Weather forecast, Atmospheric pressure – AcuRite 01035 Weather Station User Manual
Page 10
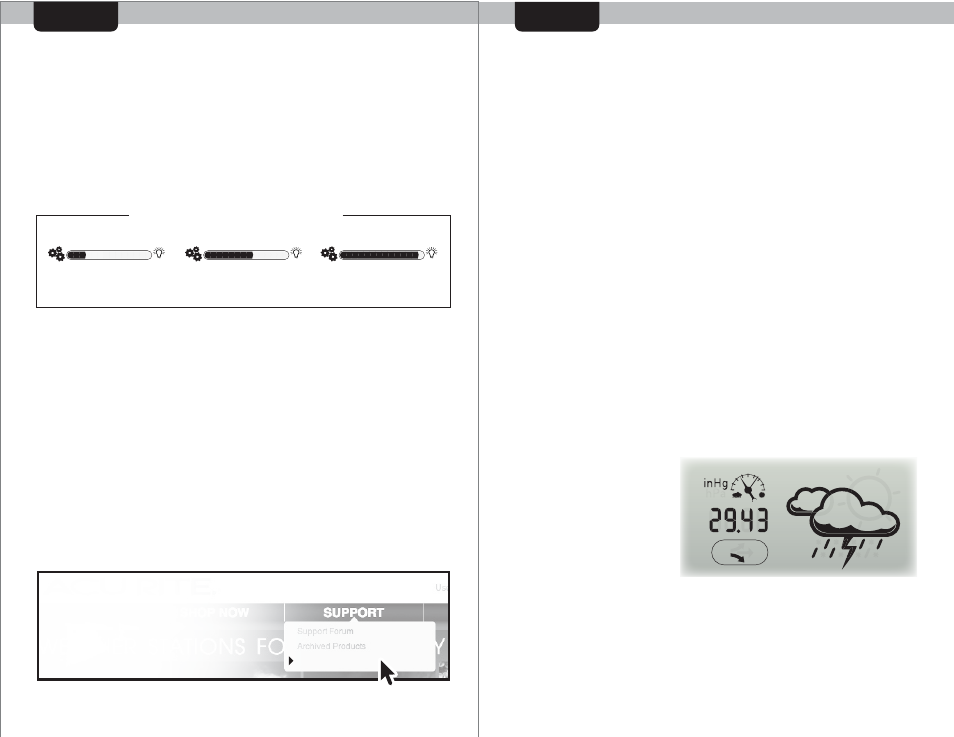
PRESSURE:
The display console
features a pressure
read-out, just to the
right of the forecast
icon. The pressure
readout area will also
indicate if the pressure
is FALLING, STEADY, or
RISING.
Weather Forecast
USE
Atmospheric Pressure
USE
FORECAST: future forecast icon
The display console features a weather forecast icon which gives you
the predicted weather forecast for the next 12 to 24 hours based on
an advanced algorithm that observes the changes in barometric
pressure and temperature. The FORECAST icon will then predict the
future (next 12 to 24 hours) weather forecast. This weather station
will provide the most accurate forecast that a single station weather
instrument can provide.
FORECAST: 14 day learning mode
This weather station has a patented “fourteen day learning mode”
calibration process. During this learning mode the weather station
will make altitude calculations that may affect the accuracy of the
forecast. Once the 14 day learning mode process is complete, the
learning mode icon will disappear and the weather forecast should
be ready for superior operation.
Atmospheric Pressure is defined as the pressure at any location on
the Earth, caused by the weight of the column of air above it. At sea
level, atmospheric pressure has an average value of one atmosphere
and gradually decreases as altitude increases. Also called
barometric pressure.
The weight of the atmosphere that envelopes Earth exerts pressure
on all points of the planet's surface. Meteorologists use barometers
to measure this atmospheric pressure (also called barometric
pressure). At sea level the atmospheric pressure is approximately 1
kilogram per square centimeter (14.7 pounds per square inch),
which will cause a column of mercury in a mercury barometer to rise
760 millimeters (30.4 inches). Variations in the atmospheric pressure
greatly affect the weather. Low pressure generally brings rain. In
areas of low air pressure, the air is less dense and relatively warm,
which causes it to rise. The expanding and rising air naturally cools,
and the water vapor in the air condenses, forming clouds and the
drops that fall as rain. In high pressure areas, the air is dense and
relatively cool, which causes it to sink. The water vapor in the sinking
air doesnʼt condense, resulting in clear skies.
...after 3 days
...half-way
completed
...one day
to go
learning mode progress indicator
17
16
www.AcuRite.com
To receive product updates
and information, Go to
PRODUCT REGISTRATION
Register a Product
