9salts, Organics, Gases, dissolved – GE E4H Series User Manual
Page 15
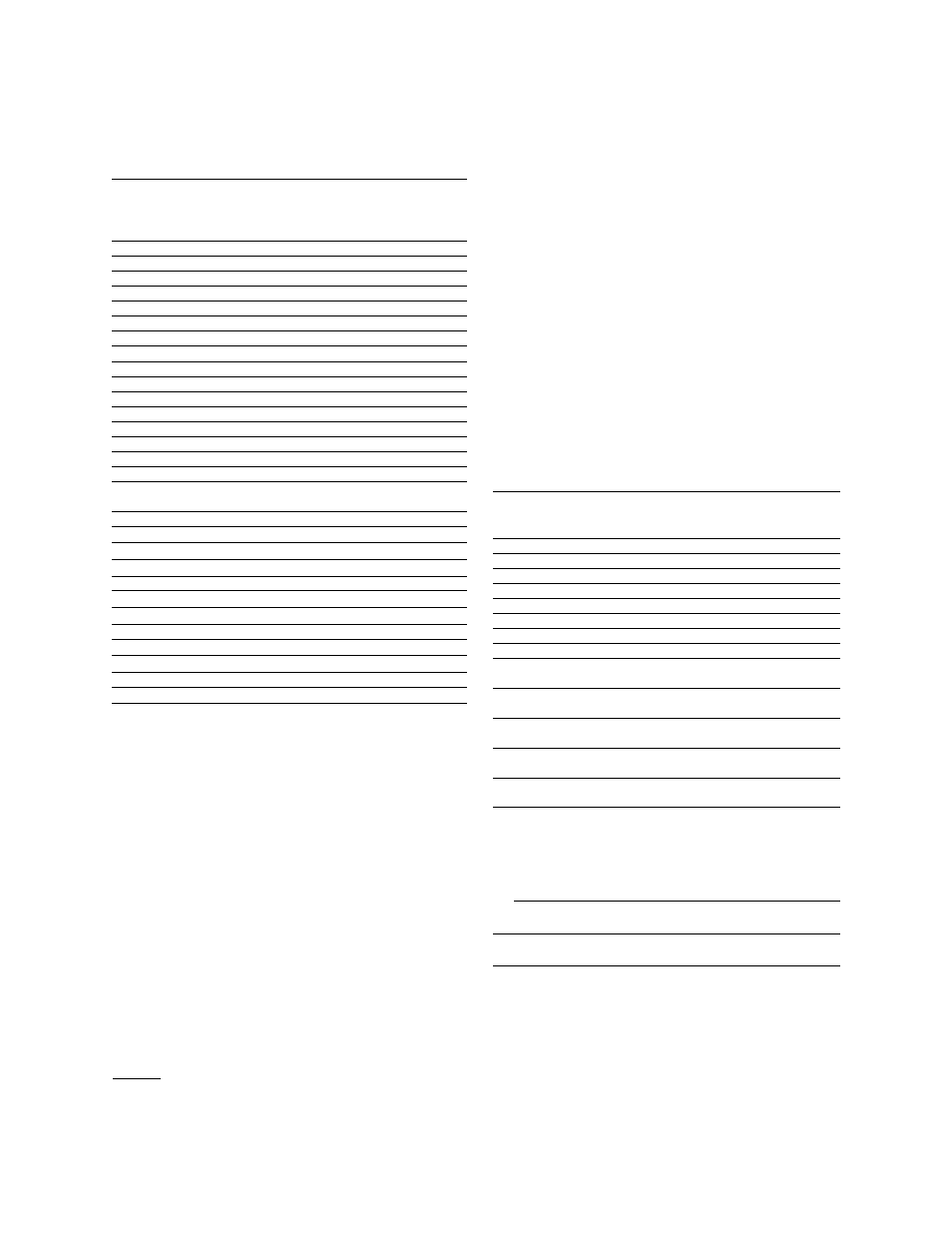
9
SALTS
CATIONS
Percent
Maximum
Percent Passage Concentration
Name
Symbol
Rejection (Avg)
Percent
Sodium
Na
+
94-96
5
5-10
Calcium
Ca
+2
96-98
3
*
Magnesium
M g
+2
96-98
3
*
Potassium
K
+1
94-96
5
5-10
Iron
Fe
+2
98-99
2
*
Manganese
M n
+2
98-99
2
*
Aluminum
Al
+3
99+
1
10-20
Ammonium
N H
4
+1
88-95
8
3-8
Copper
Cu
+2
98-99
1
10-20
Nickel
Ni
+2
98-99
1
10-20
Zinc
Zn
+2
98-99
1
10-20
Strontium
Sr
+2
96-99
3
-
Hardness
Ca & Mg
96-98
3
*
Cadmium
Cd
+2
96-98
3
10-20
Silver
Ag
+1
94-96
5
*
Mercury
Hg
+2
96-98
3
-
ANIONS
Chloride
Cl
-1
94-95
4
5-8
Bicarbonate
H C O
3
-1
95-96
4
5-10
Sulfate
S O
4
-2
99+
1
5-15
Nitrate
N O
3
-1
85-95
10
3-6
Fluoride
F
-1
94-96
5
5-8
Silicate
SiO
2
-2
80-95
10
-
Phosphate
P O
4
-3
99+
1
10-20
Bromide
Br
-1
94-96
5
5-8
Borate
B
4
O
7
-2
35-70**
-
-
Chromate
CrO
4
-2
90-98
6
8-12
Cyanide
C N
-1
90-95**
-
4-12
Sulfite
S O
3
-2
98-99
1
5-15
Thiosulfate
S
2
O
3
-2
99+
1
10-20
ORGANICS
Maximum
Molecular
Percent
Concentration
W eight
Rejection
Percent
Sucrose Sugar 342
99.9
30-35
Lactose Sugar
360
99.9
30-35
Protein
10,000 Up
99.9
50-80
Glucose
180
99.0
15-20
Phenol
94
***
-
Acetic Acid
60
***
-
Formaldehyde
30
***
-
Dyes
400 to 900
99.9
-
Biochemical
Oxygen Demand
(BOD)
90.0-99.9
Chemical
-
Oxygen Demand
(COD)
99.9
Urea
60
40-60
Reacts similar to
a salt
Bacteria & Virus
50,000 to
99.9+
500,000
-
Pyrogen
1,000
99.9+
-
to 5,000
*** Permeate is enriched in material due to preferential pas-
sage through the membrane.
GASES, DISSOLVED
Carbon Dioxide
C O
2
30-50%
Oxygen
O
2
Enriched in permeate
Chlorine
Cl
2
30-70%
To estimate passage of salts for membrane elements other than SEPA-
HR, take the passage for the SEPA-HR and multiply by the factor for the
passage for the particular membrane element. The factors are:
S E PA-SR is 1.6 times SEPA-HR passage
S E PA-PR is 2.5 times SEPA-HR passage
Operation of the SEPA-HR membrane element at pressures over 400 psig
(27.6 barg) will reduce salt passage slightly. Operation at 200 psig (13.8
