2 martensitic stainless steels – Lincoln Electric Welder User Manual
Page 5
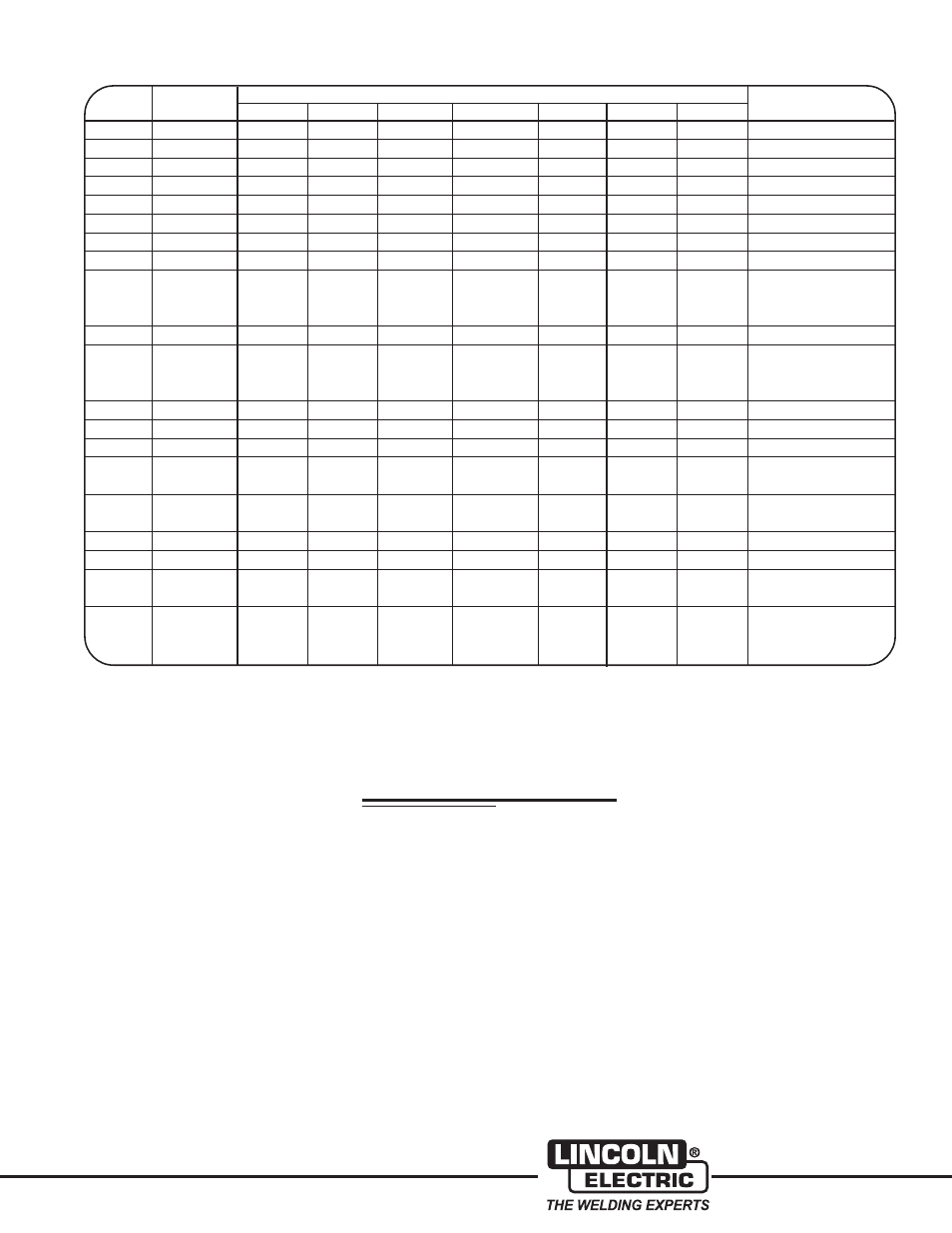
UNS
Composition - Percent *
Type
Number
C
Mn
Si
Cr
Ni
P
S
Other
405
S40500
0.08
1.00
1.00
11.5-14.5
0.04
0.03
0.10-0.30 Al
409
S40900
0.08
1.00
1.00
10.5-11.75
0.045
0.045
6 x %C min. TI
429
S42900
0.12
1.00
1.00
14.0-16.0
0.04
0.03
430
S43000
0.12
1.00
1.00
16.0-18.0
0.04
0.03
430F**
S43020
0.12
1.25
1.00
16.0-18.0
0.06
0.15 min.
