1 identification algorithm implemented on the dsp – Soft dB Zen-Ten User guide User Manual
Page 17
User manual for the ZEN 3-channel X-LMS controller
Soft dB inc.
3.3 Description of the control path identification algorithm
Note: This identification technique is based on the hypothesis that the primary noise
source to be controlled, is off during the whole identification process. However, an
identification technique for noisy conditions is provided later in this section.
3.3.1 Identification algorithm implemented on the DSP
The control paths must be identified before launching the control. While the control is
active, the control path filters (CxRx and CxEy) allow subtracting the contribution of the
control source from the reference signals and filtering the reference before LMS
optimization. As discussed in section 4.2, the PC interface makes it easy to do the
identification. The aim of this section is to explain the identification algorithm
implemented on the DSP.
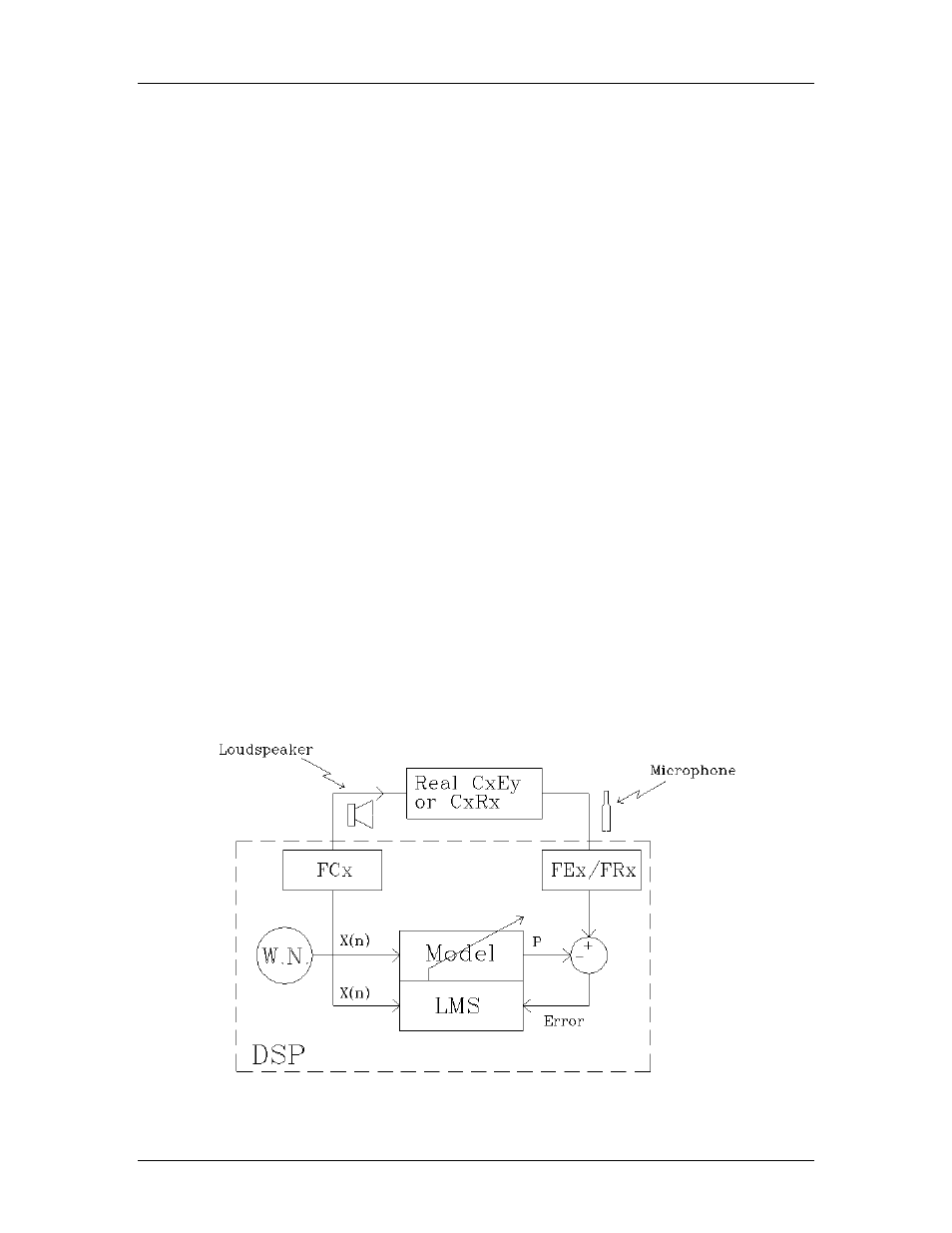
The identification algorithm is based on LMS. Figure 10 shows a schematic of the LMS
algorithm used on the DSP to identify the control path filters (CxRx and CxEy).
The DSP computes and generates white noise in control actuator x. At the same time, the
DSP predicts the input sample read at error sensor Ey or reference sensor Rx, by
computing the convolution product of the white noise with a filter (the model of the
control path). The control path model (CxRx or CxEy) is an FIR filter, and a standard
LMS algorithm is used to optimize the filter in real time. The DSP uses the sample
coming from the error or reference sensor to compute the prediction error. The energy of
the prediction error signal can be compared with the error sensor or reference signal to
estimate the convergence and the precision of the model.
Figure 10: Schematic of the identification algorithm
ZEN User Manual
p. 17
