Lac-auto-initiated tunneling mode – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F5020 User Manual
Page 35
27
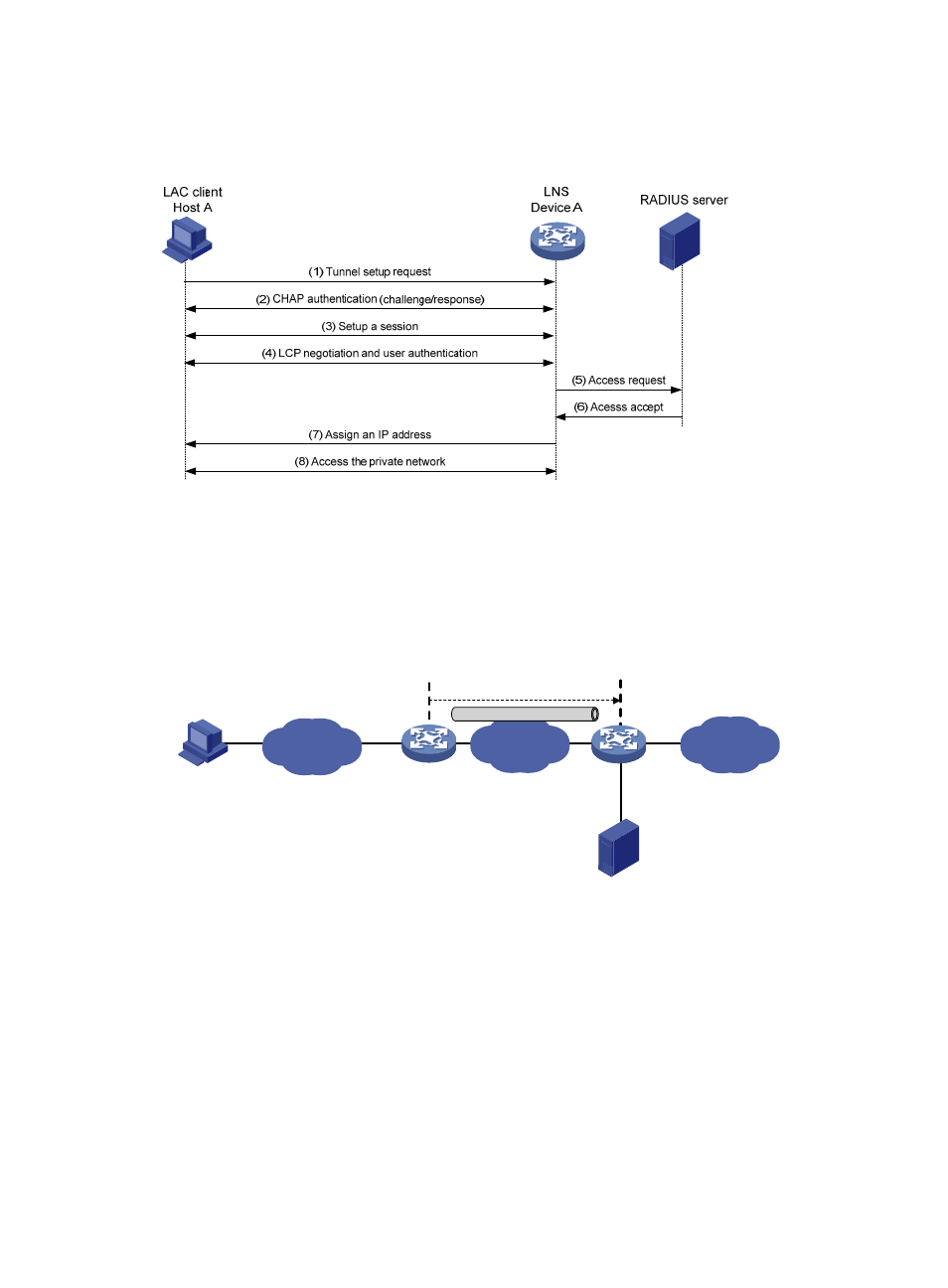
As shown in
, the workflow for establishing a client-initiated tunnel is similar to that for
establishing a NAS-initiated tunnel. (Details not shown.)
Figure 10 Establishment process for client-initiated tunnels
LAC-auto-initiated tunneling mode
In NAS-initiated mode, a remote system must successfully dial in to the LAC through PPPoE or ISDN.
In LAC-auto-initiated mode, you can use the l2tp-auto-client command on the LAC to trigger the LAC to
initiate a tunneling request to the LNS. When a remote system accesses the internal network, the LAC
forwards data through the L2TP tunnel.
Figure 11 LAC-auto-initiated tunneling mode
An LAC-auto-initiated tunnel has the following characteristics:
•
The connection between a remote system and the LAC is not confined to a dial-up connection and
can be any IP-based connection.
•
An L2TP session is established immediately after an L2TP tunnel is established. Then, the LAC and
LNS, acting as the PPPoE client and PPPoE server, respectively, perform PPP negotiation.
•
An L2TP tunnel can carry only one L2TP session.
•
The LNS assigns a private IP address to the LAC instead of to the remote system.
As shown in
, the workflow for establishing an LAC-auto-initiated tunnel is similar to that for
establishing a NAS-initiated tunnel. (Details not shown.)
LAN
Internet
Remote system
Host A
Private
network
L2TP tunnel
LAC auto initiated
LAC
Device A
LNS
Device B
RADIUS server
