Chapter 4 explanation of functions – Hitachi SJ700-2 User Manual
Page 122
Chapter 4 Explanation of Functions
The speed control normally incorporates the proportional integrated
compensation (PI control), and the motor speed is controlled so that
the difference between the frequency specified by the frequency
command and the actual motor speed is zero. However, a specific
operation mode (called drooping operation), in which one load is
driven by multiple motors, sometimes requires the proportional
control (P control). To enable the proportional (P) control mode,
assign function "43" (P/PI switching function) to one of the terminal
[1] to [8] functions (C001 to C008), and turn on the intelligent input
terminal. For the proportional control, set the value of the P control
proportional gain (H052) as the KPP value.
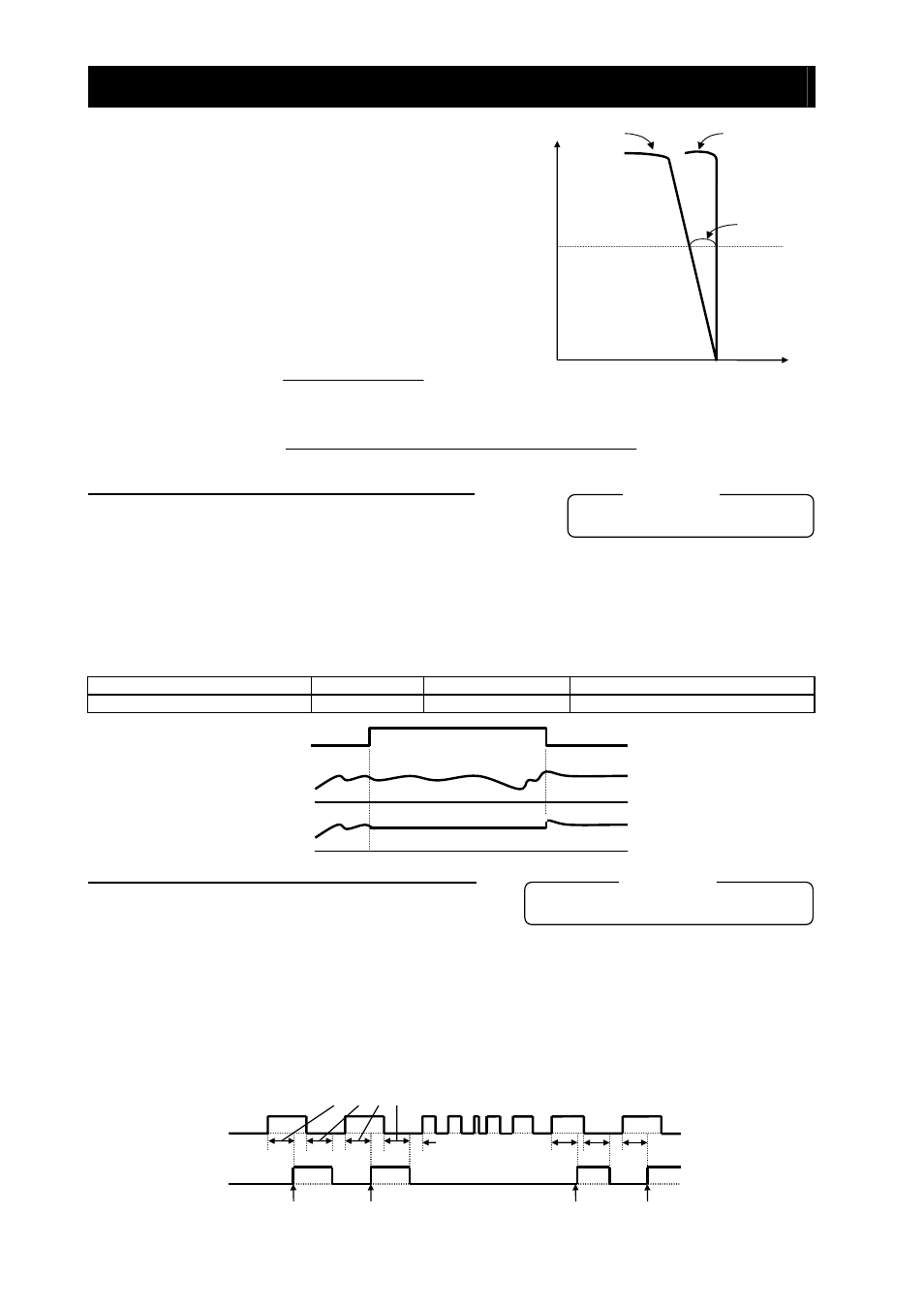
The following formula generally represents the relation between the
KPP value and momentary speed variation:
4 -
59
(Momentary speed variation) = (%)
P control mode
PI control mode
100%
0
Torque
(A)
Rotation speed
PP)
10
(Set value of K
The following formula generally represents the relation between the momentary speed variation and speed error:
(Momentary speed variation) =
× 100%
Speed error at rated torque (A)
Synchronous rotation speed at base frequency
4.2.56 Analog command holding function (AHD)
C001 to C008: Terminal [1] to [8] functions
C101 : UP/DWN holding function
Related code
- The analog command holding function allows you to make the inverter hold
the analog command input via the external analog input terminal when the
AHD terminal is on.
- While the AHD terminal is on, the up/down function can be used based on the analog signal held by this function as
reference data.
- When "01" is specified for Up/Down memory mode selection (C101), the result of up/down processing can be stored
in memory.
- If the inverter power is turned on or the RS terminal turned off with the AHD terminal left turned on, the data held
immediately before power-on or turning off the RS terminal will be used.
Item Function
code
Data
Description
Terminal [1] to [8] functions
C001 to C008
65
AHD: Analog command holding
4.2.57 Intelligent pulse counter (PCNT and PCC)
- The intelligent pulse counter function allows you to input a pulse
train via an intelligent input terminal.
- The cumulative count of input pulses can be monitored by the pulse counter monitor (d028) function.
- The value of cumulative counter cannot be stored. The counter value is cleared to zero when the inverter power is
turned on or the inverter reset.
- Turning on the PCC (pulse counter clear)terminal clears the cumulative counter.
- The frequency resolution of the input pulse can be calculated by the formula shown below (for pulse signal input with
a duty ratio of 50%). Frequencies not less than the relevant resolution cannot be input. It is recommended to use this
function up to 100Hz. For the input terminal response, see Section 4.2.79.
Frequency resolution (Hz) = 250/(input terminal response time setting [C160 to C168] + 1)
Example: When the input terminal response time is 1, the frequency resolution is 125 Hz.
ON
AHD terminal
Input analog command
Frequency command
C001 to C008: Terminal [1] to terminal [8] functions
d028: Pulse counter monitor
Related code
Input pulse
PCNT
ON
OFF
Input terminal response
1
2
3
4
Value of counter
Remark)
Set frequency remains when inverter
is switched with SET/SET3 terminal
with AHD on. Turn AHD terminal off
to re-hold the set frequency.