bar) will increase the passage of monovalent ions by approximately 2.0
times and the passage of multivalent ions will increase by 1.5 times the
400 psig (27.6 bar) passage.
For SEPA membrane elements with larger pores than the SEPA-PR it is
recommended that actual tests be run prior to estimating the permeate
quality.
The maximum concentrations given in the table are the approximate
concentrations resulting in an osmotic pressure of 500 psi (34.5 barg)
for the solution.
Compounds such as CaSO
4
which have specific solubility limits can be
controlled with proper addition of dispersants. Check with the factory for
more information on Osmonics special line of dispersants
.
* Must watch for precipitation; other ion controls maximum
concentration
*
* Extremely dependent on pH; tends to be an exception to the
rule
The following are typical rejections and passages for various salts and
organics using the SEPA
fi
-HR membrane at 400 psig (27.6 bar) operat-
ing pressure. Modules made with this membrane, such as the OSMO
fi
-
HR, can be expected to give these same passages. As can be seen,
multivalent ions tend to have less passage than do monovalent ions. If
monovalent ions are combined with multivalent ions to form a salt, the
passage will be controlled by the multivalent ion. In RO all ions must be
combined as the salt form before passages can be considered.
For estimating purposes, to obtain the expected permeate quality when
handling a solution of salts, take a simple average of the feed concentra-
tion and the
concentrate concentration and multiply this figure by the average per-
cent passage to calculate the average concentration of the
permeate.Salts or organics that are complexed with organics of large
molecular weights will tend to act like the organics with which they are
complexed.
NOTE: The actual permeate water quality will vary with the inlet water quality and can only be veri-
fied by actual analysis of the permeate stream.
Figure 1.2
Typical Membrane Element
Rejections/Passages
