Figure b-1. ai/sampleclock and ai/convertclock, Analog output – National Instruments NI 6238 User Manual
Page 141
Appendix B
Troubleshooting
B-2
ni.com
In an isolated device, leaving the AI GND terminal unconnected will cause
the signal to drift and eventually rail.
How can I use the AI Sample Clock and AI Convert Clock signals on
an M Series device to sample the AI channel(s)?
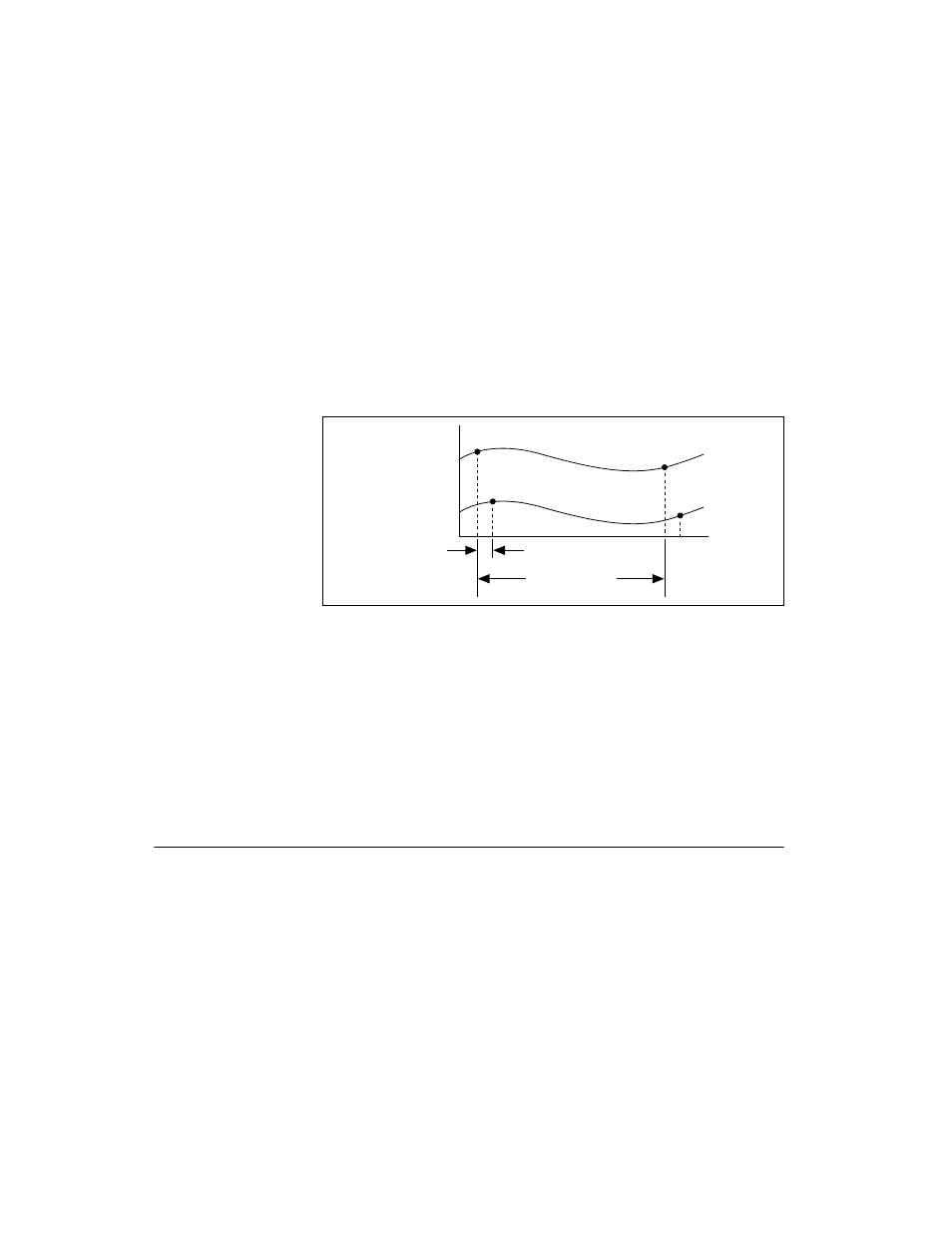
M Series devices use ai/SampleClock and ai/ConvertClock to perform
interval sampling. As Figure B-1 shows, ai/SampleClock controls the
sample period, which is determined by the following equation:
1/sample period = sample rate
Figure B-1. ai/SampleClock and ai/ConvertClock
ai/ConvertClock controls the convert period, which is determined by the
following equation:
1/convert period = convert rate
This method allows multiple channels to be sampled relatively quickly in
relationship to the overall sample rate, providing a nearly simultaneous
effect with a fixed delay between channels.
Analog Output
I am seeing glitches on the output signal. How can I minimize it?
When you use a DAC to generate a waveform, you may observe glitches on
the output signal. These glitches are normal; when a DAC switches from
one voltage to another, it produces glitches due to released charges. The
largest glitches occur when the most significant bit of the DAC code
changes. You can build a lowpass deglitching filter to remove some of these
glitches, depending on the frequency and nature of the output signal. Visit
ni.com/support
for more information on minimizing glitches.
Channel 0
Channel 1
Convert Period
Sample Period
