C-compatible interface, Step-by-step part selection and software setup – Rainbow Electronics MAX6651 User Manual
Page 16
Temperature Monitoring and Fan Control
The circuit shown in
Figure 10
provides complete tem-
perature monitoring and fan control. The MAX1617A (a
remote/local temperature serial interface with SMBus)
monitors temperature with a diode-connected transis-
tor. Based on the temperature readings provided by
the MAX1617A, the µC can adjust the fan speed pro-
portionally with temperature. Connecting the
ALERT
output of the MAX1617A to the
FULL ON input of the
MAX6650/MAX6651 (see the General-Purpose Input/
Output section) allows the fan to turn on fully if the
MAX1617A detects an overtemperature condition.
MAX6501 Hardware Fail-Safe
Figure 11
shows an application using a MAX6501 as a
hardware fail-safe. The MAX6650 has its GPIO1 config-
ured as
FULL ON input. The MAX6501 TOVER pin goes
low whenever its temperature goes above a preset value.
This pulls the
FULL ON pin (GPIO1) low, forcing the fan to
spin at its maximum speed.
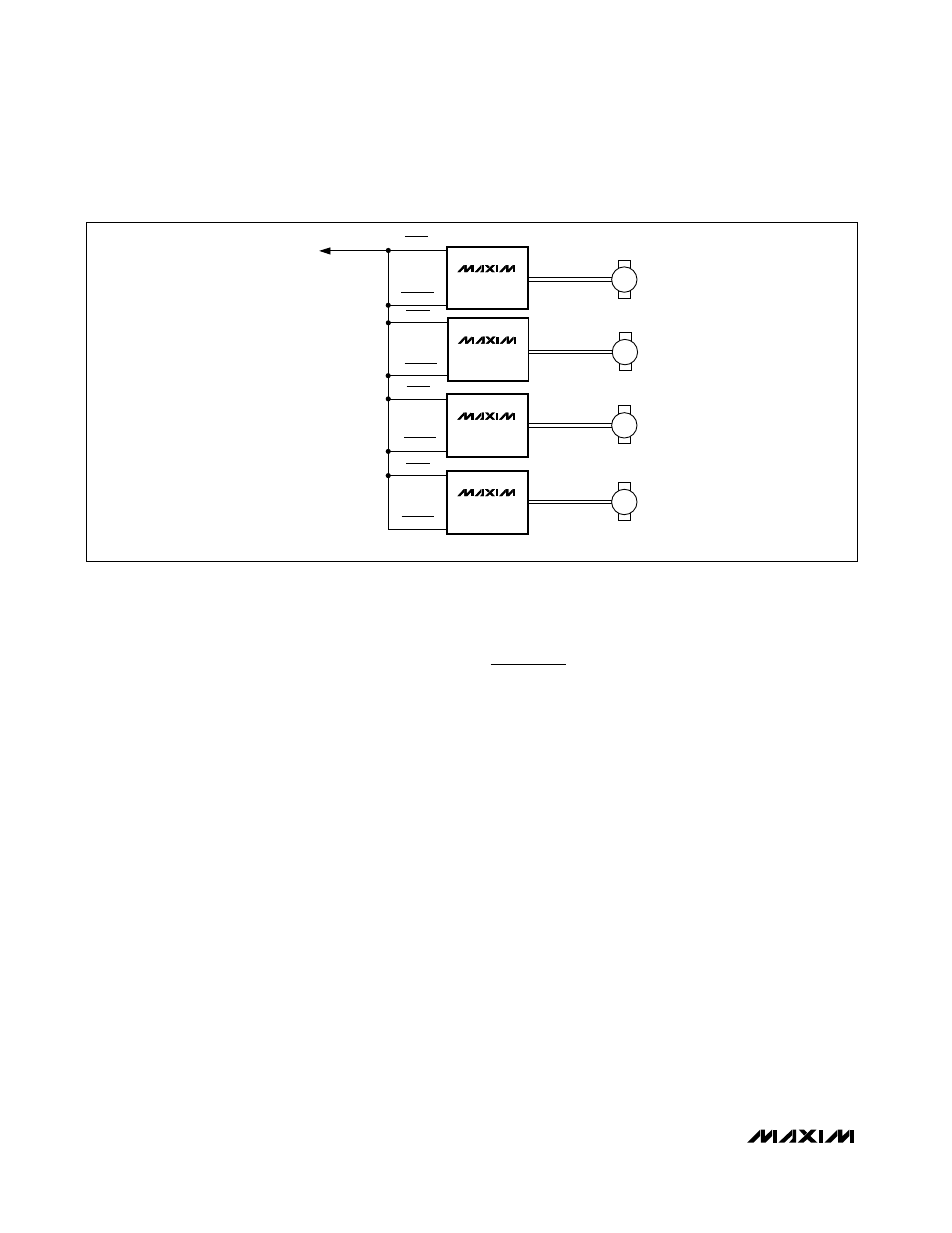
Figure 12
shows the use of
multiple MAX6501s. The MAX6501 has an open-drain
output, allowing multiple devices to be wire ORed to the
FULL ON input. This configuration allows fail-safe moni-
toring of multiple locations around the system.
Hot-Swap Application
Hot swapping of a fan can be detected using the circuit
in
Figure 13
where GPIO2 is configured to generate an
alert whenever it is pulled low. As long as the fan card
is connected, GPIO2 is high. However, when the fan
card is removed, a 2.2k
Ω resistor pulls GPIO2 low,
causing an interrupt. This signals to the system that a
hot swap is occurring.
Step-by-Step Part Selection
and Software Setup
Determining the Fan System Topology
The MAX6650/MAX6651 support three fan system
topologies. These are single fan control, parallel fan
control, and synchronized fan control.
Single Fan Control
The simplest configuration is a single MAX6650 for
each fan. If two or more fans are required per system,
then additional MAX6650 controllers are used (one per
fan). The advantage of this configuration is the ability to
independently control each fan. The disadvantage is
cost, size, and complexity.
For single fan control, use the MAX6650 (unless addi-
tional GPIOs are needed).
Parallel Fan Control
If multiple fans are required but independent control is
not, then a single MAX6650/MAX6651 connected to two
or more fans in parallel may make sense (Figure 7). The
obvious advantage is simplicity, size, and cost savings.
If all the fans connected in parallel are the same type,
they will tend to run at similar speeds. However, if one
or more of the fans are wearing out, speed mismatches
can occur. The MAX6651 allows the system to monitor
MAX6650/MAX6651
Fan-Speed Regulators and Monitors
with SMBus/I
2
C-Compatible Interface
16
______________________________________________________________________________________
MAX6550
GPIO1
MAX6550
GPIO1
MAX6550
GPIO1
FAN
1
FAN
2
FAN
3
MAX6550
GPIO1
FAN
4
GPIO0
GPIO0
GPIO0
GPIO0
ALERT
FULL ON
ALERT
ALERT
ALERT
FULL ON
FULL ON
FULL ON
TO INT PIN
ON NC
Figure 9. N+1 Application
