Chapter 5 - authentication, Authentication, Table 5-1 authentication – Tut Systems SMS2000 User Manual
Page 45
Authentication
TUT Systems, Inc
Page 45 of 104
P/N 220-06288-20
Chapter 5 - Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a subscriber.
Authentication
The SMS2000 is capable of performing authentication by using an external server (OCS
or RADIUS). For more information on using the OCS for authentication, see the OCS
User’s Guide. For more information on RADIUS, see Chapter 13, “Using SMS2000 with
a RADIUS Server.” Scenarios for performing these functions in various configurations
are described below.
Note:
The SMS2000 can authorize machines based on source MAC address
(sometimes called “machine authentication”, VLAN ID, SNMP information, IP
address, or any combination of these using groups and rules.
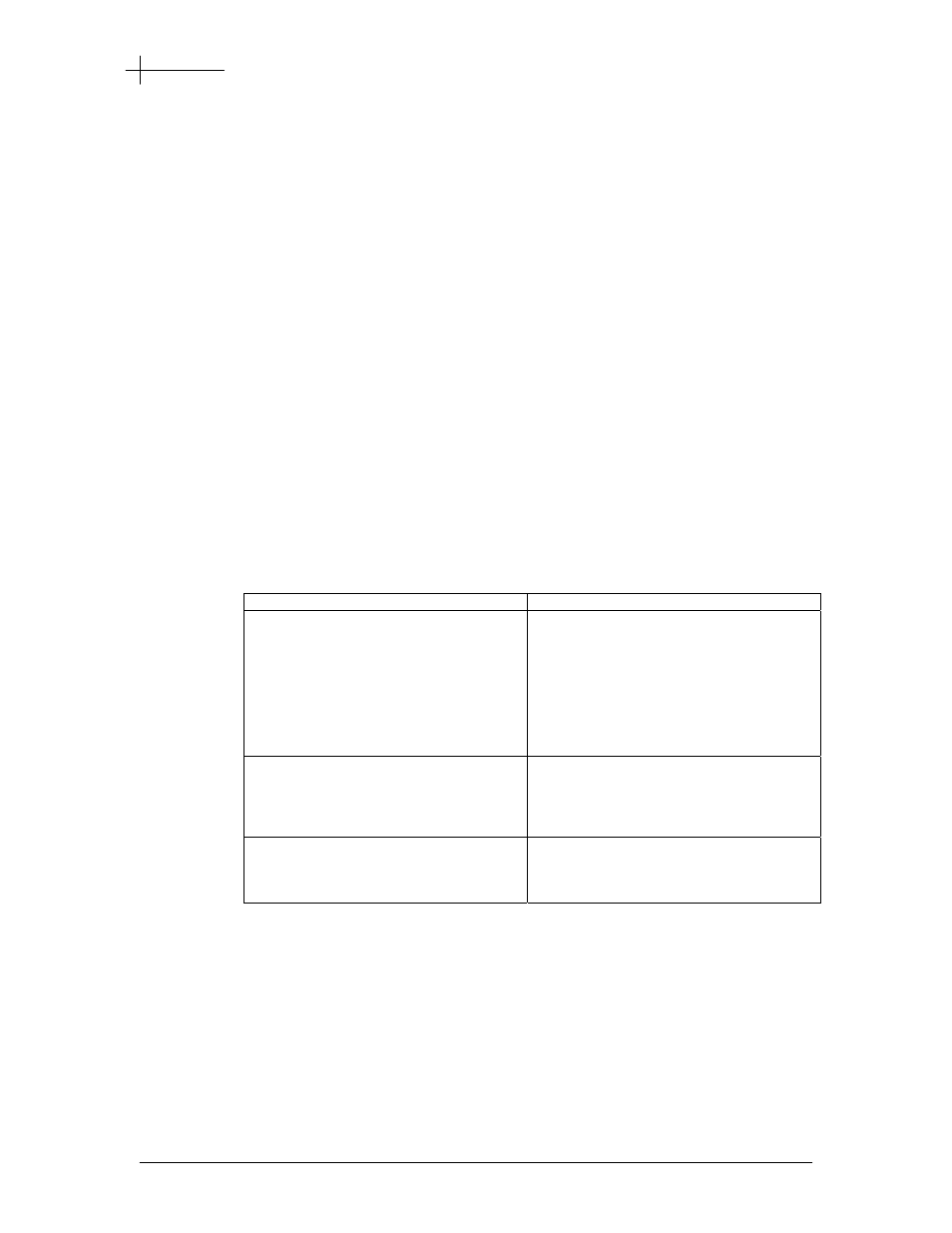
Table 5-1 shows how authentication is performed with no external server, with RADIUS,
and with the OCS.
Table 5-1 Authentication
Server Functionality
With No External Server
The SMS2000 has no database capable of
authentication, however it can be used to
authorize machines based on source MAC
address (sometimes called “machine
authentication”), VLAN ID, SNMP information,
IP address, or any combination of these using
groups and rules. For more information on using
groups and rules, see Chapter 10, “Groups and
Rules.”
With RADIUS
The SMS2000 behaves like a standard network
access server (that is, a dial-in network server)
and supports RADIUS authentication.
The client enters a user name and password on a
Web page generated locally by the SMS2000.
With OCS
The OCS can be configured to authenticate
clients. The OCS can also be configured to allow
some subscribers (such as servers) network
access without authentication.
