Power flow, Single speed power flow and torque distribution, Gearing and torque distribution – Spicer Drive Axles Failure Analysis Service Manual User Manual
Page 17
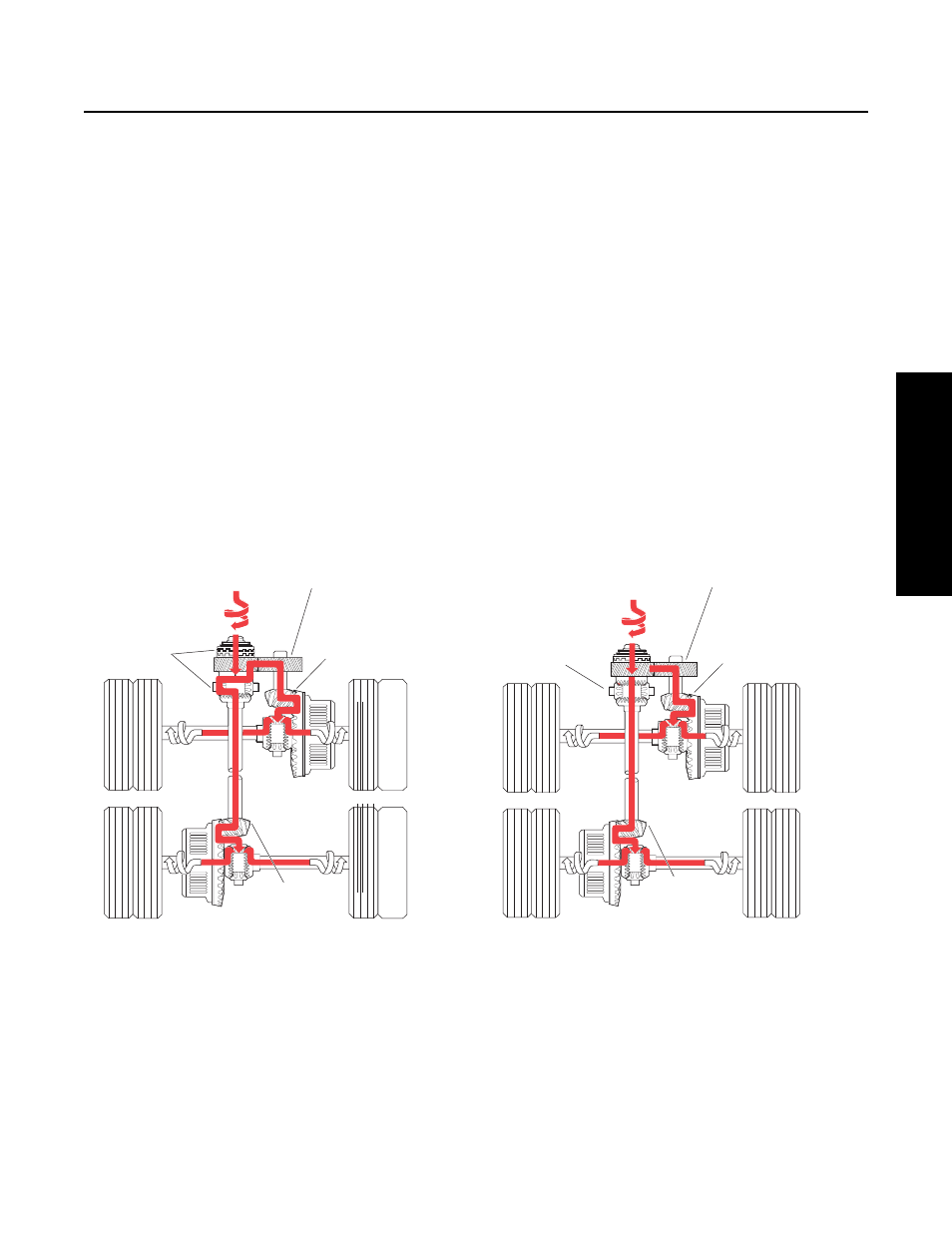
Gearing and Torque Distribution
16
G
e
arin
g an
d T
orque
D
is
tri
buti
on
Power Flow
For technical reference, this section describes and illustrates the way power flows through an axle under different gearing and
differential configurations.
Single Speed Power Flow and Torque Distribution
Inter-axle Differential is Operating
Torque (power flow) from the vehicle driveline is transmitted to the input shaft and the inter-axle differential spider. At this point,
the differential distributes torque equally to both axles.
For the forward axle, torque is transmitted from the helical-side gear to the pinion helical gear, drive pinion, ring gear, wheel dif-
ferential, and axle shafts.
For the rear axle, torque is transmitted from the output shaft side gear, through the output shaft to the inter-axle driveline, to the
drive pinion, ring gear, wheel differential, and axle shafts.
Torque Distribution - Lockout Disengaged:
Torque Distribution - Lockout Engaged:
Input torque
Inter-axle
differential
operating
Drive is from differential
through helical gears to
forward axle gearing.
Drive is from
differential
through output
shaft to rear
axle gearing.
Torque is transmitted to both axles
through inter-axle differential action.
In high range, the
drive is through the
pinion and ring gear
only (both axles).
Lockout Disengaged
Input torque
Inter-axle differential
not operating
Drive is from input shaft
through helical gears to
forward axle gearing.
Drive is from
output shaft
side gear to
rear axle gearing.
Torque is transmitted to both axles
without inter-axle differential action.
In high range, the
drive is through the
pinion and ring gear
only (both axles).
Lockout Engaged
