Troubleshooting magic-pak: hw/hwc – Armstrong World Industries HWC PREMIER 183 User Manual
Page 193
9-8
TROUBLESHOOTING
Magic-Pak: HW/HWC
SRM-HW/HWC 8/99
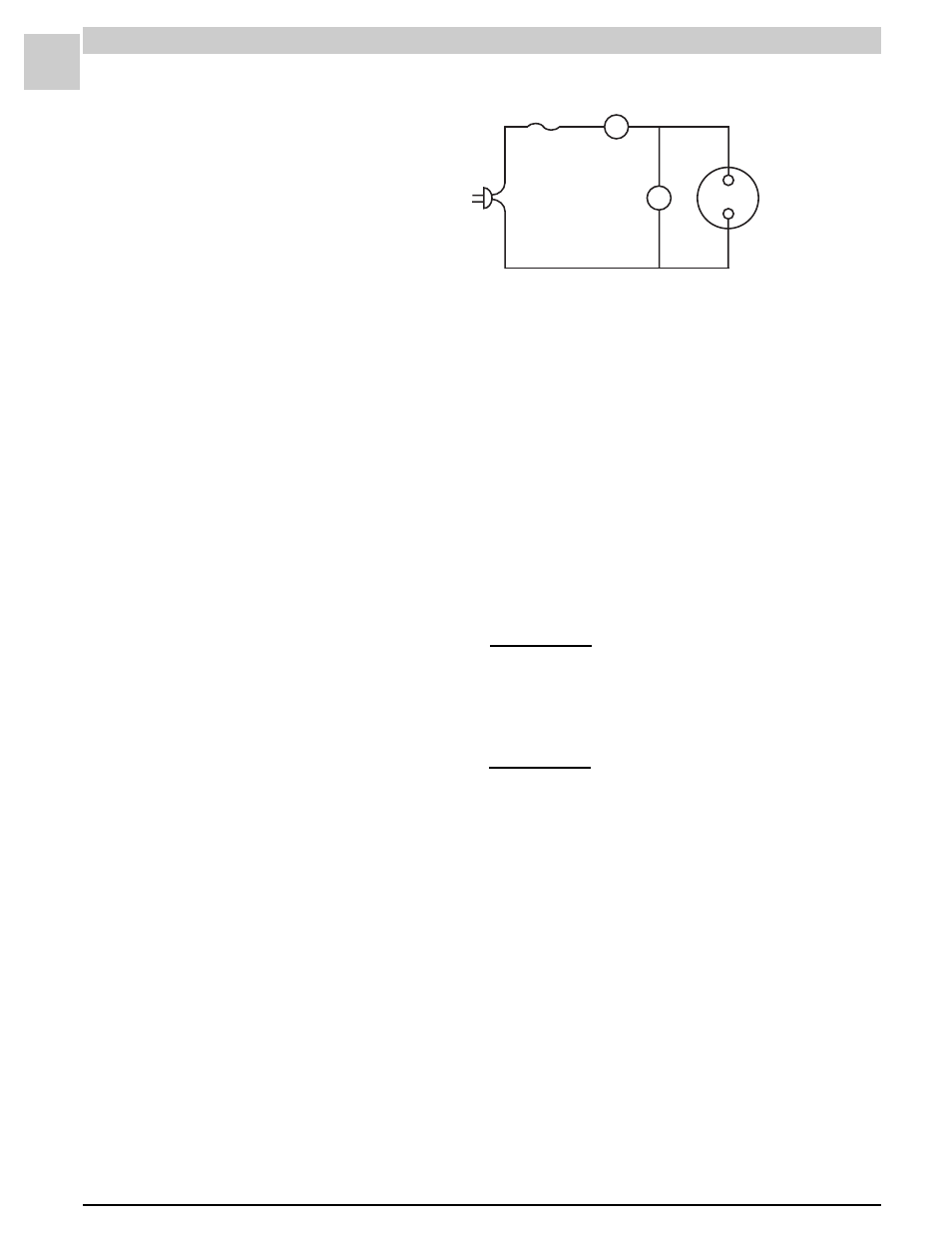
Before starting the test, take a reading of the line voltage at the outlet that
will be used.
Double check the connections, making sure that the amp meter is on.
Plug the test leads into the wall outlet. Wait a few seconds and read the
amp meter (
CAUTION:
there is only approximately ten seconds to do this
or the capacitor could be damaged). Unplug the jumper and record the
readings.
Using the calculator, divide the amp meter reading by ten (the number of
loops in one of the test leads). This is the correct amp reading which is
needed to finish the calculations. This information and the voltage at the
outlet is all that is needed to calculate the capacitance of the capacitor.
Nominal
Voltage
Source
Fuse
(10 Loops)
Voltmeter
Capacitor
To Be Tested
V
A
Ammeter
FIGURE 9-1
Determining Capacitance (MFD) Rating with a Test
Cord
Example
This calculation provides the actual capacitance of the capacitor. Com-
pare this reading to the listed rating on the capacitor. It should be within
+/– 10% of the actual capacitor rating. If it does not fall within this range,
the capacitor is defective and should be replaced.
The capacitor should always be checked before replacing an electric
motor. Eliminate the capacitor as a possible cause of the problems
before the decision is made to replace the motor. A good practice is also
to replace the capacitor whenever a motor is replaced, as the capacitor
does have a service life cycle. The capacitor is a very important part of
the motor electrical system. Always check the capacitor along with the
motor when a fault is noted.
*For 50 Hz electrical systems, use 3180 as the constant multiplier.
2650 x 1 Amp
115 Volts
= 23 MFD
2650 x Amps
Volts
= Capacitance (MFD)
In the following calculation, a constant multiplier (2650) is used for 60 Hz
electrical systems.*
