Figure 6-4 exciter block diagram, 7 buffer amplifier, 8 exciter synthesizer – Viking 242-2009-632 User Manual
Page 82
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
6-10
March 1999
Part No. 001-2009-600
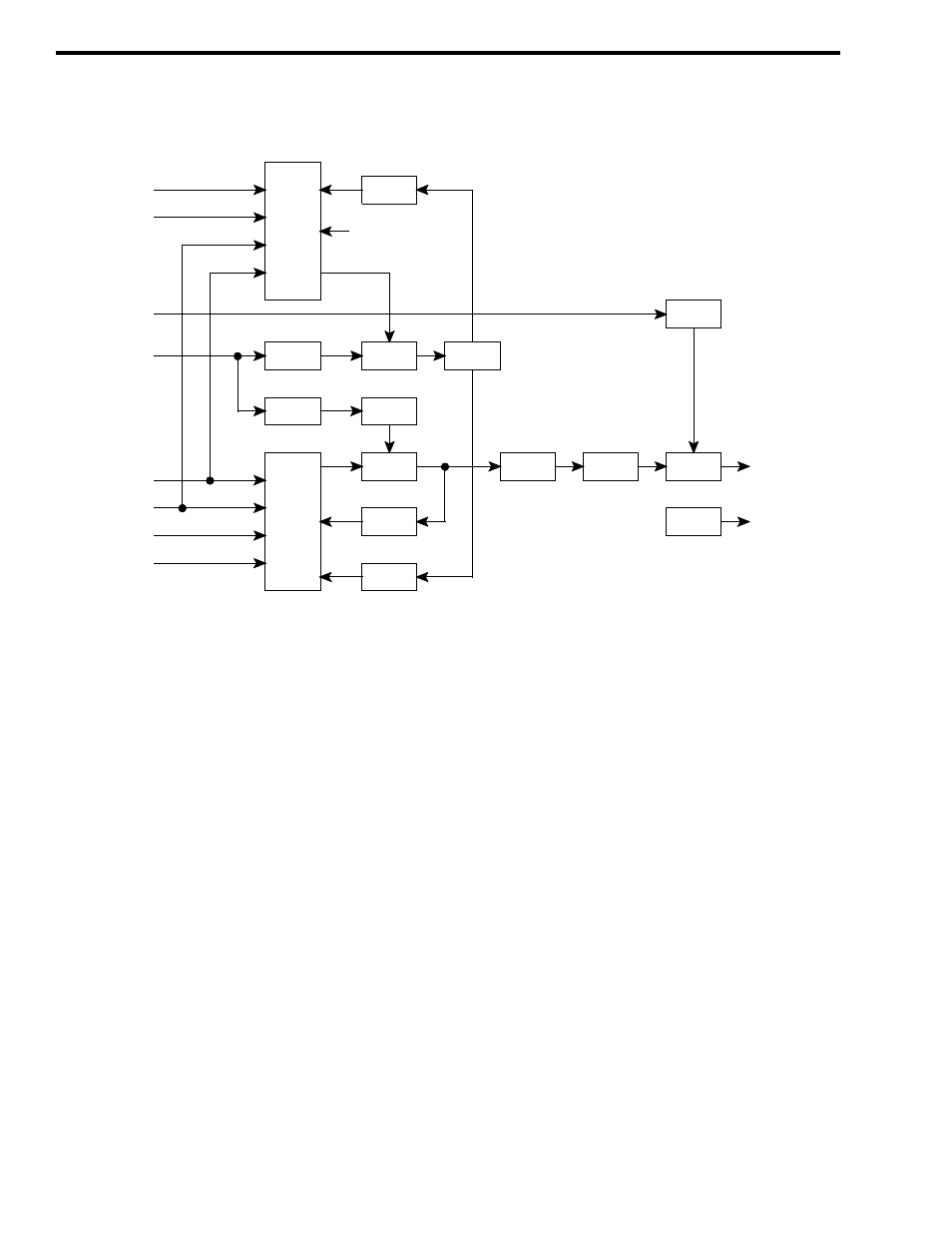
Figure 6-4 EXCITER BLOCK DIAGRAM
BUFFER
DATA
CLK
BUFFER
VCO
BUFFER
AMP
SYN CS EX
SYN LK EX
U403
Q406/Q407
U404B
BUFFER
Q410/Q411
Q412
Q413
AMP
Q405
Q403/Q404
BUFFER
Y401
TCXO
U404A
U402A
U402B
EX MOD
LPTT
SWITCH
TO PA
A007
AMP
AMP
U407B
V REF EX
HS LK EX
HS CS EX
U401
BUFFER
Q401/Q402
SYNTHESIZER
MAIN
PD
OUT
IN
REF
IN
F
SYNTHESIZER
PD
OUT
IN
REF
IN
F
HIGH STABILITY
TX OCXO
FROM Q204
6.2.7 BUFFER AMPLIFIER
A cascode amplifier formed by Q401 and Q402
provides amplification and also isolation between the
TCXO and Synthesizer U401. A cascode amplifier is
used because it provides high gain, high isolation and
consumes only a small amount of power. The input
signal to this amplifier is coupled from TCXO Y401,
pin 5 by C415. C415 also provides DC blocking.
Bias for the amplifier is provided by R420, R421,
R422, R423 and R418. L401 is an RF choke. RF
bypass is provided by C411, C413 and C414. The
output of Q401/Q402 is coupled to U401, pin 11 by
C412.
6.2.8 EXCITER SYNTHESIZER
The synthesizer inputs/outputs are shown in Fig-
ures 6-3 and 6-4. The synthesizer output signal is the
transmit frequency. This signal is produced by a VCO
(voltage-controller oscillator) that is frequency con-
trolled by a DC voltage produced by synthesizer chip
U403. This DC voltage is filtered by a loop filter
made up of C805, C806 and R804 in the VCO
circuitry.
Frequencies are selected by programming
counters in U403 to divide by a certain number. This
programming is provided through J401, pins 12, 19
and 20. The frequency stability of the synthesizer is
established by the
±
0.1 PPM stability of the high sta-
bility loop that is stable from -40
°
C to +70
°
C
(-40
°
F to +158
°
F).
The VCO frequency of A007 is controlled by a
DC voltage produced by integrating the phase detec-
tor output pulses of U403. The phase detector senses
the phase and frequency of two input signals and
causes the VCO control voltage to increase or decrease
if they are not the same. When the frequencies are the
same, the VCO is then "locked" on frequency.
