Greenheck Fan Canopy Type Kitchen Hoods 452413 User Manual
Page 13
13
Kitchen Hoods • Type I and Type II
Airflow
2 in.
(50.8 mm)
Rotating Vane
Anemometer
Nominal Filter Size (H x L)
Imperial
Conversion
Factor
Metric
Conversion
Factor
Inches
Millimeters
16 x 16
400 x 400
1.63
.157
16 x 20
500 x 400
2.13
.198
20 x 16
400 x 500
1.90
.177
20 x 20
500 x 500
2.48
.230
Total hood volume
=
(Filter 1 Volume)
+
(Filter 2 Volume)
+
(Filter 3 Volume)
(Imperial)
=
474.6
+
455.4
+
470.1
=
1400.1 cfm
(Metric)
=
809
+
880
+
799
=
2488 m
3
/hr
For a nominal filter size of 20 x 16, the conversion factor is 1.90 Imperial (.177 Metric)
Volume for one filter
=
Conversion Factor x
Average Velocity
(Imperial)
=
1.90
x
249.8 ft/min.
= 474.6 cfm
(Metric)
=
.177
x
4568 m/hr
= 809 m
3
/hr
Example: Exhaust only hood with three 20 x 16 filters
Measured velocities in ft/min. for one 20 x 16 filter
Average Velocity
=
Sum of Velocity Readings
Number of Readings
(Imperial)
=
255 + 250 + 256 + 248 + 240
5
= 249.8 ft/min.
(Metric)
=
4663 + 4572 + 4681 + 4535 + 4389
5
= 4568 m/hr
255
(4663.44 m/h)
248
(4535.42 m/h)
256
(4681.73 m/h)
240
(4389.12 m/h)
250
(4572 m/h)
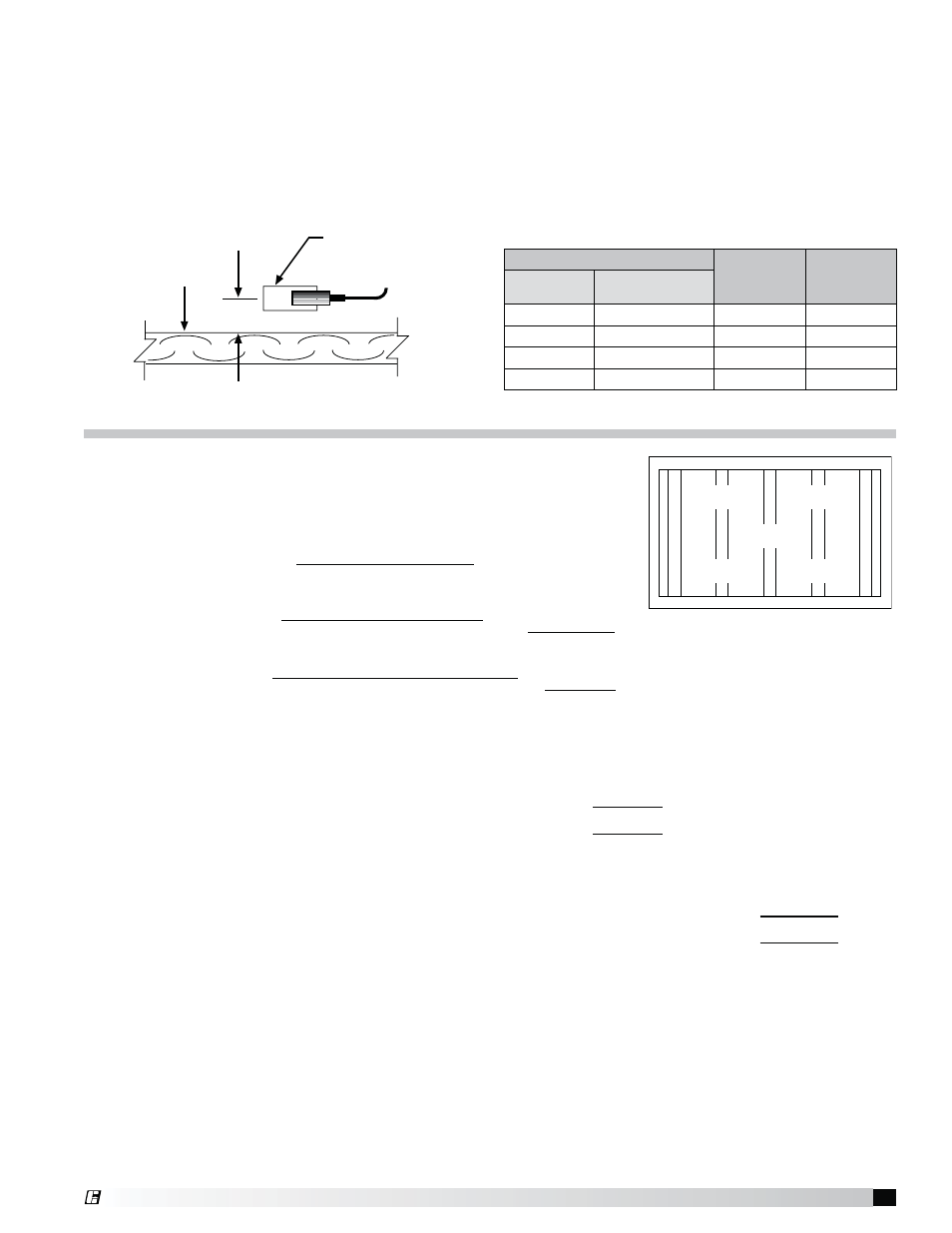
Measure and record the velocity of each location.
A digital 2.75 in. (69.85 mm) rotating vane anemometer
or equivalent is suggested. The center of the
anemometer should be held 2 in. (50.8 mm) from the
face of the filters. It is helpful to make a bracket to keep
the anemometer at the 2 in. (50.8 mm) distance and
parallel to the filter. Both squareness and distance are
very important for accuracy.
Calculate the average velocity for the filter.
3. Determine the filter’s conversion factor from the
table.
4. Calculate the filter’s volume in CFM (m
3
/hr) by
multiplying the average velocity by the conversion
factor.
5. Calculate the hood’s volume by repeating the
process for the remaining filters and summing the
individual filter volumes.
®