0.06 Mo
430FSe**
S43023
0.12
1.25
1.00
16.0-18.0
0.06
0.06
0.15 min. Se
430Ti
S43036
0.10
1.00
1.00
16.0-19.5
0.75
0.04
0.03
5 x %C - Ti min.
434
S43400
0.12
1.00
1.00
16.0-18.0
0.04
0.03
0.75-1.25 Mo
436
S43600
0.12
1.00
1.00
16.0-18.0
0.04
0.03
0.75-1.25 Mo;
5 x %C min.
Nb(Cb) + Ta
442
S44200
0.20
1.00
1.00
18.0-23.0
0.04
0.03
444
S44400
0.025
1.00
1.00
17.5-19.5
1.00
0.04
0.03
1.75-2.5 Mo, 0.035 N
0.2 + 4 (%C + %N);
(Ti +Nb(Cb) )
446
S44600
0.20
1.50
1.00
23.0-27.0
0.04
0.03
0.25 N
18-2FM**
S18200
0.08
2.50
1.00
17.5-19.5
0.04
0.15 min.
18SR
0.04
0.3
1.00
18.0
2.0 Al; 0.4 Ti
26-1
S44625
0.01
0.40
0.40
25.0-27.5
0.50
0.02
0.02
0.75-1.5 Mo; 0.015N;
(E-Brite)
0.2 Cu; 0.5 (Ni+Cu)
26-1Ti
S44626
0.06
0.75
0.75
25.0-27.0
0.5
0.04
0.02
0.75-1.5 Mo; 0.04 N;
0.2 Cu; 0.2-1.0 Ti
29-4
S44700
0.01
0.30
0.20
28.0-30.0
0.15
0.025
0.02
3.5-4.2 Mo
29-4-2
S44800
0.01
0.30
0.20
28.0-30.0
2.0-2.5
0.025
0.02
3.5-4.2 Mo
Monit
S44635
0.25
1.00
0.75
24.5-26.0
3.5-4.5
0.04
0.03
3.5-4.5 Mo;
0.3-0.6 (Ti + Nb(Cb) )
Sea-cure/
S44660
0.025
1.00
0.75
25.0-27.0
1.5-3.5
0.04
0.03
2.5-3.5 Mo;
Sc-1
0.2 + 4 (%C + %N)
(Ti + Nb(Cb) )
of a number of standard and several
non-standard ferritic stainless steels.
They are characterized by weld and
HAZ grain growth which can result in
low toughness of welds.
To weld the ferritic stainless steels,
filler metals should be used which
match or exceed the Cr level of the
base alloy. Type 409 is available as
metal cored wire and Type 430 is
available in all forms. Austenitic
Types 309 and 312 may be used for
dissimilar joints. To minimize grain
growth, weld heat input should be
minimized, Preheat should be limited
to 300-450°F and used only for the
higher carbon ferritic stainless steels
(e.g., 430, 434, 442 and 446). Many
of the highly alloyed ferritic stainless
steels are only available in sheet and
tube forms and are usually welded
by GTA without filler metal.
3.2
MARTENSITIC
STAINLESS STEELS
The martensitic stainless steels
contain 11 to 18% Cr, up to 1.20% C
and small amounts of Mn and Ni
and, sometimes, Mo. These steels
will transform to austenite on heating
and, therefore, can be hardened by
formation of martensite on cooling.
This group includes Types 403, 410,
414, 416, 420, 422, 431 and 440.
Both standard and non-standard
martensitic stainless steels are listed
in Table II. They have a tendency
toward weld cracking on cooling
when hard brittle martensite is
formed.
Chromium and carbon content of the
filler metal should generally match
these elements in the base metal.
Type 410 filler is available as covered
electrode, solid wire and cored wire
and can be used to weld types 402,
410, 414 and 420 steels. Type
410NiMo filler metal can also be
used. When it is necessary to match
the carbon in Type 420 steel, Type
420 filler, which is available as solid
wire and cored wire, should be used.
Types 308, 309 and 310 austenitic
filler metals can be used to weld the
martensitic steels to themselves or to
other steels where good as-
deposited toughness is required.
Preheating and interpass temperature
in the 400 to 600°F (204 to 316°C)
range is recommended for most
3
*Single values are maximum values.
(From ASM Metals Handbook, Ninth Edition, Volume 3)
TABLE I — Nominal Compositions of Ferritic Stainless Steels
**These grades are generally
considered to be unweldable.
