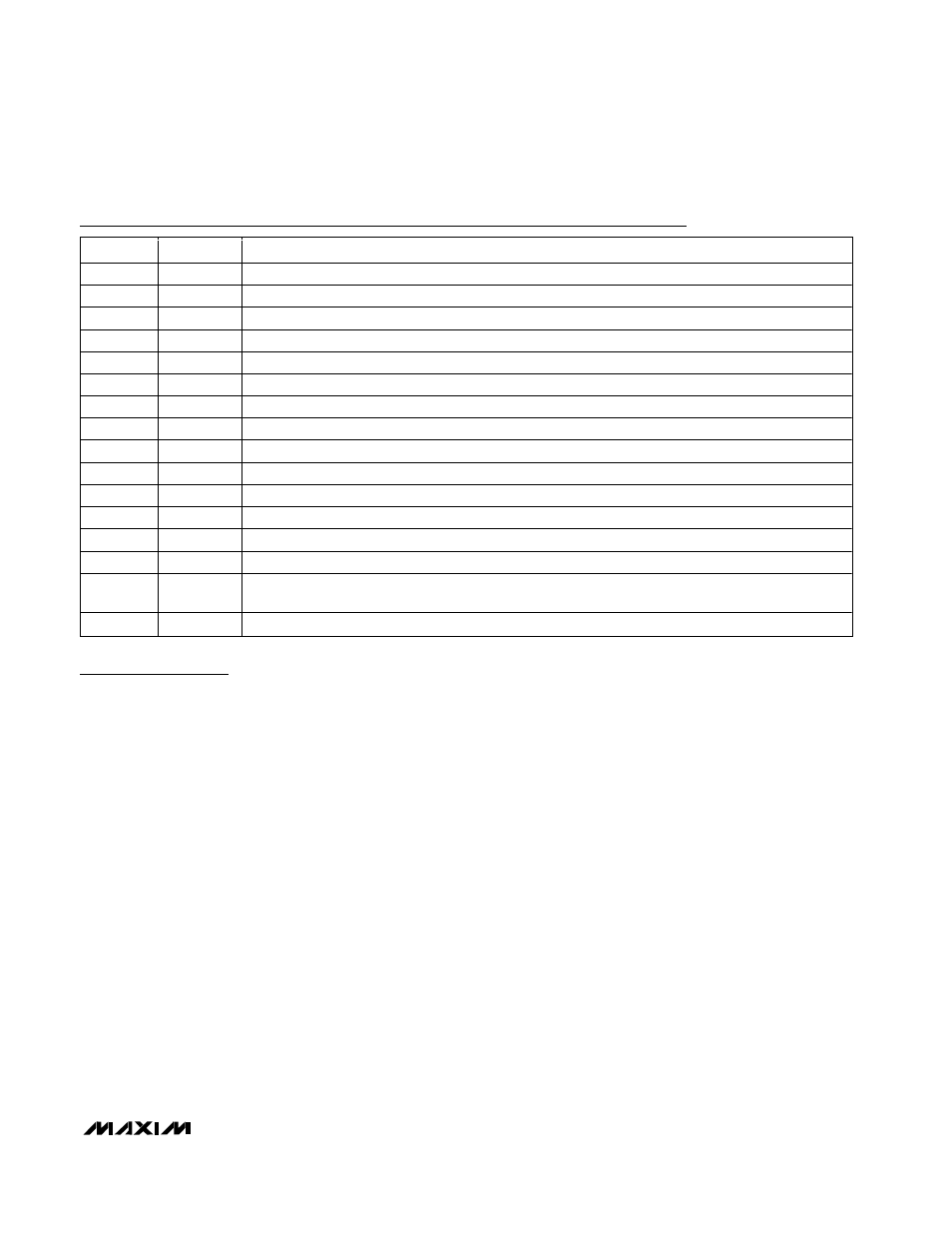
PIN
NAME
FUNCTION
1
VFAN
Fan Drive Power-Supply Input. 4.5V to 13.5V.
2
V
CC
Supply Voltage Input. +3V to +5.5V. Bypass V
CC
to ground with a 0.1µF capacitor.
3
DXP
Input: Remote-Junction Anode. Place a 2200pF capacitor between DXP and DXN for noise filtering.
4
DXN
Input: Remote-Junction Cathode. DXN is internally biased to a diode voltage above ground.
5
FAN
Open-Drain Output to Fan Low Side. Connect a minimum 1µF capacitor between FAN and VFAN.
6
ADD1
SMBus Address Select Pin. ADD0 and ADD1 are sampled upon power-up.
7
PGND
Power Ground
8
AGND
Analog Ground
9
OVERT
Overtemperature Shutdown Output. Active-low output (programmable for active high if desired). Open drain.
10
ADD0
SMBus Slave Address Select Pin. ADD0 and ADD1 are sampled upon power-up.
11
ALERT
SMBus Alert (Interrupt) Output. Open-drain, active-low output.
12
SMBDATA
SMBus Serial Data Input/Output. Open drain.
13
GAIN
Gain Control. Connect an external resistor from GAIN to V
CC
to reduce the gain of the current-sense mode.
14
SMBCLK
SMBus Clock Line from Controller. This line tolerates inputs up to V
CC
even if MAX6660 is not powered.
15
STBY
Hardware Standby Input. Drive
STBY low to reduce supply current. Temperature and comparison
data are retained in standby mode.
16
TACH IN
Fan Tachometer Input. Tolerates voltages up to VFAN.
Detailed Description
The MAX6660 is a remote temperature sensor and fan
controller with an SMBus interface. The MAX6660 con-
verts the temperature of a remote-junction temperature
sensor to a 10-bit + sign digital word. The remote tem-
perature sensor can be a diode-connected transistor,
such as a 2N3906, or the type normally found on the
substrate of many processors’ ICs. The temperature
information is provided to the fan-speed regulator and
is read over the SMBus interface. The temperature
data, through the SMBus, can be read as a 10-bit +
sign two’s complement word with a 0.125°C resolution
(LSB) and is updated every 0.25s.
The MAX6660 incorporates a closed-loop fan controller
that regulates fan speed with tachometer feedback. The
temperature information is compared to a threshold and
range setting, which enables the MAX6660 to automati-
cally set fan speed proportional to temperature. Full con-
trol of these modes is available, including being able to
open either the thermal control loop or the fan control
loop. Figure 1 shows a simplified block diagram.
ADC
The ADC is an averaging type that integrates over a
60ms period with excellent noise rejection. A bias cur-
rent is steered through the remote diode, where the for-
ward voltage is measured, and the temperature is com-
puted. The DXN pin is the cathode of the remote diode
and is biased at 0.65V above ground by an internal
diode to set up the ADC inputs for a differential mea-
surement. The worst-case DXP-DXN differential input
voltage range is 0.25V to 0.95V. Excess resistance in
series with the remote diode causes about +1/2°C error
per ohm. Likewise, 200mV of offset voltage forced on
DXP-DXN causes approximately 1°C error.
A/D Conversion Sequence
A conversion sequence is initiated every 250ms in the
free-running autoconvert mode (bit 6 = 0 in the
Configuration register) or immediately by writing a One-
Shot command. The result of the new measurement is
available after the end of conversion. The results of the
previous conversion sequence are still available when
the ADC is converting.
Remote-Diode Selection
Temperature accuracy depends on having a good-
quality, diode-connected small-signal transistor.
Accuracy has been experimentally verified for all
devices listed in Table 1. The MAX6660 can also direct-
Pin Description
