Quickpath interconnect controller, Hyper-threading – HP SL6000 User Manual
Page 12
QuickPath Interconnect controller
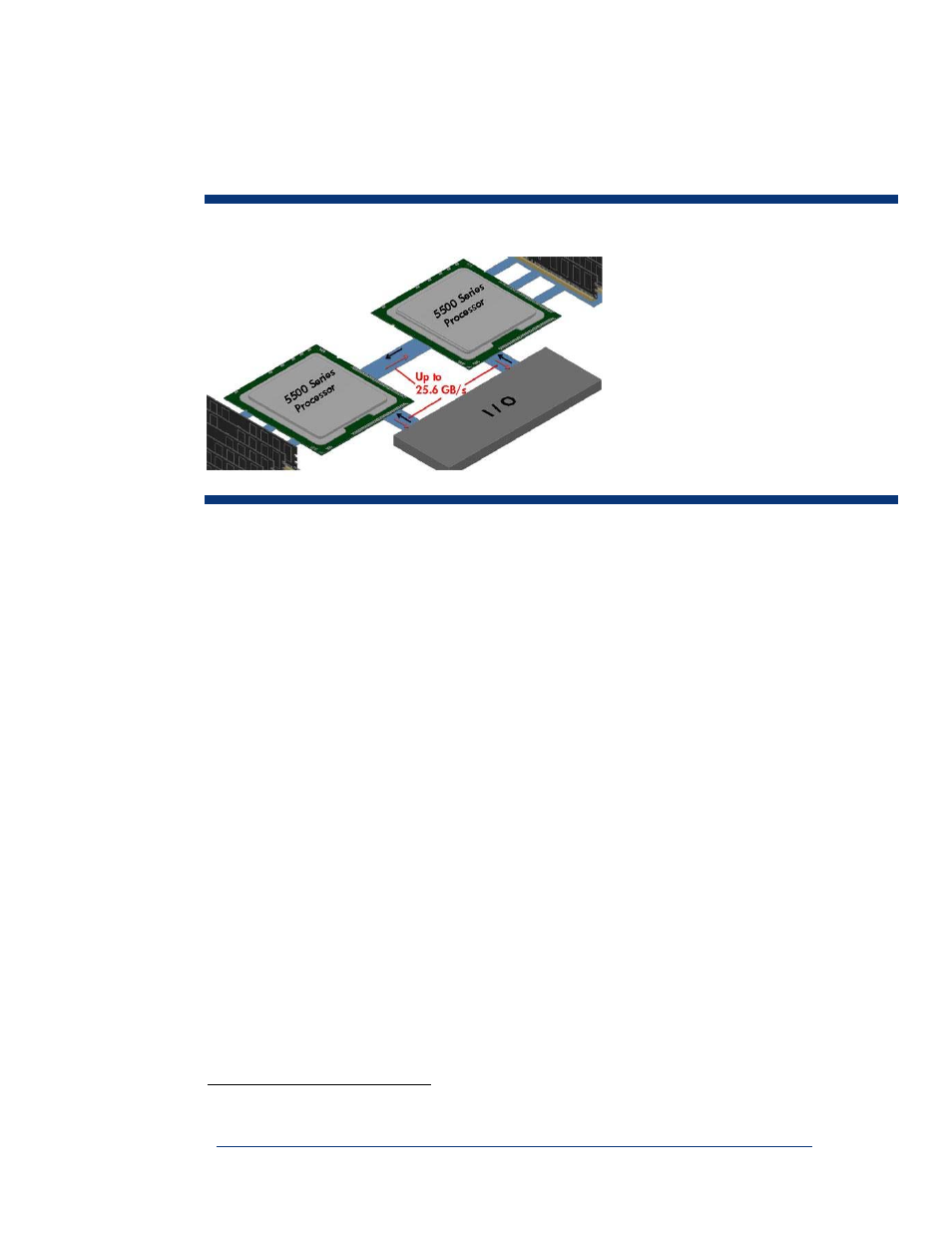
Intel Xeon 5500 Series processors attain their performance potential through Intel QuickPath
architecture (Figure 10). High-speed, point-to-point interconnects directly connect the processors with
one another. Intel QuickPath architecture also connects each processor to distributed shared memory
and to the I/O chipset.
Figure 10. Block diagram of
QuickPath architecture
Each QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) consists of two unidirectional links that operate simultaneously in
opposite directions using differential signaling. Unlike a typical serial bus, the QPIs transmit data
packets in parallel across multiple lanes, and packets are broken into multiple parallel transfers. Each
link is comprised of twenty 1-bit lanes. Data transfer uses a maximum of 16 bits, while the protocol
and error correction use the remaining 4 bits. The interconnect performs a maximum of 6.4
gigatransfers per second and has a bandwidth of 12.8 gigabytes per second in each direction, for a
total bandwidth of 25.6 gigabytes per second. If an application requests data from the memory of
another processor, the QPI uses high-bandwidth inter-processor communication to retrieve the data.
To reduce power requirements, administrators can use the ROM-Based Setup Utility (RBSU)
to set QPI
links to enter a low power state when the QPI links are not active. Once this feature is enabled, the
Intel processor determines when to put the QPI links into a low power state. This reduces power use
with minimal performance impact.
Hyper-Threading
With Intel Hyper-Threading Technology, also called Simultaneous Multi-threading Technology (SMT),
each core can execute two computational threads at the same time. This means that a single
processor can simultaneously execute up to eight threads. In addition, the high-bandwidth memory
subsystem supplies data faster to the two computational processes than traditional front side buses,
and the low-latency cache hierarchy allows more instructions to be processed simultaneously. Hyper-
Threading improves performance per watt, allowing Intel-based ProLiant G6 servers to accomplish
more using the same or less power than servers based on previous-generation Intel processors.
2
RBSU information is provided in the software configuration guide for each server tray. Additional information is
provided in the “HP ROM-Based Setup Utility User Guide” at
12
