Global data out mode – ProSoft Technology MVI46-MBP User Manual
Page 49
Reference MVI46-MBP
♦ SLC Platform
Modbus Plus Communication Module
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
Page 49 of 101
February 19, 2008
Step Description
6
Status is monitored for each device in the Device Definition File that is expected to return
Global In data to the module. This status is updated on an on-going basis and is
transferred to the SLC processor for processing. This data includes the node status value
and a counter incremented each time global input data is received.
In order for the Global Data In mode to operate, the minimum configuration
includes setting the Device Definition File and the Global Input Timeout values. If
this or other data is to transfer to the SLC processor using the Input File, the
Input File Map, Input File Size, and Input File Update parameters must also be
set.
It is important to understand how the Input File Map determines what data is
transferred from the module to the processor. The Input File Map is a 32-word
data block that selects the module's internal data registers to transfer to the Input
File. The Input File Map is copied to the module during module configuration. The
structure of this data block is as follows:
Word
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
28
29
30
31
Input File
Input File Map
0
1
100
101
200
201
202
405
4141
4142
4143
Register Data
Configuration and
Status Data
0
1
100
101
200
201
202
405
3999
4000
4141
4142
4143
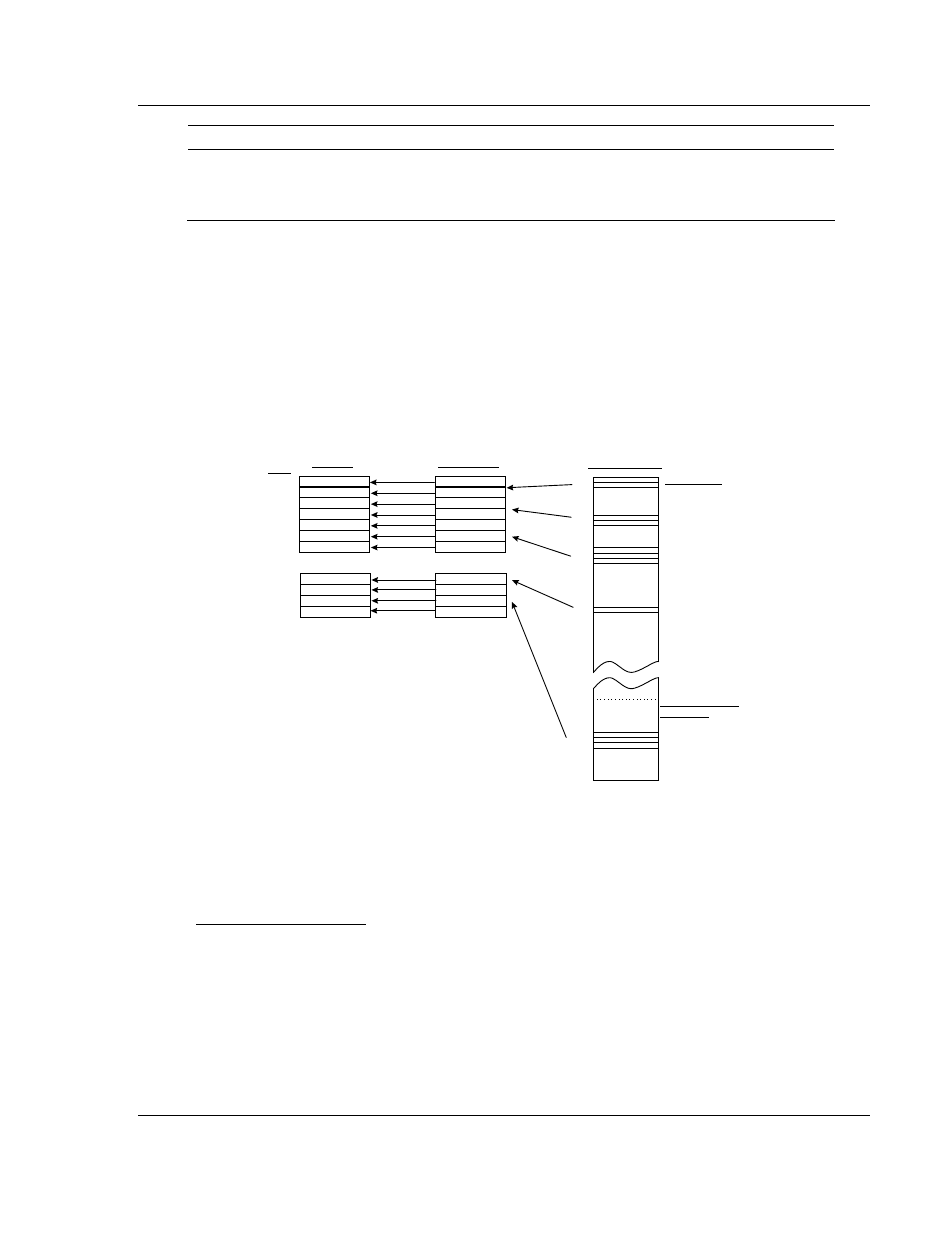
The Input File Map acts as a data routing table,
allowing the user to configure the source of data
for the Input File data transferred to the ControlLogx
processor on a high-priority basis.
Module Database
Each scan of the module's program places the data into the input image using
this Input File Map to select data out of the module's database. Any data in the
module's database can be assigned to the high-speed Input File data using this
map.
Global Data Out Mode
When the MVI46-MBP module's Global Output capability is enabled, up to 32
words of data can be transferred onto the Modbus Plus network by the module.
This data, typically reserved for high-speed data such as for application control
data, is transmitted each time the module receives the network token.
