7 multicast – PLANET GSW-4804SF User Manual
Page 77
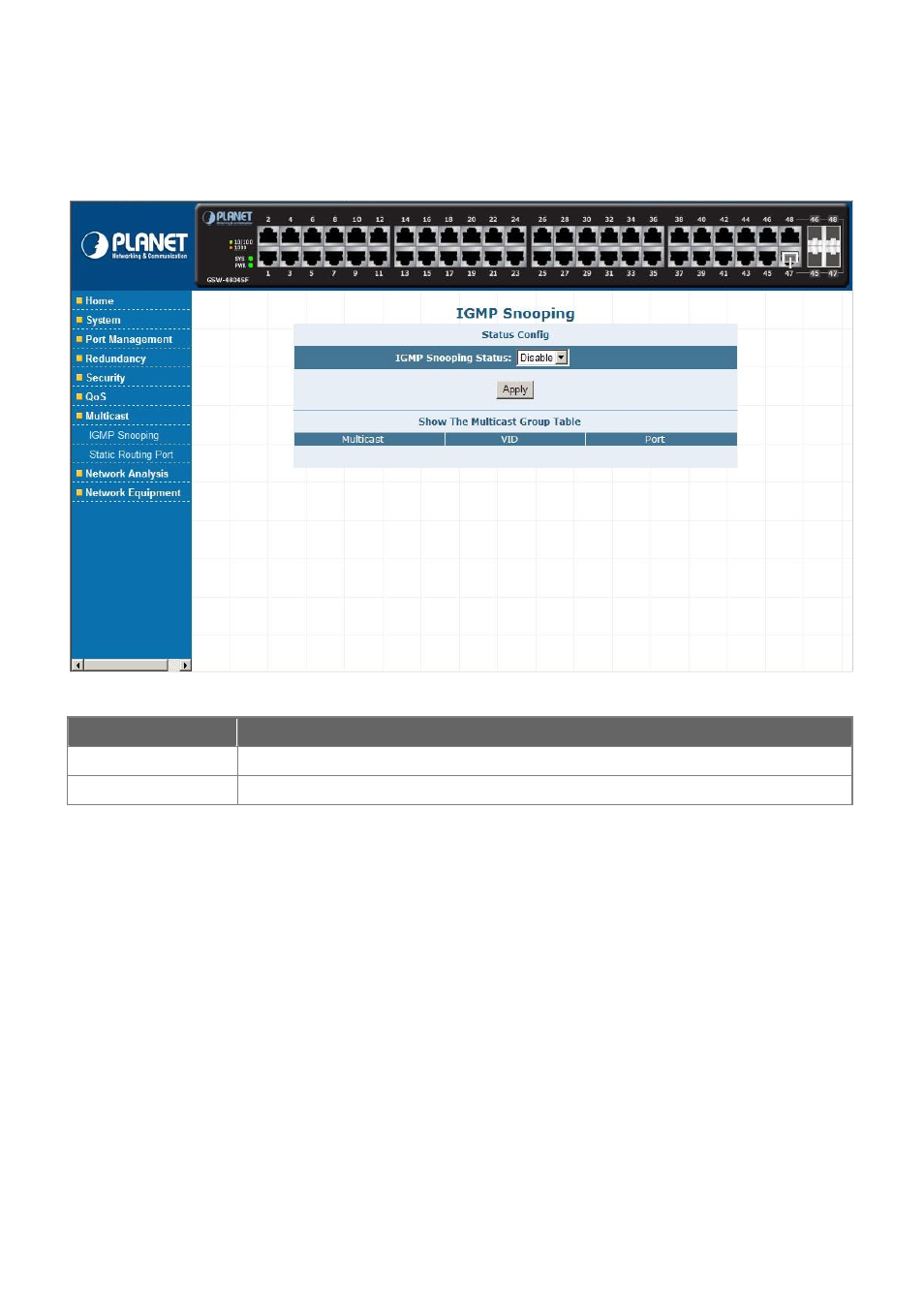
User’s Manual of GSW-4804SF
-77-
4.7 Multicast
This section provides Multicast Configuration, such as IGMP Snooping, Static Routing Port and the screen appears as
Figure
4-73
and
Table 4-30
describes the Multicast object of the Switch.
Figure 4-73
Multicast Web Screen
Table 4-30
Descriptions of the Multicast Web Screen Objects
Theory
Computers and network devices that want to receive multicast transmissions need to inform nearby routers that they will
become members of a multicast group. The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is used to communicate this
information. IGMP is also used to periodically check the multicast group for members that are no longer active. In the case
where there is more than one multicast router on a sub network, one router is elected as the ‘queried’. This router then keeps
track of the membership of the multicast groups that have active members. The information received from IGMP is then used to
determine if multicast packets should be forwarded to a given sub network or not. The router can check, using IGMP, to see if
there is at least one member of a multicast group on a given subnet work. If there are no members on a sub network, packets
will not be forwarded to that sub network.
IGMP Versions 1 and 2
Multicast groups allow members to join or leave at any time. IGMP provides the method for members and multicast routers to
communicate when joining or leaving a multicast group.
IGMP version 1 is defined in RFC 1112. It has a fixed packet size and no optional data.
Object
Description
IGMP Snooping
Provide IGMP Snooping Disable or Enable.
Explained in section 4.7.1.
Static Routing Port
Allow define the Static Routing Port of the Switch.
Explained in section 4.7.2.
