0 selection of a welding process – Lincoln Electric Welder User Manual
Page 20
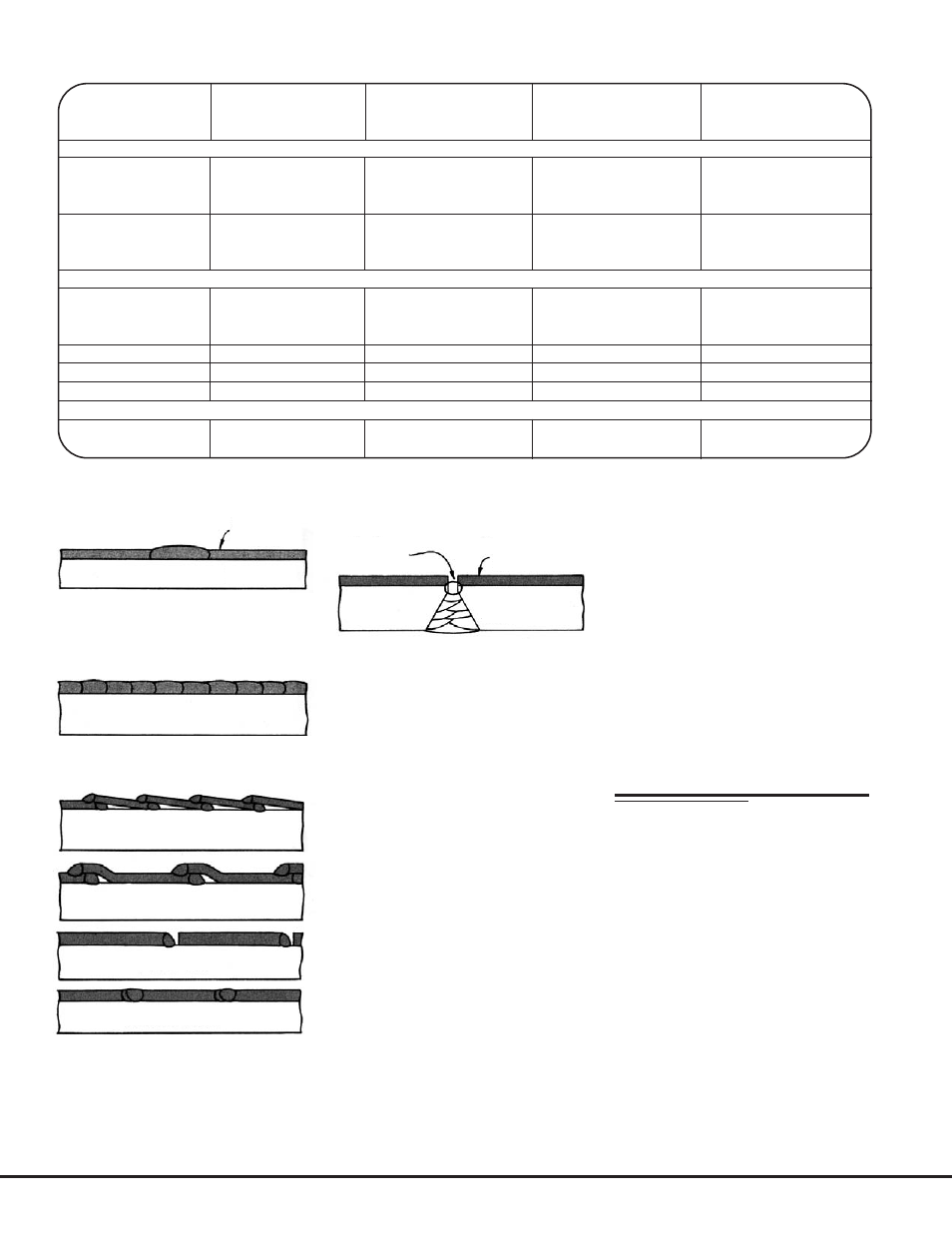
18
sheets are plug welded at frequent
intervals to join them closely to the
shell.
2. Overlapping welds deposited on
the steel surface.
3. Small strips are overlapped or
placed side-by-side and welded to
the shell. Sometimes this technique is
referred to as “wallpapering”
Welding Clad Steel
Clad steel consists of stainless steel
sheet permanently bonded to mild
steel plate. To join clad steel plates,
first weld the mild steel with mild
steel electrodes. Do not tie into the
stainless cladding with the mild steel
electrodes. After gouging the back-
side of the first mild steel bead, weld
from the stainless side using
stainless steel electrodes.
Joining Manganese Steel
E308-X or E309-XX electrodes are
used to weld manganese steel to
carbon steel or to manganese steel.
The stainless welds provide excellent
joint strength and ductility but are
difficult to flame cut. Therefore, when
a manganese steel piece must be
replaced periodically, such as dipper
teeth, Wearshield Mangjet
®
electrode
can be recommended. Wearshield
15CrMn electrode has better crack
resistance, but the deposit is difficult
to flame cut.
Thick Harfacing Deposits
E308-X or E309-XX deposits
increase the toughness of thick
hardfacing deposits. For best results,
use one layer of stainless between
each two layers of hardfacing.
9.0
SELECTION OF
A WELDING
PROCESS
Joint Cleanliness
For high-quality welds, stainless steel
joints must be clean. The choice of
power brushing, degreasing, pickling,
grinding or simply wiping depends
upon the application and amount of
dirt. Here are some specific hints:
1. Remove all moisture by blowing
with dry air or heating with a torch.
Beware of moisture in air lines, damp
rags and humidity deposited
overnight.
2. Eliminate organic contaminants like
oil, paints, anti-spatter compounds,
grease, pencil marks, cutting
compounds, adhesive from
Bare
Dissimilar
Covered
Welding
PH Stainless
Designation
UNS No.
Electrodes
Wire
Steels
Martensitic Types
17-4PH
S17400
AMS 5827B, E630
AMS 5826
E or ER309,
and
(17-4 PH) or
(17-4 PH) or
E or ER309 Cb
15-5 PH
S15500
E308
ER308
Stainless W
S17600
E308 or
AMS 5805C
E or ERNiMo-3,
ENiMo-3
a
(A-286) or
E or ER309
ERNiMo-3
b
Semiaustenitic Types
17-7PH
S17700
AMS 5827B
AMS 5824A
E or ER310,
(17-4 PH),
(17-7 PH)
ENiCrFe-2, or
E308, or E309
ERNiCr-3
PH 15-7Mo
S15700
E308 or E309
AMS 5812C (PH 15-7Mo)
E or ER309, E or ER310
AM350
S35000
AMS 5775A (AM350)
AMS 5774B (AM350)
E or ER308, E or ER309
AM355
S35500
AMS 5781A (AM355)
AMS 5780A (AM355)
E or ER308, E or ER309
Austenitic Types
A-286
K66286
E309 or E310
ERNiCrFe-6 or
E or ER309,
ERNiMo-3
E or ER310
a. See AWS A5.11-97, Specification for Nickel and Nickel Alloy Welding Electrodes for Shielded Metal Arc Welding
b. See AWS A5.14-97, Specification for NIckel and Nickel Alloy Bare Welding Electrodes and Rod.
TABLE XIV — Filler Metals for Welding Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steels
First Pass
Second Pass
Back
Gouge
Stainless
Steel
Stringer Beads
Mild Steel
Stainless
Steel
Mild Steel
Plug Weld
