Figure 7-9. buffered period measurement, Semi-period measurement, Single semi-period measurement – National Instruments NI 6238 User Manual
Page 74: Semi-period measurement -9, Single semi-period measurement -9
Chapter 7
Counters
© National Instruments Corporation
7-9
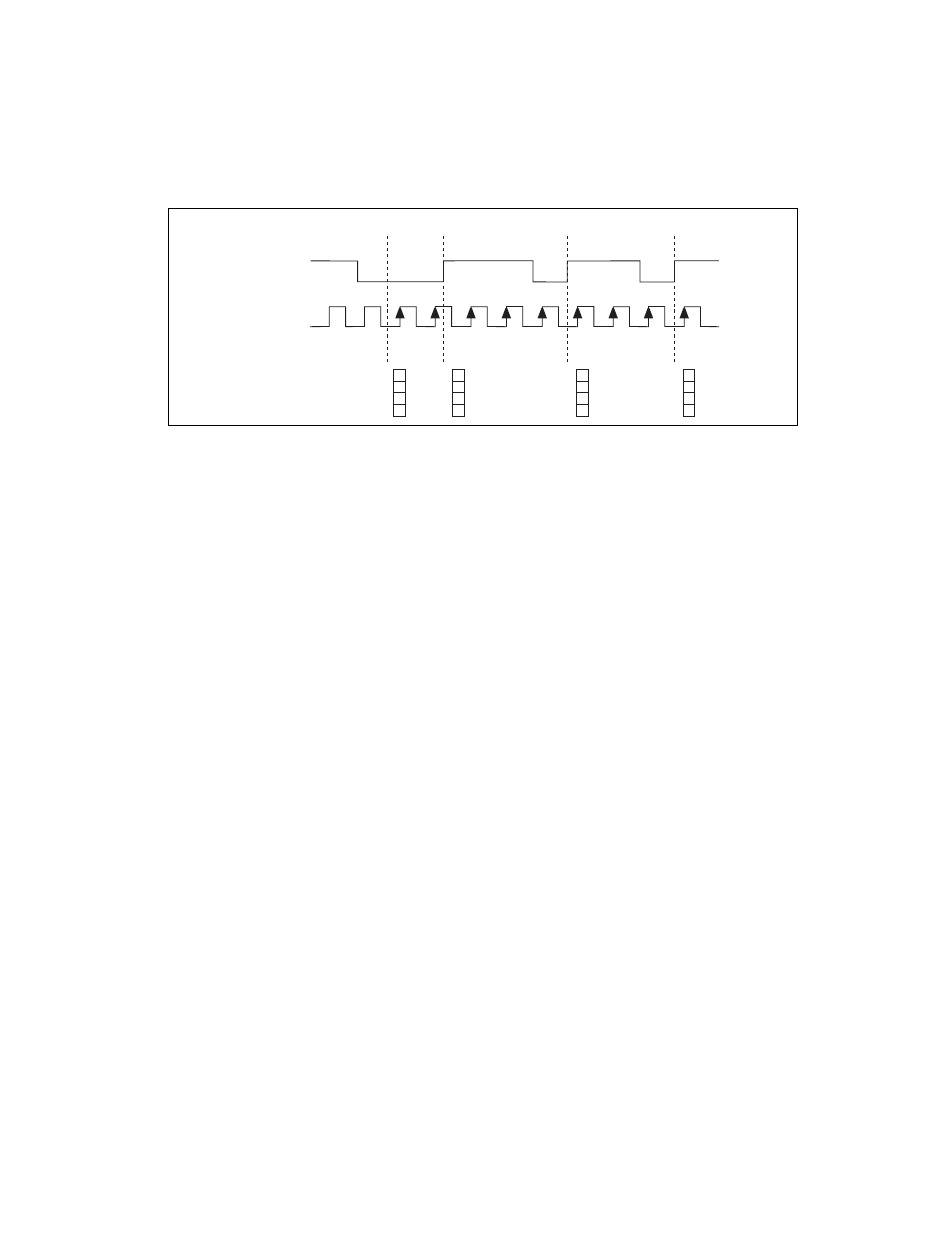
Figure 7-9. Buffered Period Measurement
Note that if you are using an external signal as the Source, at least one
Source pulse should occur between each active edge of the Gate signal.
This condition ensures that correct values are returned by the counter. If this
condition is not met, consider using duplicate count prevention.
For information on connecting counter signals, refer to the
Semi-Period Measurement
In semi-period measurements, the counter measures a semi-period on its
Gate input signal after the counter is armed. A semi-period is the time
between any two consecutive edges on the Gate input.
You can route an internal or external periodic clock signal (with a known
period) to the Source input of the counter. The counter counts the number
of rising (or falling) edges occurring on the Source input between two
edges of the Gate signal.
You can calculate the semi-period of the Gate input by multiplying the
period of the Source signal by the number of edges returned by the counter.
Single Semi-Period Measurement
Single semi-period measurement is equivalent to single pulse-width
measurement.
SOURCE
GATE
Counter Value
Buffer
1
1
2
3
3
2
3
3
1
1
2
2
2
2
3
3
2
(Discard)
(Discard)
(Discard)
3
Counter Armed
