10 snmp – Planet Technology SGSW-2402 User Manual
Page 22
18
NOTE
Slave switch IP will be covered by Master one, and disappear temporarily. The slave IP
address can be the same as Master IP address. Thus, if master switch is malfunction, you
can still access the other switch by same IP address.
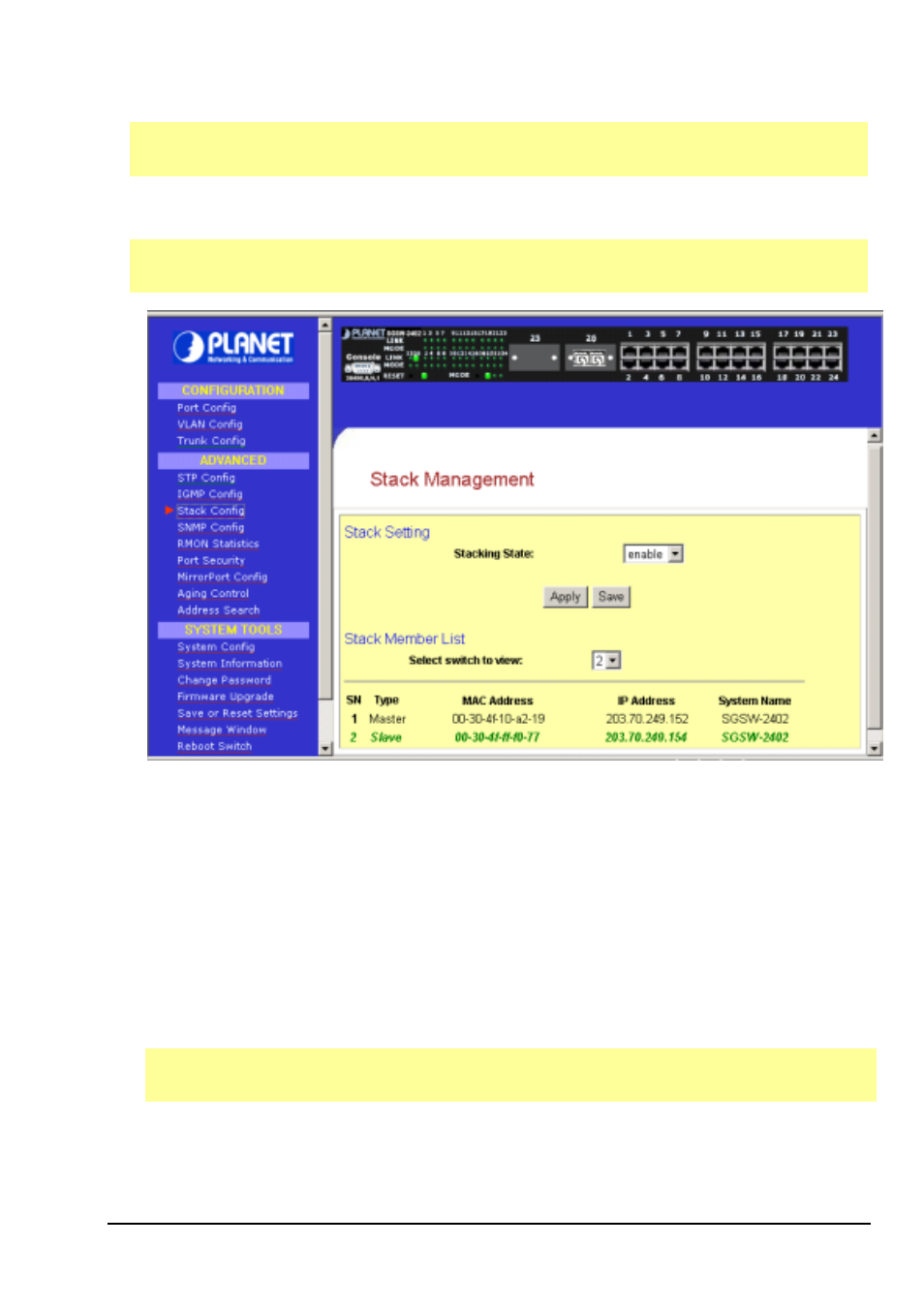
You can key in Master IP (ex:203.70.249.152), and choose “Stack Config”, then all the stack member list
will be displayed . You can then choose the switch you want to configure from the “Select switch to view”
list.
NOTE
If you have difficulty on selecting another switch, you may be connecting to the slave switch’s
web, please close the browser window, use the “arp –d * ” DOS command to clear the ARP
table and then reopen the web.
Figure 3-11 The Stack screen page
3.10 SNMP
The management switch provides Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) over the UDP/IP
transport protocol as defined in RFC 1517 for network management applications.
To control the access of the system, a list of community entries is defined. Each community entry consists
of a community string and its access privilege. The Access privilege is either “Read Only” or “Read-Write”.
Only SNMP messages with correct community string and allowable operation are responded by the
system. The community list is configurable by all management operations. Only SNMP community with
“Read-Write” can view the whole list and make modifications. A “Read Only” community can only see its
own community entry.
NOTE
In a stack environment, for master switch to know which switch you want to view and set by
SNMP, either the switches’ IP or community name must be different. Thus, if you have
stacked several switches by single IP, their community name must be different.
Trap messages are generated to report system events spontaneously as defined in RFC 1215. The
system can generate traps defined in the MIB it supports.
A list of “Trap Receivers” is defined in management as the target of each trap message. A Trap Receiver
